
The oxidation states of S atoms in ${S_4}{O_6}^{2 - }$ from left to right respectively, are:
A. +6, 0, 0, +6
B. +3, 1, +1, +3
C. +5, 0, 0, +5
D. None of the above
Answer
523.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, first we need to understand the meaning of oxidation state. An oxidation is the process which determines what part of the reaction is being oxidized and what part is being reduced in a redox reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that an oxidation state refers to two things:
Oxidation as well as reduction in terms of electron transfer occurs in a redox reaction and electron-half-equations
Now, let’s consider the structure of ${S_4}{O_6}^{2 - }$
Then, we see that in the middle two sulfur have 0 oxidation states as an atom which is bonded with similar atoms has an oxidation state of 0. So, the total oxidation state of sulfur in the compound is 10. Then, the oxidation state of the leftmost and the rightmost sulfur is +5, as oxygen is more electronegative.
Therefore, the oxidation state of sulfur is n − 2 − 2 − 1+ 0 = 0; n = 5
So, the oxidation state of sulfur is +5 isolated S−S linkage have zero oxidation state.
⇒Thus, the oxidation state becomes +5, 0, 0, + 5.
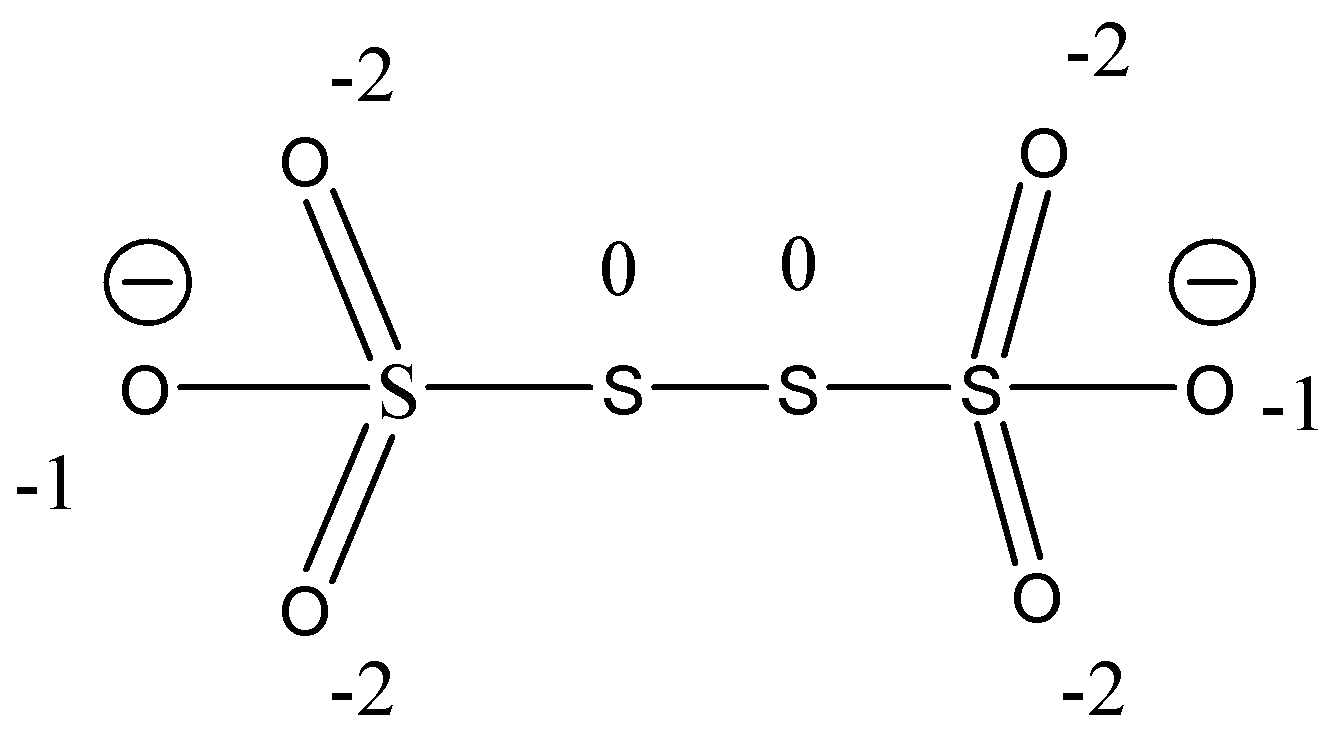
$\therefore $The option C is correct answer.
Note:
We need to remember that in oxoacids, sulfur shows a tetrahedral structure with respect to oxygen. And oxoacids are the acids that contain oxygen. The oxoacids have a minimum of one \[S = O\]bond and one \[S - OH\]bond. Also, there are terminal peroxide groups, terminal\[S = S\], terminal and bridging oxygen atoms in these oxoacids.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that an oxidation state refers to two things:
Oxidation as well as reduction in terms of electron transfer occurs in a redox reaction and electron-half-equations
Now, let’s consider the structure of ${S_4}{O_6}^{2 - }$
Then, we see that in the middle two sulfur have 0 oxidation states as an atom which is bonded with similar atoms has an oxidation state of 0. So, the total oxidation state of sulfur in the compound is 10. Then, the oxidation state of the leftmost and the rightmost sulfur is +5, as oxygen is more electronegative.
Therefore, the oxidation state of sulfur is n − 2 − 2 − 1+ 0 = 0; n = 5
So, the oxidation state of sulfur is +5 isolated S−S linkage have zero oxidation state.
⇒Thus, the oxidation state becomes +5, 0, 0, + 5.

$\therefore $The option C is correct answer.
Note:
We need to remember that in oxoacids, sulfur shows a tetrahedral structure with respect to oxygen. And oxoacids are the acids that contain oxygen. The oxoacids have a minimum of one \[S = O\]bond and one \[S - OH\]bond. Also, there are terminal peroxide groups, terminal\[S = S\], terminal and bridging oxygen atoms in these oxoacids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




