
The number of tetrahedral voids present in a bcc lattice is:
A.$4$
B.$2$
C.$1$
D.$8$
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint:We know that a unit cell is the smallest representation of an entire crystal. All crystal lattices are made up of repeating unit cells. In a unit cell, coordination number of an atom is the number of atoms it touches.
Complete step by step answer:
We can say the body centered cubic unit cell has the atoms at each the eight corners of a cube plus one atom in the centre of the cube. Each of the corner atoms is the corner of another cube so the corners atoms are shared by an 8 unit cell.
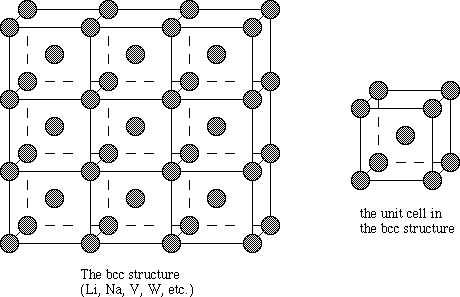
We have a simple way to find the number of tetrahedral Voids in a lattice. Here if the number of spheres that are unit cells is considered to be “n”, then the number of voids would be twice as many.
Therefore, the number of tetrahedral voids would be $2n$.
We have to know that bcc has 2 atoms per unit cell, the number of tetrahedral voids is \[2 \times 2 = 4\].
The number of tetrahedral voids in BCC is $4$.
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Note:
We also remember that in a body centered cubic unit cell each corner is occupied by an identical particle and in addition to that one atom occupies the body centre. Those atoms that occupy the corners do not touch each other, however they all touch the atom which occupies the body centre. Hence each atom is surrounded by eight nearest neighbors and coordination number is 8.
We can calculate the number of atoms in body centered cubic cell as follows,
No of atom
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;shared\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{Number\;of\;corners}}} \right) + \dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{number\;of\;centre\;atom}}$
Example 1: We can calculate the number of tungsten atoms as,
The no of atoms
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;shared\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{Number\;of\;corners}}} \right) + \dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{number\;of\;centre\;atom}}$
The number of tungsten atoms$ = \left( {\dfrac{8}{8}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{1} = 2$
The number tungsten atoms present in each unit cell of that metal is two.
Example 2: The structure of the rutile $\left( {Ti{O_2}} \right)$ is Bcc array.
The number of ${O^{2 - }}$ ion has to be calculated as,
No of atoms
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;shared\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{Number\;of\;corners}}} \right) + \dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{number\;of\;centre\;atom}}$
No of atoms=$\left( {\dfrac{8}{8}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{1} = 2$
The number of ${O^{2 - }}$ atoms is two.
Complete step by step answer:
We can say the body centered cubic unit cell has the atoms at each the eight corners of a cube plus one atom in the centre of the cube. Each of the corner atoms is the corner of another cube so the corners atoms are shared by an 8 unit cell.

We have a simple way to find the number of tetrahedral Voids in a lattice. Here if the number of spheres that are unit cells is considered to be “n”, then the number of voids would be twice as many.
Therefore, the number of tetrahedral voids would be $2n$.
We have to know that bcc has 2 atoms per unit cell, the number of tetrahedral voids is \[2 \times 2 = 4\].
The number of tetrahedral voids in BCC is $4$.
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Note:
We also remember that in a body centered cubic unit cell each corner is occupied by an identical particle and in addition to that one atom occupies the body centre. Those atoms that occupy the corners do not touch each other, however they all touch the atom which occupies the body centre. Hence each atom is surrounded by eight nearest neighbors and coordination number is 8.
We can calculate the number of atoms in body centered cubic cell as follows,
No of atom
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;shared\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{Number\;of\;corners}}} \right) + \dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{number\;of\;centre\;atom}}$
Example 1: We can calculate the number of tungsten atoms as,
The no of atoms
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;shared\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{Number\;of\;corners}}} \right) + \dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{number\;of\;centre\;atom}}$
The number of tungsten atoms$ = \left( {\dfrac{8}{8}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{1} = 2$
The number tungsten atoms present in each unit cell of that metal is two.
Example 2: The structure of the rutile $\left( {Ti{O_2}} \right)$ is Bcc array.
The number of ${O^{2 - }}$ ion has to be calculated as,
No of atoms
$ = \left( {\dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;shared\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{Number\;of\;corners}}} \right) + \dfrac{{Number\;of\;atom\;per\;unit\;cell}}{{number\;of\;centre\;atom}}$
No of atoms=$\left( {\dfrac{8}{8}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{1} = 2$
The number of ${O^{2 - }}$ atoms is two.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




