
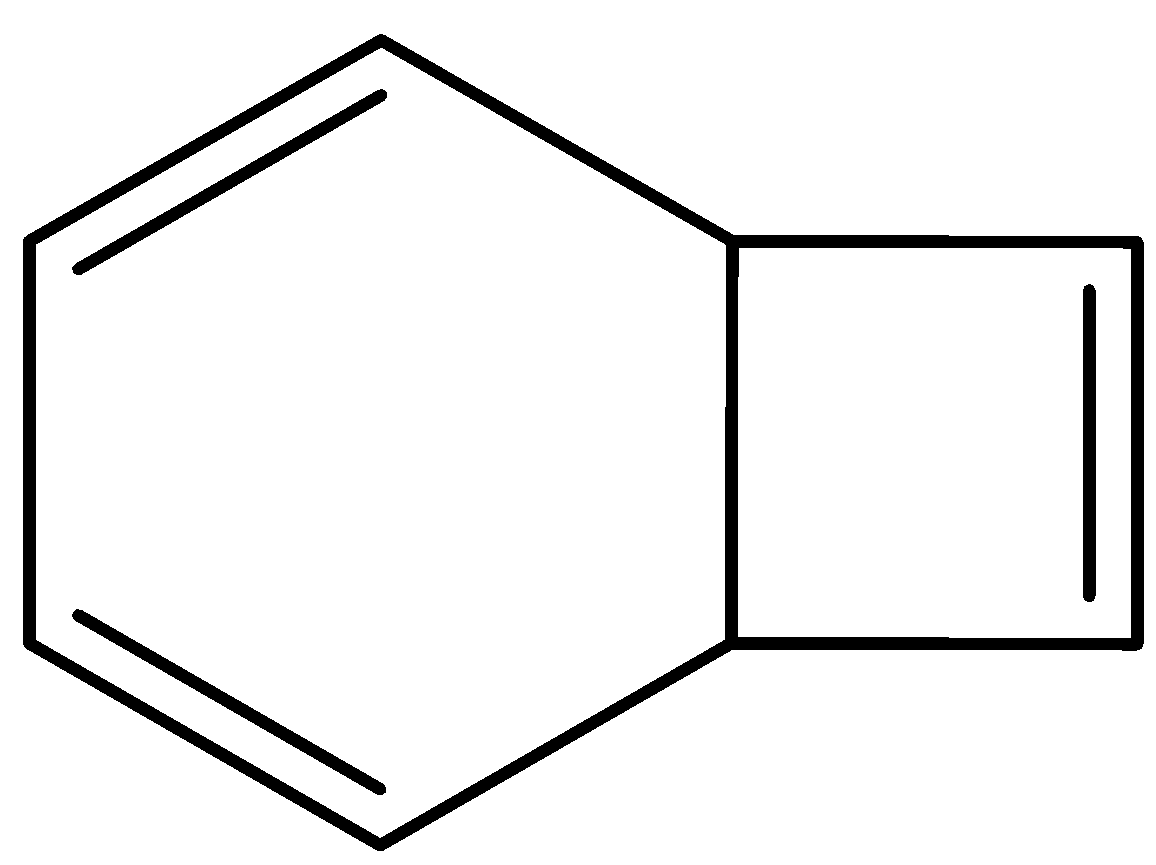
The number of \[s{{p}^{2}}-s{{p}^{2}}\] sigma bonds in the compound given below is:
A. 1
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5

Answer
594k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, identify the hybridisation of all the carbon atoms present in the structure by taking into account the $\sigma $- bonds and the $\pi $ - bonds.
Complete answer:
We know that $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized carbon atoms are tetrahedral carbons in this compound. They are not planar. The $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atoms are planar carbon atoms. Also, they have vacant p-orbitals.
Carbon atoms are usually $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized when all the bonds around them are single $\sigma $-bonds, $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized when 1 double bond or 1 $\pi $ - bond along with 3 $\sigma $- bonds is present and $sp$ hybridized when 1 triple bond or 2 $\pi $ - bonds along with 2 $\sigma $- bonds are present.
So here, all the carbons having a double bond will be $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized.
In this given compound, the carbon atoms that are joining the six membered ring and four membered rings are $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized. They are not planar. The rest of the carbon atoms in this given compound is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized. There are 6 $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atoms. Now we want to look at the $\sigma $ - bonds.
The $\sigma $- bonds are the single bonds connected with these carbon atoms. One of the bonds in the double bonds will be a $\sigma $- bond and the other will be a $\pi $- bond.
There are 4 \[s{{p}^{2}}-s{{p}^{2}}\] sigma bonds in this compound. 3 in the six-membered ring and 1 in the 4-membered ring.
Therefore, the correct option is ‘C. 4’
Note: Note that in this problem, there are 3 $\sigma $- bonds that occur along with the $\pi $ - bonds. The fourth sigma bond is the one that is present between 2 $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbons that are joined with double bonds to 2 other carbon atoms. Thus, this $\sigma $- bond is solitary. Do not forget to take this into account.
Complete answer:
We know that $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized carbon atoms are tetrahedral carbons in this compound. They are not planar. The $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atoms are planar carbon atoms. Also, they have vacant p-orbitals.
Carbon atoms are usually $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized when all the bonds around them are single $\sigma $-bonds, $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized when 1 double bond or 1 $\pi $ - bond along with 3 $\sigma $- bonds is present and $sp$ hybridized when 1 triple bond or 2 $\pi $ - bonds along with 2 $\sigma $- bonds are present.
So here, all the carbons having a double bond will be $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized.
In this given compound, the carbon atoms that are joining the six membered ring and four membered rings are $s{{p}^{3}}$hybridized. They are not planar. The rest of the carbon atoms in this given compound is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized. There are 6 $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atoms. Now we want to look at the $\sigma $ - bonds.
The $\sigma $- bonds are the single bonds connected with these carbon atoms. One of the bonds in the double bonds will be a $\sigma $- bond and the other will be a $\pi $- bond.
There are 4 \[s{{p}^{2}}-s{{p}^{2}}\] sigma bonds in this compound. 3 in the six-membered ring and 1 in the 4-membered ring.
Therefore, the correct option is ‘C. 4’
Note: Note that in this problem, there are 3 $\sigma $- bonds that occur along with the $\pi $ - bonds. The fourth sigma bond is the one that is present between 2 $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbons that are joined with double bonds to 2 other carbon atoms. Thus, this $\sigma $- bond is solitary. Do not forget to take this into account.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




