
The number of octahedral sites per sphere in fcc structure are:
A.8
B.4
C.2
D.1
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: In the face-centred cubic arrangement of the unit cell, there are 8 atoms present at the corners of a cubic unit cell and 1 atom at each of the six face centres of the unit cell. If we observe a three-dimensional structure of a crystal lattice we will see the gaps in between the spheres. These gaps or empty spaces are called the voids. Every unit cell has octahedral voids, if present, equal to the number of atoms in that unit cell.
Complete step by step answer:
The rule which is stated above is that the octahedral sites will be equal to the number of spheres present in the unit cell. Hence, the total number of octahedral sites will be equal to the number of packing spheres. A fcc unit cell contains 4 atoms(sphere) per unit cell. Hence, the total number of octahedral sites per unit cell in fcc structure are 4.
The diagram of a fcc crystal lattice is:
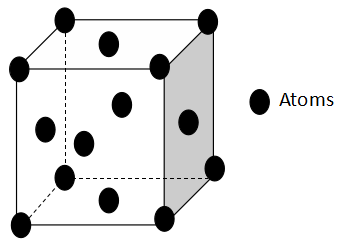 Therefore, the number of octahedral sites per sphere in fcc structure is 1.
Therefore, the number of octahedral sites per sphere in fcc structure is 1.
Therefore, the correct option is option D.
Note:
A unit cell is defined as the most basic and least volume consuming repeating structure in any solid. It is generally used to visually simplify the crystalline patterns solids arrange themselves in as they have the same properties as the whole crystal structure. When the unit cell repeats itself in 3 dimensional, the network is called a lattice.In addition to octahedral voids we also have tetrahedral voids. The void surrounded by four spheres sitting at the corners of a regular tetrahedron is known as a tetrahedral void. less than 1 for weak electrolytes. Higher the dielectric constant of a solvent more is its ionising power and more will be the dissociation. Dilution of solution affects the amount of solvent and therefore the dissociation. It also depends on the volume. When the volume increases the equilibrium of the given reaction would shift towards the side where the gaseous molecules are more and therefore the degree of dissociation towards the side increases.
Complete step by step answer:
The rule which is stated above is that the octahedral sites will be equal to the number of spheres present in the unit cell. Hence, the total number of octahedral sites will be equal to the number of packing spheres. A fcc unit cell contains 4 atoms(sphere) per unit cell. Hence, the total number of octahedral sites per unit cell in fcc structure are 4.
The diagram of a fcc crystal lattice is:

Therefore, the correct option is option D.
Note:
A unit cell is defined as the most basic and least volume consuming repeating structure in any solid. It is generally used to visually simplify the crystalline patterns solids arrange themselves in as they have the same properties as the whole crystal structure. When the unit cell repeats itself in 3 dimensional, the network is called a lattice.In addition to octahedral voids we also have tetrahedral voids. The void surrounded by four spheres sitting at the corners of a regular tetrahedron is known as a tetrahedral void. less than 1 for weak electrolytes. Higher the dielectric constant of a solvent more is its ionising power and more will be the dissociation. Dilution of solution affects the amount of solvent and therefore the dissociation. It also depends on the volume. When the volume increases the equilibrium of the given reaction would shift towards the side where the gaseous molecules are more and therefore the degree of dissociation towards the side increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




