
The number of non – congruent rectangle that can be formed on a chess board is
(a) 30
(b) 32
(c) 33
(d) 36
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we first of all need to determine the dimension of the chess board then we will make possible combinations of rectangles that can be formed on the chess board. Finally we will add all the possible non – congruent rectangles to get the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A chess board is in the shape of a square having 64 smaller squares of the same dimensions.
A chess board has \[8\times 8\] blocks, that is its length of 8 blocks and breadth has 8 blocks.
If the rectangle formed has one side length \[\approx \] 1 unit then it looks like 1.Now if we have to make rectangles out of it then we need to determine the possible length and breadth of it.
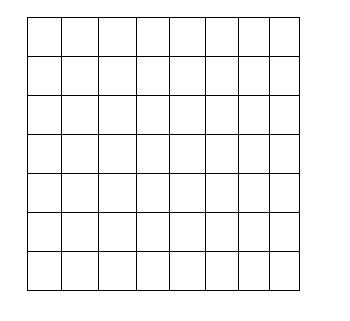
If the rectangle is of dimension \[1\times 1\] then it looks like, .

If the rectangle taken is of dimension \[2\times 1\], then it looks like, .

If dimension is \[1\times 2\], then it is as,

Similarly, all the possible combinations which can be made of length as ‘1 unit’ are:
(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (1, 8)
So, a total number of 8 non – congruent rectangles are of length 1.
Also, for length 2 we have possible combinations as,
(2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (2, 7), (2, 8)
Here (2, 1) is not considered as we need non – congruent rectangles and (1, 2) & (2, 1) are congruent.
So, a total of 7 non – congruent rectangles of length 2.
Now for length ‘3 unit’ we have possible combinations, (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (3, 7), (3, 8).
A total of 6 non – congruent rectangles.
Similarly for length to be 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 we get 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 non – congruent rectangles respectively.
Hence to determine the total number we need to add all the possible combinations.
So, the total number of rectangles are, 8 + 7 + 6 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 36.
Therefore, we have the total number of non – congruent rectangles that can be formed on a chess board is 36, which is option (d).
Note: The possibility of error in this question can be considering (1, 2) and (2, 1) type rectangles as two different rectangles, which would be wrong because we need non – congruent rectangles and (1, 2) & (2, 1) are congruent. This is applicable for any rectangles of dimension (a, b) & (b, a).
Complete step-by-step answer:
A chess board is in the shape of a square having 64 smaller squares of the same dimensions.
A chess board has \[8\times 8\] blocks, that is its length of 8 blocks and breadth has 8 blocks.
If the rectangle formed has one side length \[\approx \] 1 unit then it looks like 1.Now if we have to make rectangles out of it then we need to determine the possible length and breadth of it.

If the rectangle is of dimension \[1\times 1\] then it looks like, .

If the rectangle taken is of dimension \[2\times 1\], then it looks like, .

If dimension is \[1\times 2\], then it is as,

Similarly, all the possible combinations which can be made of length as ‘1 unit’ are:
(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (1, 7), (1, 8)
So, a total number of 8 non – congruent rectangles are of length 1.
Also, for length 2 we have possible combinations as,
(2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (2, 7), (2, 8)
Here (2, 1) is not considered as we need non – congruent rectangles and (1, 2) & (2, 1) are congruent.
So, a total of 7 non – congruent rectangles of length 2.
Now for length ‘3 unit’ we have possible combinations, (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (3, 7), (3, 8).
A total of 6 non – congruent rectangles.
Similarly for length to be 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 we get 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 non – congruent rectangles respectively.
Hence to determine the total number we need to add all the possible combinations.
So, the total number of rectangles are, 8 + 7 + 6 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 36.
Therefore, we have the total number of non – congruent rectangles that can be formed on a chess board is 36, which is option (d).
Note: The possibility of error in this question can be considering (1, 2) and (2, 1) type rectangles as two different rectangles, which would be wrong because we need non – congruent rectangles and (1, 2) & (2, 1) are congruent. This is applicable for any rectangles of dimension (a, b) & (b, a).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




