
The moon is constantly falling towards the earth
(A) This statement is absurd
(B) This statement is correct
(C) This statement is wrong
(D) Nothing can be said on the basis of given information.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint : : The gravitational force between the earth and the moon is what keeps the moon in orbit around the earth. Gravitational force is responsible for the stone or any object falling back to the ground after being thrown upward.
Complete step by step answer
Usually, we observe that when we throw an object vertically upward, it accelerates back to the ground. However, when we throw it at an angle to the horizontal, it follows a parabolic path coming back to the ground but away from our position. Usually, the basic projectile class, we assume the distance moved by the object is small relative to the size of the earth hence the portion of the ground can be assumed flat. Nonetheless, the earth is round, and when the object is thrown far enough, it tends to fall back to the earth but will constantly miss the earth and continue in a circular motion around the earth (path C in diagram). Hence, that object can be said to be falling constantly towards the earth but missing constantly too.
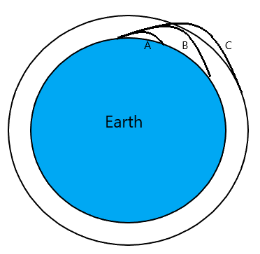
Similar is the case of the moon, and hence, the moon can be said to be falling towards the earth.
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note
For clarity, for an object to have a circular orbit around the earth (i.e. constantly miss the earth), it must have a horizontal component of velocity (actually tangential component), i.e. velocity parallel to the surface of the earth.
Satellites which are taken to orbit the earth are usually given the tangential velocity required to keep them orbiting at that height above ground. Whenever an object no longer has this velocity, they fall straight to the earth.
Complete step by step answer
Usually, we observe that when we throw an object vertically upward, it accelerates back to the ground. However, when we throw it at an angle to the horizontal, it follows a parabolic path coming back to the ground but away from our position. Usually, the basic projectile class, we assume the distance moved by the object is small relative to the size of the earth hence the portion of the ground can be assumed flat. Nonetheless, the earth is round, and when the object is thrown far enough, it tends to fall back to the earth but will constantly miss the earth and continue in a circular motion around the earth (path C in diagram). Hence, that object can be said to be falling constantly towards the earth but missing constantly too.

Similar is the case of the moon, and hence, the moon can be said to be falling towards the earth.
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note
For clarity, for an object to have a circular orbit around the earth (i.e. constantly miss the earth), it must have a horizontal component of velocity (actually tangential component), i.e. velocity parallel to the surface of the earth.
Satellites which are taken to orbit the earth are usually given the tangential velocity required to keep them orbiting at that height above ground. Whenever an object no longer has this velocity, they fall straight to the earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




