
The monomer of natural rubber is:
A)
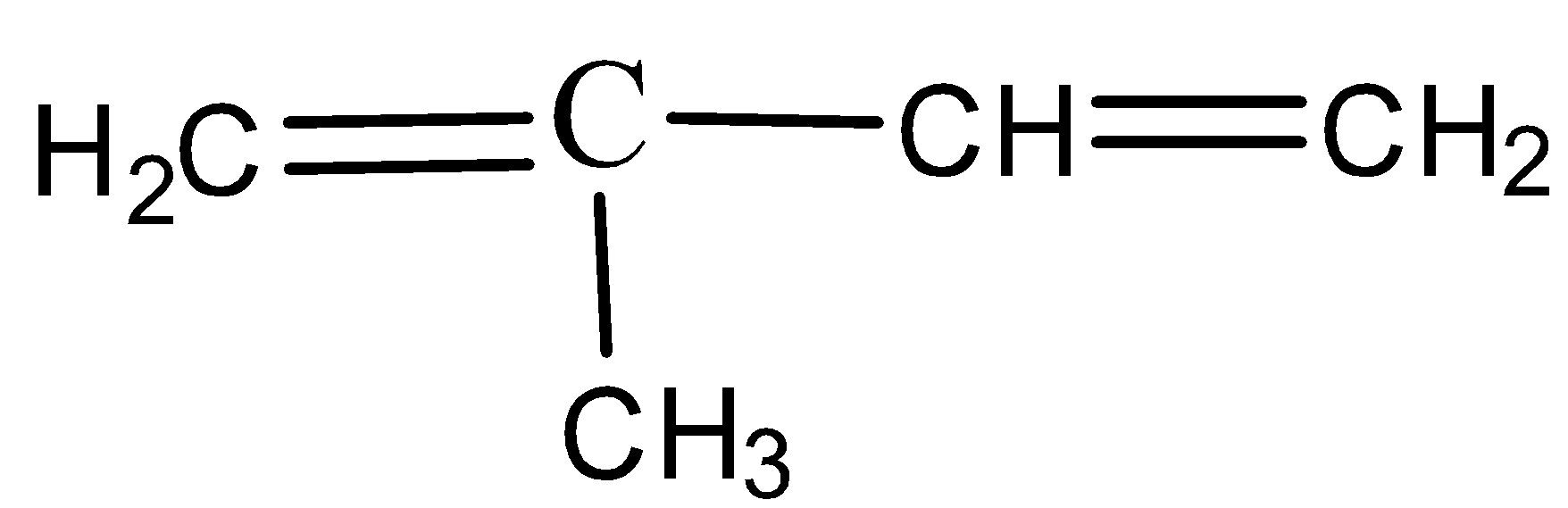
B)
C)
D) None of these


Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: The answer to this question is based on the concept of the physical chemistry that includes the polymerisation topic where the monomer unit combines to form a polymer and this concept gives the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
We have come across the chapters in the physical chemistry classes which deal with the topic polymerisation and also several parameters related to it, that is, kinetics of polymerisation, types of polymerisation and also on.
We shall now see what does polymerisation mean and this can help us to deduce the required answer.
- Polymerisation is the process in which two or more monomer units combine to form long chain compounds that are the polymers.
- Polymers play an important role in our daily lives.
- Most of the things we use are made of polymer , for instance clothes, toys, comb, thread and many more.
- Therefore, polymers have a wide range of applications and thus are the important components of the industrial process.
- There are various types of polymerisation like addition polymerisation, condensation polymerisation, copolymerisation etc., that are based on the mechanism of polymerisation.
We shall see the monomer unit of rubber that is obtained naturally from the plants.
- Rubber is made up of small monomer units that are called as isoprene units. These isoprene units are made of unsaturated carbon atom with a methyl group attached to one of the four carbon atom and the IUPAC name is given by, 2-methyl 1,3-butadiene which is as shown below,
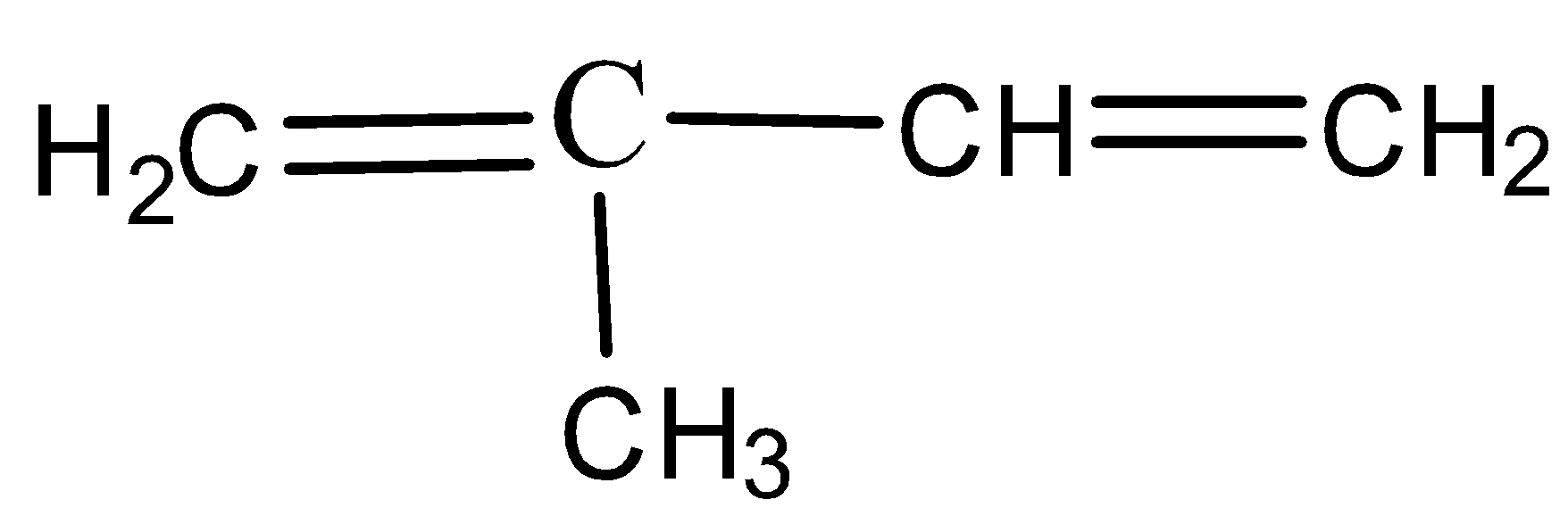
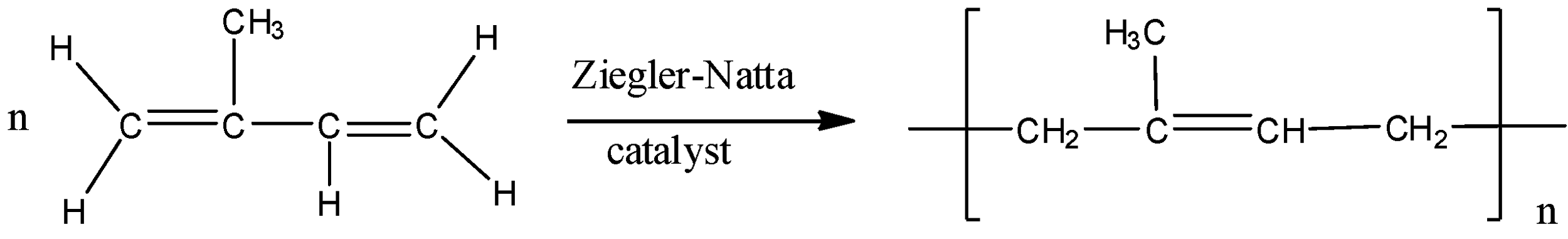
The polymerization process takes place in the presence of Ziegler-Natta catalyst and the reaction is as shown below:
So the correct answer is “A”:
Note: The isoprene obtained naturally is a volatile liquid and is colourless and this unsaturated hydrocarbon is obtained even while processing petroleum or coal tar. Naturally it is obtained by trees like eucalyptus, oak etc.
Complete step by step answer:
We have come across the chapters in the physical chemistry classes which deal with the topic polymerisation and also several parameters related to it, that is, kinetics of polymerisation, types of polymerisation and also on.
We shall now see what does polymerisation mean and this can help us to deduce the required answer.
- Polymerisation is the process in which two or more monomer units combine to form long chain compounds that are the polymers.
- Polymers play an important role in our daily lives.
- Most of the things we use are made of polymer , for instance clothes, toys, comb, thread and many more.
- Therefore, polymers have a wide range of applications and thus are the important components of the industrial process.
- There are various types of polymerisation like addition polymerisation, condensation polymerisation, copolymerisation etc., that are based on the mechanism of polymerisation.
We shall see the monomer unit of rubber that is obtained naturally from the plants.
- Rubber is made up of small monomer units that are called as isoprene units. These isoprene units are made of unsaturated carbon atom with a methyl group attached to one of the four carbon atom and the IUPAC name is given by, 2-methyl 1,3-butadiene which is as shown below,

The polymerization process takes place in the presence of Ziegler-Natta catalyst and the reaction is as shown below:

So the correct answer is “A”:
Note: The isoprene obtained naturally is a volatile liquid and is colourless and this unsaturated hydrocarbon is obtained even while processing petroleum or coal tar. Naturally it is obtained by trees like eucalyptus, oak etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




