
The minimum number of carbon atoms in an alkane having four primary carbon atoms are:
(1) $4$
(2) $8$
(3) $5$
(4) $6$
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: As we know that a primary carbon atom is the one which is bound to only one other carbon atom and in case of alkane, a primary carbon is bound with three hydrogen atoms and results in making of an acyclic structure.
Complete Step by step answer:
- A primary carbon atom is the one which is bound to only one other carbon atom and in case of alkane, a primary carbon is bound with three hydrogen atoms and results in making of an acyclic structure and not a ring structure. We can easily identify a primary, secondary or tertiary carbon in a compound by just counting the number of carbons attached to the main carbon or one at least one carbon.
- Primary carbon is attached with one other carbon, a secondary carbon is the one attached to the two other carbons and a tertiary carbon is the one attached to the three other carbon atoms and a quaternary carbon has four carbons attached to one carbon. For instance, ethane with one simple primary carbon, propane with two carbons attached to one primary carbon etc .
- Similarly in the given question the alkane having four primary carbon atoms can be a neopentane where the main chain is having three carbon atoms and two methyl groups attached to central carbon atom and the structure can be given as follows:
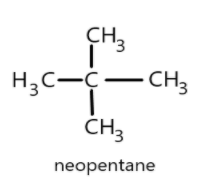
Neopentane has the simplest structure and the primary carbon has five carbon atoms each attached with three hydrogen atoms giving a molecular formula as \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\].
Therefore the correct answer is (3).
Note: Neopentane is a flammable gas substance at room temperature and pressure with a boiling point of only ${9.5^ \circ }C$ and melting point of $ - {16.5^ \circ }C$. It can liquefy in cold weather or cool places. Its carbocation is one of the most stable among all the carbocations without any resonance.
Complete Step by step answer:
- A primary carbon atom is the one which is bound to only one other carbon atom and in case of alkane, a primary carbon is bound with three hydrogen atoms and results in making of an acyclic structure and not a ring structure. We can easily identify a primary, secondary or tertiary carbon in a compound by just counting the number of carbons attached to the main carbon or one at least one carbon.
- Primary carbon is attached with one other carbon, a secondary carbon is the one attached to the two other carbons and a tertiary carbon is the one attached to the three other carbon atoms and a quaternary carbon has four carbons attached to one carbon. For instance, ethane with one simple primary carbon, propane with two carbons attached to one primary carbon etc .
- Similarly in the given question the alkane having four primary carbon atoms can be a neopentane where the main chain is having three carbon atoms and two methyl groups attached to central carbon atom and the structure can be given as follows:

Neopentane has the simplest structure and the primary carbon has five carbon atoms each attached with three hydrogen atoms giving a molecular formula as \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\].
Therefore the correct answer is (3).
Note: Neopentane is a flammable gas substance at room temperature and pressure with a boiling point of only ${9.5^ \circ }C$ and melting point of $ - {16.5^ \circ }C$. It can liquefy in cold weather or cool places. Its carbocation is one of the most stable among all the carbocations without any resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




