
The major product of the reaction:
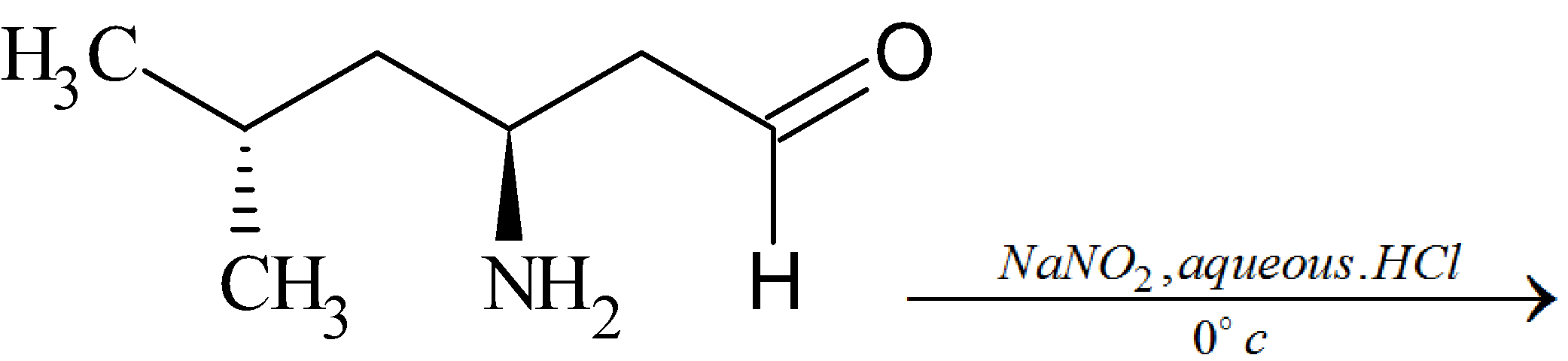
(A)
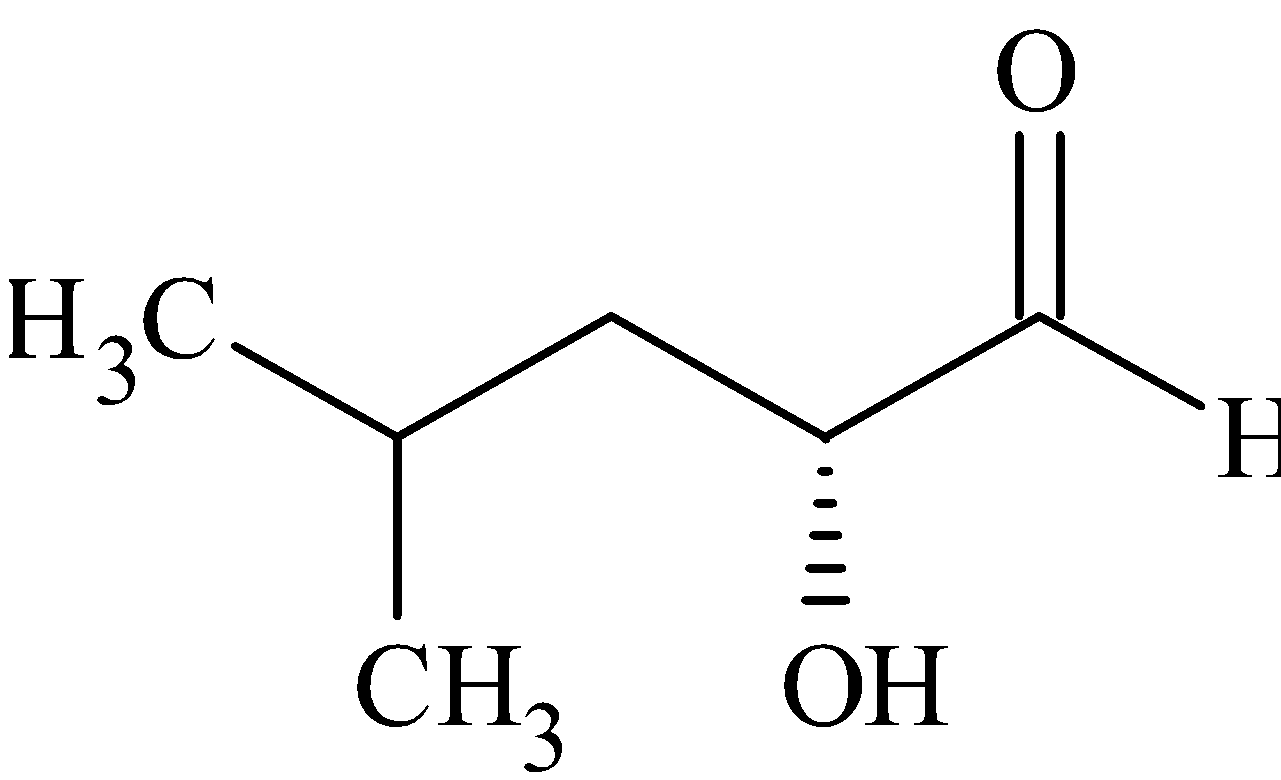
(B)

(C)
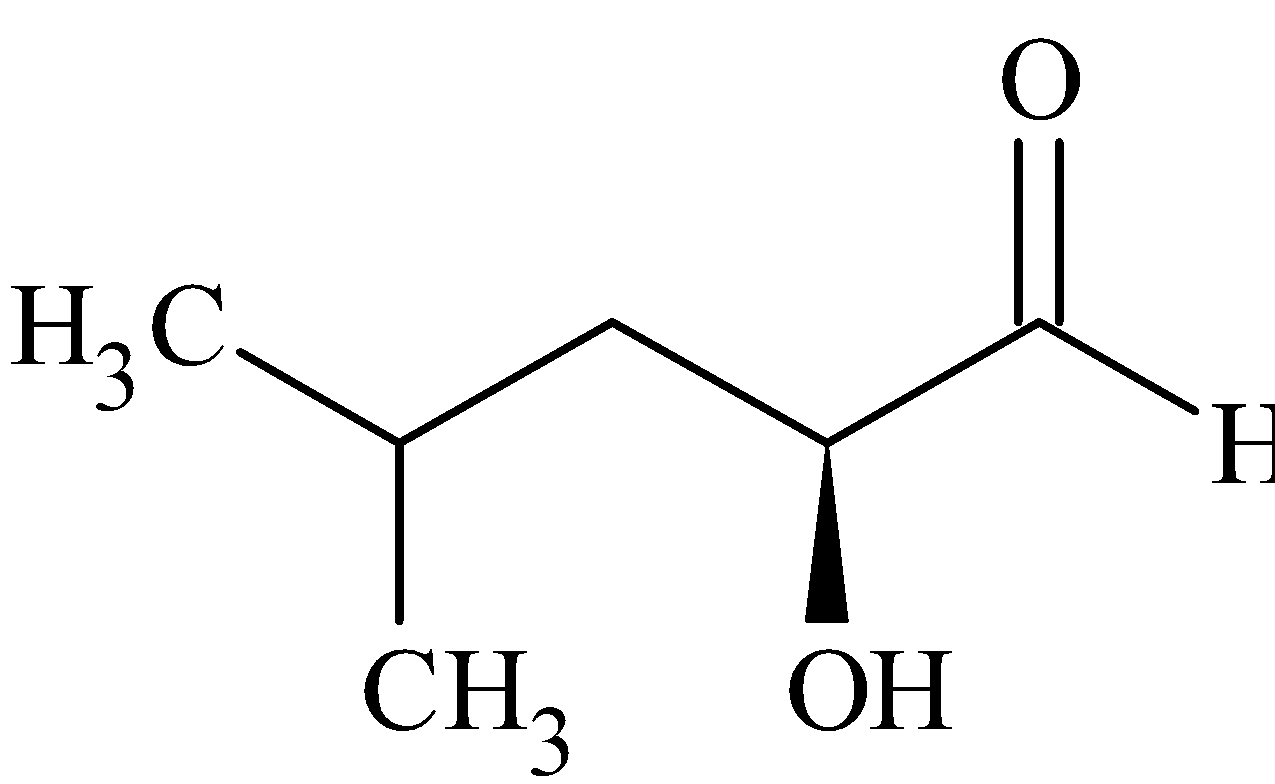
(D)

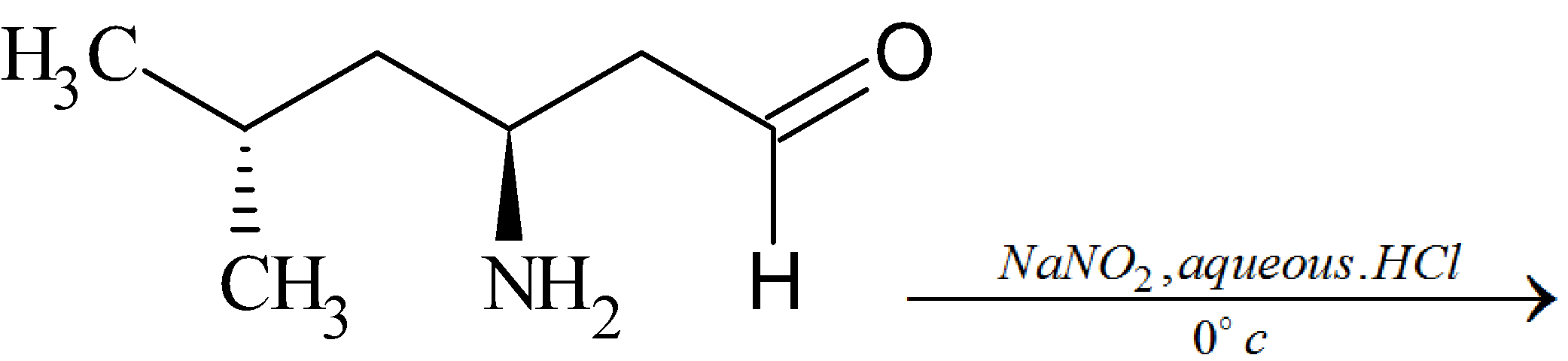




Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction given, is one of the most important reactions of carbocation where carbocation undergoes reactions by elimination of a proton. By this reaction nitrogen gas is evolved quantitatively widely used in estimation of amino acids and proteins.
Complete answer:
In the heterolytic fission of C-X bond in a molecule. In this case, if X is more electronegative than carbon then the X pulls away the bonding pair of electrons towards itself. X accumulates negative charge and C accumulates positive charge on it.
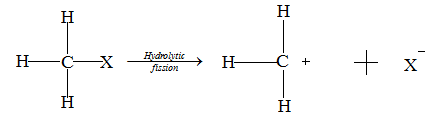
The positively charged species is known as a carbocation (here $CH_3^ + $) and the negatively charged species is known as a carbanion (here${X^ - }$).
There are four different ways a carbocation undergoes a reaction:
-Elimination of a proton
-Reaction with nucleophiles
-Addition to unsaturated compounds
-Molecular rearrangement
In the reaction given in the question, the carbocation undergoes the reaction by elimination of a proton. Let's go stepwise to understand the reaction better.
Step 1: Formation of diazonium cation
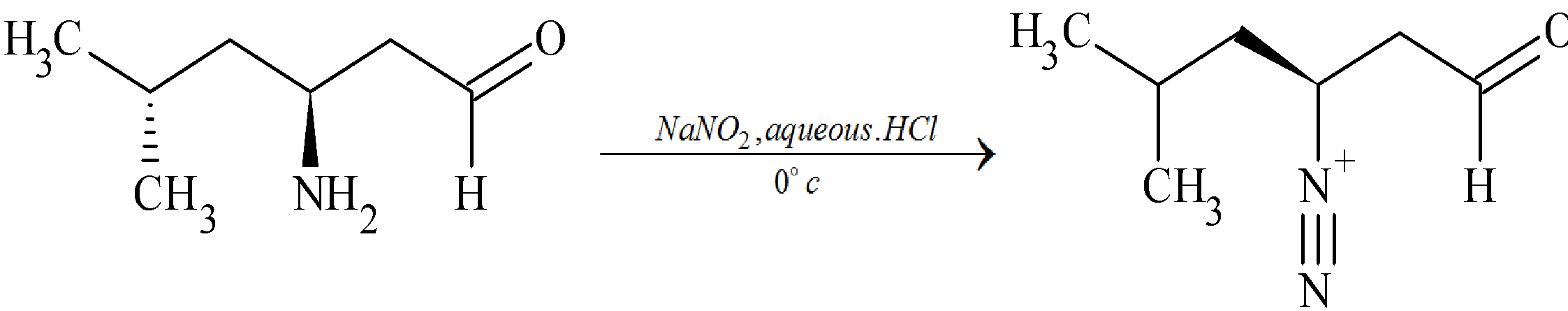
(2S)-2-amino-4-methylpentanal reacts with nitrous acid at ${0^ \circ }C$ to give diazonium cation ((2S)-4-methyl-1-oxopentane-2-diazonium)
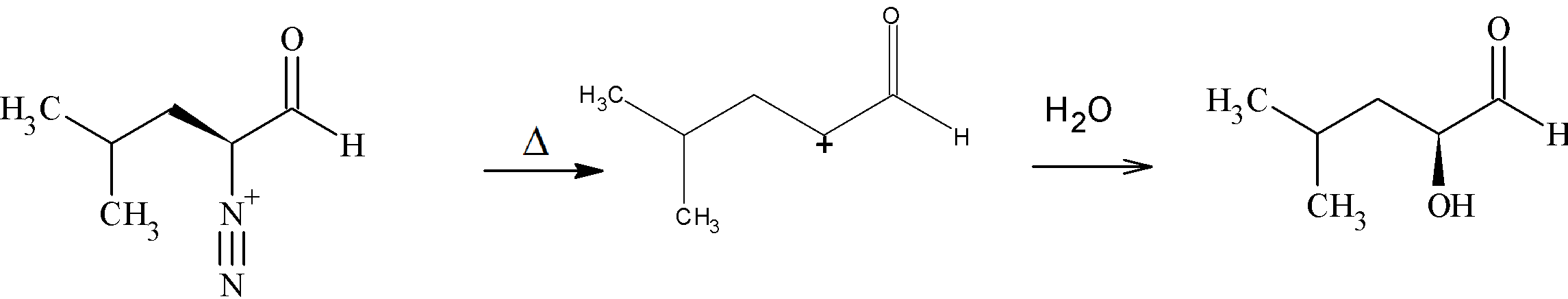
Step 2: Elimination of a ${N_2}$ followed by addition of water to it gives (2S)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanal. The carbocation formed here is a primary carbocation.
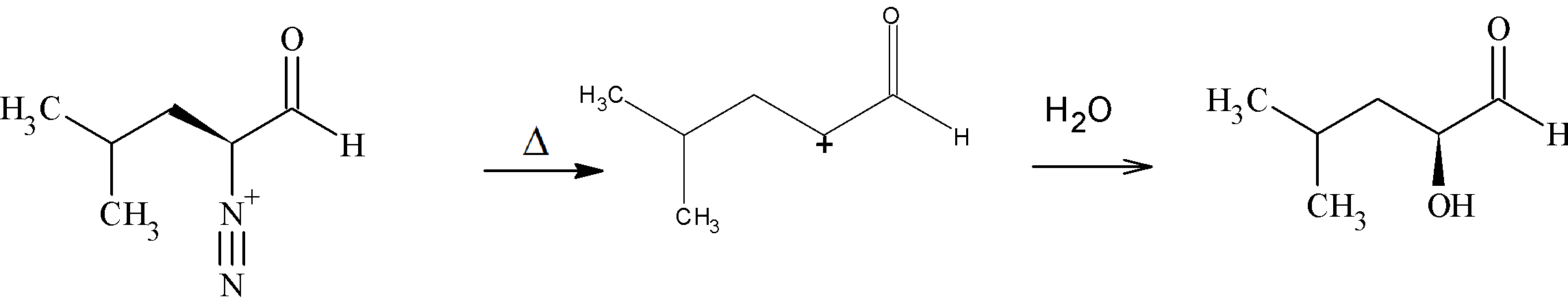
Thus, from the above discussion, we can come to a conclusion that Option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Even alkene can be formed as the product if we make certain changes that are in step 2 after the formation of the carbocation, it loses a proton to form alkene. In case in place of the aliphatic compound the aromatic compound under the same chemical and physical condition is allowed to react then, the reaction of carbocation will be by molecular rearrangement.
Complete answer:
In the heterolytic fission of C-X bond in a molecule. In this case, if X is more electronegative than carbon then the X pulls away the bonding pair of electrons towards itself. X accumulates negative charge and C accumulates positive charge on it.

The positively charged species is known as a carbocation (here $CH_3^ + $) and the negatively charged species is known as a carbanion (here${X^ - }$).
There are four different ways a carbocation undergoes a reaction:
-Elimination of a proton
-Reaction with nucleophiles
-Addition to unsaturated compounds
-Molecular rearrangement
In the reaction given in the question, the carbocation undergoes the reaction by elimination of a proton. Let's go stepwise to understand the reaction better.
Step 1: Formation of diazonium cation

(2S)-2-amino-4-methylpentanal reacts with nitrous acid at ${0^ \circ }C$ to give diazonium cation ((2S)-4-methyl-1-oxopentane-2-diazonium)

Step 2: Elimination of a ${N_2}$ followed by addition of water to it gives (2S)-2-hydroxy-4-methylpentanal. The carbocation formed here is a primary carbocation.

Thus, from the above discussion, we can come to a conclusion that Option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Even alkene can be formed as the product if we make certain changes that are in step 2 after the formation of the carbocation, it loses a proton to form alkene. In case in place of the aliphatic compound the aromatic compound under the same chemical and physical condition is allowed to react then, the reaction of carbocation will be by molecular rearrangement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




