
The major product of the following reaction:
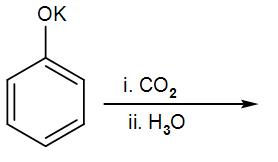
A)
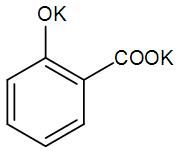
B)
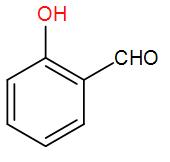
C)
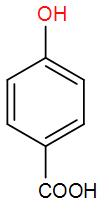
D)
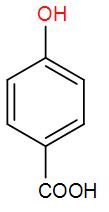
E) None of the above





Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:. To solve this, proceed through Kolbe Schmitt Reaction. This reaction is also known as Kolbe's reaction and is a type of addition reaction. When phenol is treated with sodium hydroxide, phenoxide ion is generated.
Complete step by step answer:
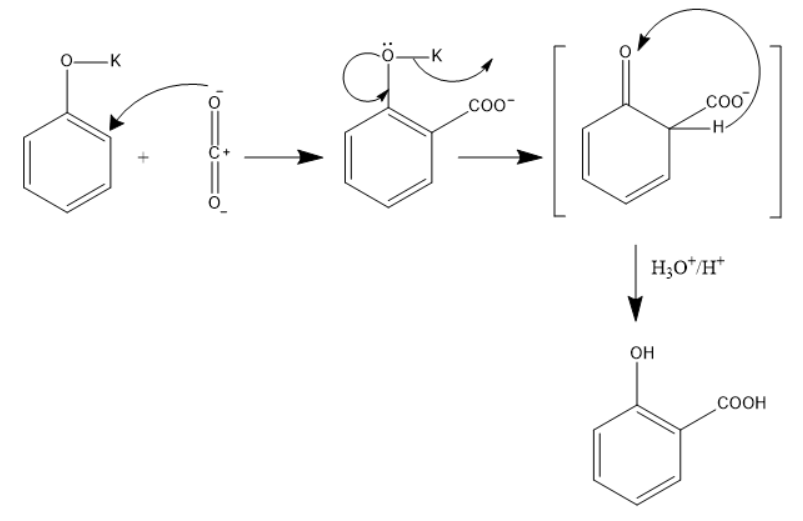
In this reaction Phenol behaves as a weak acid and it reacts with the base KOH to form potassium phenoxide.
Now this potassium phenoxide ion and the weak electrolyte $C{{O}_{2}}$
(in which the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the carbon), forms a bond at the ortho-position of the phenoxide i.e. a COO- group is attached.
The potassium ion leaves and the electrons on the Oxygen atom forms a double bond with the benzene ring. This is also an intermediate form.
The phenoxide ion is more basic when we compare it with the carboxylic acid, So, the hydrogen present at the ortho-position along with the COO- shifts towards the phenoxide ion, thus OH is formed.
In the next step it reacts with ${{H}_{3}}O/{{H}^{+}}$
which is also the acidification of an acid, salicylic acid or Ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid is formed.
We can see the mechanism for the reaction in the diagram below.
So, the correct answer option (E) “None of the above”.
Note: There’s a difference between Kolbe’s reaction and Kolbe’s electrolysis:
In Kolbe's electrolysis, the electrochemical oxidative decarboxylation of carboxylic acid salts leads to radicals, which dimerize. It is best applied to the synthesis of symmetrical dimers, but in some cases can be used with a mixture of two carboxylic acids to furnish unsymmetrical dimers.
Complete step by step answer:
In this reaction Phenol behaves as a weak acid and it reacts with the base KOH to form potassium phenoxide.
Now this potassium phenoxide ion and the weak electrolyte $C{{O}_{2}}$
(in which the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the carbon), forms a bond at the ortho-position of the phenoxide i.e. a COO- group is attached.
The potassium ion leaves and the electrons on the Oxygen atom forms a double bond with the benzene ring. This is also an intermediate form.
The phenoxide ion is more basic when we compare it with the carboxylic acid, So, the hydrogen present at the ortho-position along with the COO- shifts towards the phenoxide ion, thus OH is formed.
In the next step it reacts with ${{H}_{3}}O/{{H}^{+}}$
which is also the acidification of an acid, salicylic acid or Ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid is formed.
We can see the mechanism for the reaction in the diagram below.

So, the correct answer option (E) “None of the above”.
Note: There’s a difference between Kolbe’s reaction and Kolbe’s electrolysis:
In Kolbe's electrolysis, the electrochemical oxidative decarboxylation of carboxylic acid salts leads to radicals, which dimerize. It is best applied to the synthesis of symmetrical dimers, but in some cases can be used with a mixture of two carboxylic acids to furnish unsymmetrical dimers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




