
The major organic product formed from the following reaction is:
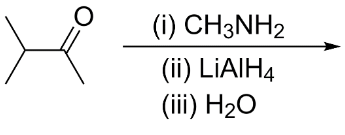
A.
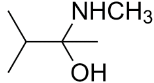
B.
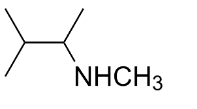
C.
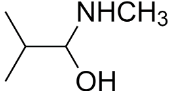
D.
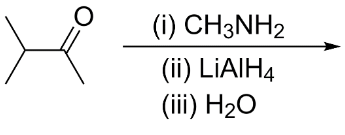




Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint:To determine the major organic product formed from the reaction, we need to know what type of reactions are taking place. We can see that the reactant ketone is first reacted with a primary amine and the product formed is further reacted with reducing agent lithium aluminum hydride.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the given reaction, the reactant is 3-methylbutan-2-one. It is a ketone and is also known as methyl isopropyl ketone. It is an uncommon solvent.
When a ketone is reacted with a primary amine, it first undergoes nucleophilic addition to give carbinolamine and then further undergoes elimination and dehydrates to form a substituted imine.
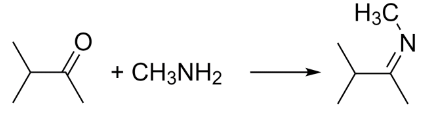
So, 3-dimethylbutan-2-imine is formed when 3-methylbutan-2-one is reacted with methylamine. This imine formed can be further reduced to an amine.
Now when a nitrile or a substituted imine is reacted with lithium aluminum hydride in the presence of water, the electrophilic carbon is attacked by the nucleophilic hydride to form an anion which is converted into a secondary amine upon addition of water.
Lithium aluminum hydride $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ or LAH is an inorganic compound that is often used as a reducing agent, especially to reduce amides, carboxylic acids, and esters.
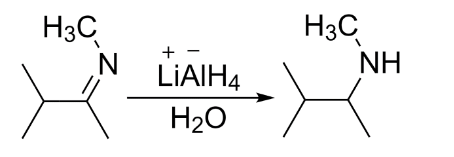
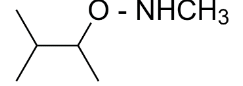
So, 3-dimethylbutan-2-amine is formed. It is a secondary amine.
The major organic product formed from the following reaction is option (B) 3-dimethylbutan-2-amine.
Note:It should be noted that the reaction between the ketone and the primary amine is carried out in an acidic buffer. This is done so that the carboxyl C=O group can be activated and the dehydration can be facilitated without the nucleophile being inhibited.
Complete step-by-step answer:In the given reaction, the reactant is 3-methylbutan-2-one. It is a ketone and is also known as methyl isopropyl ketone. It is an uncommon solvent.
When a ketone is reacted with a primary amine, it first undergoes nucleophilic addition to give carbinolamine and then further undergoes elimination and dehydrates to form a substituted imine.
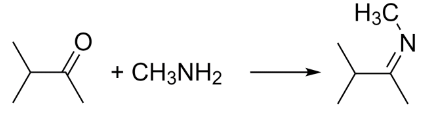
So, 3-dimethylbutan-2-imine is formed when 3-methylbutan-2-one is reacted with methylamine. This imine formed can be further reduced to an amine.
Now when a nitrile or a substituted imine is reacted with lithium aluminum hydride in the presence of water, the electrophilic carbon is attacked by the nucleophilic hydride to form an anion which is converted into a secondary amine upon addition of water.
Lithium aluminum hydride $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ or LAH is an inorganic compound that is often used as a reducing agent, especially to reduce amides, carboxylic acids, and esters.

So, 3-dimethylbutan-2-amine is formed. It is a secondary amine.
The major organic product formed from the following reaction is option (B) 3-dimethylbutan-2-amine.
Note:It should be noted that the reaction between the ketone and the primary amine is carried out in an acidic buffer. This is done so that the carboxyl C=O group can be activated and the dehydration can be facilitated without the nucleophile being inhibited.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




