
The length of intercept cut off from the line y = mx +c by the circle ${{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{y}}^2} = {a^2}$ is
A.$\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2}\left( {1 + {m^2}} \right) - {c^2}} $
B. $\dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2}\left( {1 + {m^2}} \right) - {c^2}} }}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}$
C. $\dfrac{{2\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2}\left( {1 + {m^2}} \right) - {c^2}} }}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}$
D. ${{\text{a}}^2}\left( {1 + {m^2}} \right) - {c^2}$
Answer
612.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, first we will make the diagram with the centre of the circle as (0,0) and radius as ‘a’. After this we will draw a perpendicular from centre to chord form by the given line. Then determine the length of the perpendicular and use it to calculate the length of chord.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The diagram for the question is:
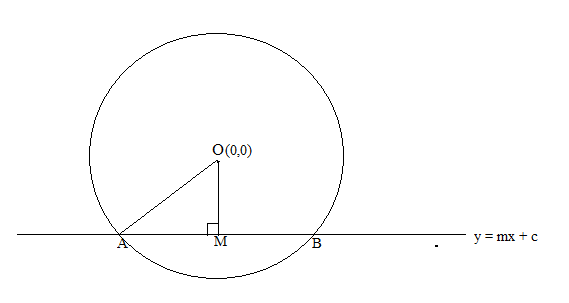
OM is the perpendicular drawn from centre o. It divides AB into two parts such that AM = BM.
OA is the radius = a
We know that length of perpendicular drawn from point(${{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}$) is given by:
d = $\dfrac{{{\text{|a}}{{\text{x}}_1} + {\text{b}}{{\text{y}}_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} + {{\text{b}}^2}} }}$
Therefore, we can say that:
OM = $\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}$
Using Pythagoras theorem, we can write:
${\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
Putting the values in above equation, we get:
${\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {{\text{a}}^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow $ ${\text{AM}} = \sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} - \dfrac{{{c^2}}}{{{{(1 + {m^2})}^{}}}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{{\text{a}}^2}(1 + {m^2}) - {c^2}}}{{{{(1 + {m^2})}^{}}}}} $
Therefore, length chord AB = $2\sqrt {\dfrac{{{{\text{a}}^2}(1 + {m^2}) - {c^2}}}{{{{(1 + {m^2})}^{}}}}} $
So, option C is correct.
Note- In the question involving finding the length of the chord, you should remember the formula for finding the length of perpendicular drawn from a point(${{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}$) which is given by:
d = $\dfrac{{{\text{|a}}{{\text{x}}_1} + {\text{b}}{{\text{y}}_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} + {{\text{b}}^2}} }}$ . You should know that the perpendicular drawn from centre on the chord divides the chord into two equal parts.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The diagram for the question is:

OM is the perpendicular drawn from centre o. It divides AB into two parts such that AM = BM.
OA is the radius = a
We know that length of perpendicular drawn from point(${{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}$) is given by:
d = $\dfrac{{{\text{|a}}{{\text{x}}_1} + {\text{b}}{{\text{y}}_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} + {{\text{b}}^2}} }}$
Therefore, we can say that:
OM = $\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}$
Using Pythagoras theorem, we can write:
${\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
Putting the values in above equation, we get:
${\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {{\text{a}}^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow $ ${\text{AM}} = \sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} - {{\left( {\dfrac{c}{{\sqrt {1 + {m^2}} }}} \right)}^2}} = \sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} - \dfrac{{{c^2}}}{{{{(1 + {m^2})}^{}}}}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{{\text{a}}^2}(1 + {m^2}) - {c^2}}}{{{{(1 + {m^2})}^{}}}}} $
Therefore, length chord AB = $2\sqrt {\dfrac{{{{\text{a}}^2}(1 + {m^2}) - {c^2}}}{{{{(1 + {m^2})}^{}}}}} $
So, option C is correct.
Note- In the question involving finding the length of the chord, you should remember the formula for finding the length of perpendicular drawn from a point(${{\text{x}}_1},{{\text{y}}_1}$) which is given by:
d = $\dfrac{{{\text{|a}}{{\text{x}}_1} + {\text{b}}{{\text{y}}_1} + c|}}{{\sqrt {{{\text{a}}^2} + {{\text{b}}^2}} }}$ . You should know that the perpendicular drawn from centre on the chord divides the chord into two equal parts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




