
The largest corpuscles in mammalian blood are
(a)Basophils
(b)Erythrocytes
(c)Monocytes
(d)Lymphocytes
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The largest corpuscle in mammalian blood has a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped or horseshoe-shaped nucleus. They are motile and have a bone marrow life span of 10-20 hours. It belongs under agranulocytes.
Complete answer:
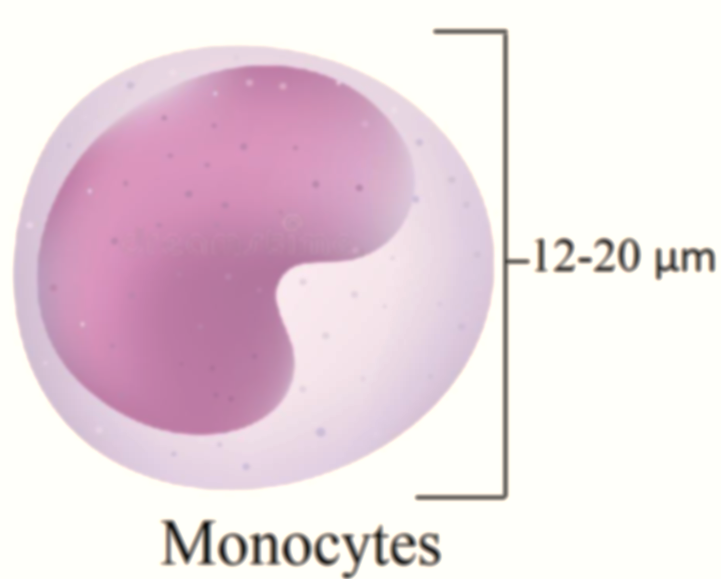
Monocytes are agranulocytes that play a major role in the phagocytosis of foreign bodies. They constitute about 4-8 percent of WBCs. Monocytes are large cells with a size of 12-20 µm. They are the largest blood cells.
Additional Information: The red blood corpuscles are also called erythrocytes and they perform the function of oxygen transport. These cells have a relatively small size of 6-8 µm.
The white blood corpuscles or leukocytes are further divided into granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes include eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils.
Basophil cells are present in the connective tissue and play an important part in allergic responses of the body. They produce immune mediators in response to interaction with various pathogens thus producing allergic reactions. They have a size of about 14-16 µm and are one of the largest corpuscles.
Lymphocytes play a major role in the immunity of the body. They are the cells that recognize specific antigens and produce antibodies against them. They are further divided into B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. B lymphocytes produce antibodies against the antigens whereas T lymphocytes recognize the infected cells and destroy them and help in recognizing the antigen.
The lymphocytes however have a smaller size that ranges from 7-8 µm.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Monocytes.’
Note:
Monocytes move to the site of infection where they differentiate into Macrophages.
Macrophages are the actual scavenger cells that perform the function of phagocytosis of foreign bodies and microbes.
So, macrophages are monocytes that enter the tissues after migrating from the bloodstream.
Monocytes have the additional function of presenting pieces of pathogens to T cells that can be recognized again and killed.
Complete answer:
Monocytes are agranulocytes that play a major role in the phagocytosis of foreign bodies. They constitute about 4-8 percent of WBCs. Monocytes are large cells with a size of 12-20 µm. They are the largest blood cells.
Additional Information: The red blood corpuscles are also called erythrocytes and they perform the function of oxygen transport. These cells have a relatively small size of 6-8 µm.
The white blood corpuscles or leukocytes are further divided into granulocytes and agranulocytes. Granulocytes include eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils.
Basophil cells are present in the connective tissue and play an important part in allergic responses of the body. They produce immune mediators in response to interaction with various pathogens thus producing allergic reactions. They have a size of about 14-16 µm and are one of the largest corpuscles.
Lymphocytes play a major role in the immunity of the body. They are the cells that recognize specific antigens and produce antibodies against them. They are further divided into B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. B lymphocytes produce antibodies against the antigens whereas T lymphocytes recognize the infected cells and destroy them and help in recognizing the antigen.
The lymphocytes however have a smaller size that ranges from 7-8 µm.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Monocytes.’
Note:
Monocytes move to the site of infection where they differentiate into Macrophages.
Macrophages are the actual scavenger cells that perform the function of phagocytosis of foreign bodies and microbes.
So, macrophages are monocytes that enter the tissues after migrating from the bloodstream.
Monocytes have the additional function of presenting pieces of pathogens to T cells that can be recognized again and killed.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




