
The IUPAC name of vinyl acetylene is:
A) \[Pent-1-en-4-yne\]
B) \[Pent-4-yne-1-en\]
C) \[but-1-en-3-yne\]
D) \[but-1-yn-3-ene\]
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Vinyl acetylene contains one carbon-carbon double bond and one carbon-carbon triple bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Alkenes are named by replacing the suffix –ane from the name of the corresponding alkane with suffix –ene. For example, alkene containing 2 carbon atoms is named as ethene by replacing the suffix –ane from the name ethane with suffix –ene.
Alkynes are named by replacing the suffix –ane from the name of the corresponding alkane with suffix –yne. For example, alkyne containing 3 carbon atoms is named ethyne by replacing the suffix –ane from the name ethane with suffix –yne.
Vinyl acetylene contains four carbon atoms, one carbon-carbon double bond and one carbon-carbon triple bond. The structure of vinylacetylene is as follows:
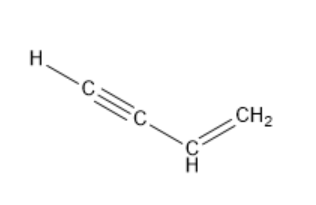
Since 4 carbon atoms are present in vinyl acetylene, the parent compound is butane. Since one carbon-carbon double bond and one carbon-carbon triple bond is present, the parent compound is butenyne. Here, the suffix –en represents a carbon-carbon double bond and a suffix –yne represents a carbon-carbon triple bond.
When multiple bonds are present, number the carbon chain from the end, which gives lowest possible locants to the carbon atoms joined by multiple bonds. A multiple bond is a double bond or a triple bond.
When both carbon-carbon double carbon-carbon and triple bonds are present in the same molecule, the carbon chain is numbered from the side which gives lowest locants to the double bonded carbon atoms.
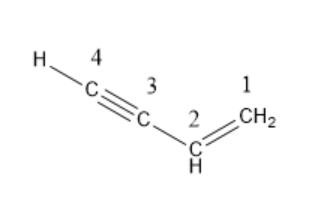
The IUPAC name of vinyl acetylene is \[but-1-en-3-yne\].
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Do not number the chain from the side containing carbon-carbon triple bond.When both carbon-carbon double carbon-carbon and triple bonds are present in the same molecule, the carbon chain is numbered from the side which gives lowest locants to the double bonded carbon atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Alkenes are named by replacing the suffix –ane from the name of the corresponding alkane with suffix –ene. For example, alkene containing 2 carbon atoms is named as ethene by replacing the suffix –ane from the name ethane with suffix –ene.
Alkynes are named by replacing the suffix –ane from the name of the corresponding alkane with suffix –yne. For example, alkyne containing 3 carbon atoms is named ethyne by replacing the suffix –ane from the name ethane with suffix –yne.
Vinyl acetylene contains four carbon atoms, one carbon-carbon double bond and one carbon-carbon triple bond. The structure of vinylacetylene is as follows:

Since 4 carbon atoms are present in vinyl acetylene, the parent compound is butane. Since one carbon-carbon double bond and one carbon-carbon triple bond is present, the parent compound is butenyne. Here, the suffix –en represents a carbon-carbon double bond and a suffix –yne represents a carbon-carbon triple bond.
When multiple bonds are present, number the carbon chain from the end, which gives lowest possible locants to the carbon atoms joined by multiple bonds. A multiple bond is a double bond or a triple bond.
When both carbon-carbon double carbon-carbon and triple bonds are present in the same molecule, the carbon chain is numbered from the side which gives lowest locants to the double bonded carbon atoms.

The IUPAC name of vinyl acetylene is \[but-1-en-3-yne\].
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Do not number the chain from the side containing carbon-carbon triple bond.When both carbon-carbon double carbon-carbon and triple bonds are present in the same molecule, the carbon chain is numbered from the side which gives lowest locants to the double bonded carbon atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




