
The inner part of a cupboard is of cuboidal shape with its length, breadth, and height in the ratio of $1:\sqrt{2}:1$. What is the angle made by the largest stick which can be inserted in the cupboard with its inside base?
Answer
614.7k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will consider a variable x such that length, breadth and height will become, $x,\sqrt{2}x,x$ respectively. We will then visualise the given situation and then we will know that the largest stick that can be inserted in a cuboid will be at the position of body diagonal. By using this, we will be able to find the answer to this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have been asked to find the angle made by the longest stick that can be inserted in the cuboidal cupboard of length, breadth and height of ratio $1:\sqrt{2}:1$ with the base. Let us first draw the figure of the given situation. So, the figure is as below.
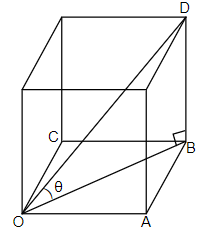
Here, we have considered OA as the length, AB as the breadth and BD as the height. Now, let us consider the angle made by the stick with the base as $\theta $. Also, we will consider a variable x such that $x,\sqrt{2}x,x$ will become the length, breadth and height of the cuboid respectively. Now, we know that for any right angled triangle, Pythagoras theorem states that, ${{\left( Base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( Perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( Hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$. So, we can say that for right angled triangle OBD,
${{\left( OB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}$
And, in triangle OAB, applying Pythagoras theorem, we can say,
${{\left( OA \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OB \right)}^{2}}$
From both the above equations, we can say that,
${{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OA \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}}\ldots \ldots \ldots \left( i \right)$
Now, we know that OA represents the length, AB represents the breadth and BD represents the height. So, we can write $OA=x,AB=\sqrt{2}x,BD=x$. Therefore, we will get equation (i) as,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}={{\left( x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{2}x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( x \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+2{{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}=4{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow OD=2x \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the longest stick that can be inserted in a cuboid will be the stick that is kept at the position of body diagonal, that is, OD. So, we can say that the angle made by OD with the base will be the angle made by the stick with the base, that is, $\theta $. We know that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}$, so for triangle OBD, we can say that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{BD}{OD}$
Now, we know that BD = x and OD = 2x. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{x}{2x} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know, $\sin 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}$. So, we can write $\dfrac{1}{2}=\sin 30{}^\circ $. Therefore, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\sin 30{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =30{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can say that the angle made by the longest stick that can be inserted in a cuboid cupboard has length, breadth and height in the ratio $1:\sqrt{2}:1$ as $30{}^\circ $.
Note: While solving this question, we need to remember that for any right angled triangle, we can apply Pythagoras theorem, that is, ${{\left( Base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( Perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( Hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$. We also need to remember that sin ratio is given by $\sin \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}$ and $\sin 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}$. We have to be careful that the longest stick would be taken as the body/space diagonal and not the face diagonal. Most students consider the face diagonal by mistake, so it must be avoided.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we have been asked to find the angle made by the longest stick that can be inserted in the cuboidal cupboard of length, breadth and height of ratio $1:\sqrt{2}:1$ with the base. Let us first draw the figure of the given situation. So, the figure is as below.

Here, we have considered OA as the length, AB as the breadth and BD as the height. Now, let us consider the angle made by the stick with the base as $\theta $. Also, we will consider a variable x such that $x,\sqrt{2}x,x$ will become the length, breadth and height of the cuboid respectively. Now, we know that for any right angled triangle, Pythagoras theorem states that, ${{\left( Base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( Perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( Hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$. So, we can say that for right angled triangle OBD,
${{\left( OB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}$
And, in triangle OAB, applying Pythagoras theorem, we can say,
${{\left( OA \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OB \right)}^{2}}$
From both the above equations, we can say that,
${{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}={{\left( OA \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BD \right)}^{2}}\ldots \ldots \ldots \left( i \right)$
Now, we know that OA represents the length, AB represents the breadth and BD represents the height. So, we can write $OA=x,AB=\sqrt{2}x,BD=x$. Therefore, we will get equation (i) as,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}={{\left( x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \sqrt{2}x \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( x \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( OD \right)}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+2{{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}=4{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow OD=2x \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the longest stick that can be inserted in a cuboid will be the stick that is kept at the position of body diagonal, that is, OD. So, we can say that the angle made by OD with the base will be the angle made by the stick with the base, that is, $\theta $. We know that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}$, so for triangle OBD, we can say that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{BD}{OD}$
Now, we know that BD = x and OD = 2x. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{x}{2x} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know, $\sin 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}$. So, we can write $\dfrac{1}{2}=\sin 30{}^\circ $. Therefore, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\sin 30{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =30{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, we can say that the angle made by the longest stick that can be inserted in a cuboid cupboard has length, breadth and height in the ratio $1:\sqrt{2}:1$ as $30{}^\circ $.
Note: While solving this question, we need to remember that for any right angled triangle, we can apply Pythagoras theorem, that is, ${{\left( Base \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( Perpendicular \right)}^{2}}={{\left( Hypotenuse \right)}^{2}}$. We also need to remember that sin ratio is given by $\sin \theta =\dfrac{Perpendicular}{Hypotenuse}$ and $\sin 30{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}$. We have to be careful that the longest stick would be taken as the body/space diagonal and not the face diagonal. Most students consider the face diagonal by mistake, so it must be avoided.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are gulf countries and why they are called Gulf class 8 social science CBSE

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE

In Indian rupees 1 trillion is equal to how many c class 8 maths CBSE

Who created the image of Bharat Mata for the first class 8 social science CBSE

What is the Balkan issue in brief class 8 social science CBSE





