
The image of an object formed by a concave lens is:
A) Virtual, inverted and diminished
B) Virtual, upright and diminished
C) Virtual, inverted and enlarged
D) Virtual, upright and enlarged
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Concave lens is a diverging lens. Light rays diverge from each other after passing through a concave lens. So they can’t meet at some real point to form an image. Hence, the image is never real for a concave lens.
Explanation:
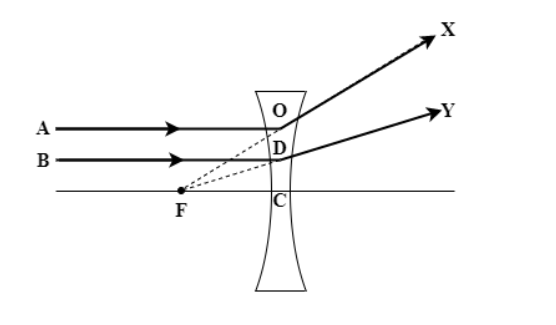
(a) When object is at infinity
When the object is placed at infinity, parallel light rays come from it to fall on the lens (AO and BD in this attached figure). Now, all the rays diverge from each other so they actually never meet really. It seems that they are emerging from a fixed point from the incoming ray’s side and that point is known as the focal point of the lens. So the formed image is indeed a point at the focus of the lens.
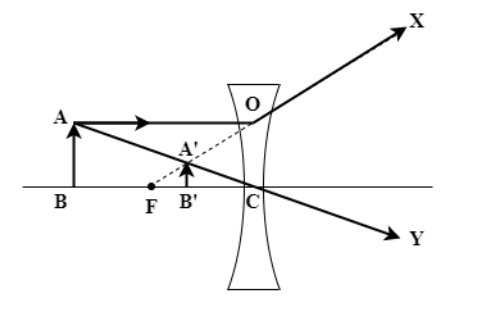
(b) When object is between infinity and focus
When the object is placed between infinity and the focus of the lens, from the top of the object (point A) the parallel to ground ray AO falls on the lens and diverges away such that it seems to come out from the focus OF. Another ray from A passes straight through the center as AC and backward extended OX and AC meets at A’ to form the image A’B’ within the lens and the focus (shown in the attached figure). This image is virtual as it’s on the side of the incoming ray of the lens. It’s upright and diminished in size.
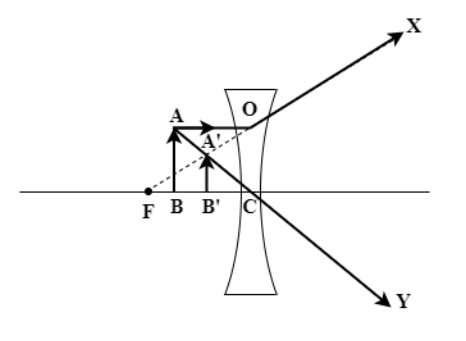
(c) When object is between focus and the lens
When the object is placed between the focus and the lens, from the top of the object (point A) the parallel to ground ray AO falls on the lens and diverges away such that it seems to come out from the focus OF. Another ray from A passes straight through the center as AC and backward extended OX and AC meets at A’ to form the image A’B’ within the lens and the focus (shown in the attached figure). This image is virtual as it’s on the side of the incoming ray of the lens. It’s upright and diminished in size.
Correct answer:The image of the object will be, (b) virtual, upright and diminished.
Note: To find the type of image formed by any lens, from the upper point of the image just draw a line parallel to ground straight to the lens. Now, this ray will always move in a path such that it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus. Now draw another ray from the top of the object that passes through the center of the lens without any deviation. Now, the image will form where these two rays meet. If they actually meet then it will be a real image or if it appears that these rays are coming out from an apparent meeting point backward then the image will be real.
Explanation:
(a) When object is at infinity
When the object is placed at infinity, parallel light rays come from it to fall on the lens (AO and BD in this attached figure). Now, all the rays diverge from each other so they actually never meet really. It seems that they are emerging from a fixed point from the incoming ray’s side and that point is known as the focal point of the lens. So the formed image is indeed a point at the focus of the lens.

(b) When object is between infinity and focus
When the object is placed between infinity and the focus of the lens, from the top of the object (point A) the parallel to ground ray AO falls on the lens and diverges away such that it seems to come out from the focus OF. Another ray from A passes straight through the center as AC and backward extended OX and AC meets at A’ to form the image A’B’ within the lens and the focus (shown in the attached figure). This image is virtual as it’s on the side of the incoming ray of the lens. It’s upright and diminished in size.

(c) When object is between focus and the lens
When the object is placed between the focus and the lens, from the top of the object (point A) the parallel to ground ray AO falls on the lens and diverges away such that it seems to come out from the focus OF. Another ray from A passes straight through the center as AC and backward extended OX and AC meets at A’ to form the image A’B’ within the lens and the focus (shown in the attached figure). This image is virtual as it’s on the side of the incoming ray of the lens. It’s upright and diminished in size.

Correct answer:The image of the object will be, (b) virtual, upright and diminished.
Note: To find the type of image formed by any lens, from the upper point of the image just draw a line parallel to ground straight to the lens. Now, this ray will always move in a path such that it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus. Now draw another ray from the top of the object that passes through the center of the lens without any deviation. Now, the image will form where these two rays meet. If they actually meet then it will be a real image or if it appears that these rays are coming out from an apparent meeting point backward then the image will be real.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




