
The hybridisation of carbon in carbon dioxide molecule is:
[A] $s{{p}^{2}}$
[B] sp
[C] $s{{p}^{3}}$
[D] None
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: We can find out hybridisation of an atom by identifying the number and the types of bond it makes with other atomic orbitals. To find the hybridisation of carbon here, firstly draw the structure of the carbon dioxide molecule with its proper bonding with the oxygen atoms. If there are no double bonds, the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$, if there is one double bond hybridisation is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and if there are two or more than two double bonds, hybridisation is sp.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the formula of carbon dioxide is $C{{O}_{2}}$ . As we can see, it contains one atom of carbon and a molecule of oxygen.
In the valence bond theory, as we know atomic orbitals overlap with other atomic orbitals to form a molecule and thus creating new hybrid orbitals. This is known as the phenomenon of hybridisation.
In carbon dioxide, carbon serves as the central atom and it is bonded to the two oxygen atoms through a covalent double bonding. We know that a double bonding involves a –sigma bond and a –pi bond.
Now that we know the type of bonds in carbon dioxide thus to find the hybridisation of a molecule of carbon dioxide, firstly we have to draw its structure which is-
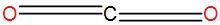
We define hybridisation in terms of -‘s’ and ‘p’ orbitals. If there are no double bonds, the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$ but we can see that this is not the case here. An atom with a single double bond has a hybridisation of $s{{p}^{2}}$ and an atom with two or more double bonds has a hybridisation of sp. Now, here we can see that there are two double bonds thus hybridisation of carbon in carbon dioxide is sp. So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We can use the VSEPR theory which is the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory to correlate the hybridisation with the shape as well as the geometry of a molecule. Molecules settle in a shape where the electronic repulsion is the minimum and thus creates as lower energy shape as possible. Hybridization affects the bonds and the types of the bonds the molecule makes and thus is correlated to the shape of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the formula of carbon dioxide is $C{{O}_{2}}$ . As we can see, it contains one atom of carbon and a molecule of oxygen.
In the valence bond theory, as we know atomic orbitals overlap with other atomic orbitals to form a molecule and thus creating new hybrid orbitals. This is known as the phenomenon of hybridisation.
In carbon dioxide, carbon serves as the central atom and it is bonded to the two oxygen atoms through a covalent double bonding. We know that a double bonding involves a –sigma bond and a –pi bond.
Now that we know the type of bonds in carbon dioxide thus to find the hybridisation of a molecule of carbon dioxide, firstly we have to draw its structure which is-
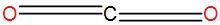
We define hybridisation in terms of -‘s’ and ‘p’ orbitals. If there are no double bonds, the hybridisation is $s{{p}^{3}}$ but we can see that this is not the case here. An atom with a single double bond has a hybridisation of $s{{p}^{2}}$ and an atom with two or more double bonds has a hybridisation of sp. Now, here we can see that there are two double bonds thus hybridisation of carbon in carbon dioxide is sp. So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We can use the VSEPR theory which is the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory to correlate the hybridisation with the shape as well as the geometry of a molecule. Molecules settle in a shape where the electronic repulsion is the minimum and thus creates as lower energy shape as possible. Hybridization affects the bonds and the types of the bonds the molecule makes and thus is correlated to the shape of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




