
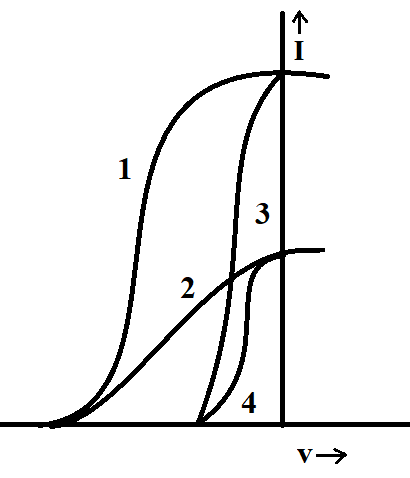
The given graph shows the variations of photo-electric current (I) versus applied voltage (V) for two different photosensitive materials and for two different intensities of the incident radiations. Identify the pairs of curves that correspond to different material but same intensity of incident radiations.

Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: If the intensity of light of a given wavelength is increased, there is an increase in the number of photons incident on a given area in a given time. But the energy of each photon remains the same. Additionally, the stopping potential increases linearly with frequency of the incident radiation for a given photosensitive material.
Complete step by step answer:
The phenomena of emission of electrons from a metallic surface when it is subjected to electromagnetic radiation of sufficiently high frequency is incident on it, is called photoelectric effect. The photo (light) generated electrons are called photoelectrons.
If we allow radiations of a fixed frequency to fall on any photosensitive material and the accelerating potential between the two electrodes is kept fixed then the photoelectric current is found to be increasing linearly with the intensity of radiation.
Since photoelectric current is directly proportional to the number of photoelectrons emitted per second, this implies that the number of photoelectrons emitted per second is proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation.
The value of retarding potential at which the photoelectric current becomes zero is called cut off potential or stopping potential for the given frequency of the incident radiation.
From the given figure it is clear that curves 1 and 2 have the same stopping potential. Similarly curves 3 and 4 have the same value of stopping potential. So curves 1 and 2 correspond to the same material, whereas 3 and 4 correspond to the same.
Therefore, (2 and 4) and (1 and 3) are the pairs of curves that correspond to different materials but have the same intensity of incident radiations.
Note: For a frequency of the incident radiation which is less than the threshold frequency of the photosensitive material, no photoelectron emission is possible. Regardless of howsoever large is the intensity of the incident radiation.
Complete step by step answer:
The phenomena of emission of electrons from a metallic surface when it is subjected to electromagnetic radiation of sufficiently high frequency is incident on it, is called photoelectric effect. The photo (light) generated electrons are called photoelectrons.
If we allow radiations of a fixed frequency to fall on any photosensitive material and the accelerating potential between the two electrodes is kept fixed then the photoelectric current is found to be increasing linearly with the intensity of radiation.
Since photoelectric current is directly proportional to the number of photoelectrons emitted per second, this implies that the number of photoelectrons emitted per second is proportional to the intensity of the incident radiation.
The value of retarding potential at which the photoelectric current becomes zero is called cut off potential or stopping potential for the given frequency of the incident radiation.
From the given figure it is clear that curves 1 and 2 have the same stopping potential. Similarly curves 3 and 4 have the same value of stopping potential. So curves 1 and 2 correspond to the same material, whereas 3 and 4 correspond to the same.
Therefore, (2 and 4) and (1 and 3) are the pairs of curves that correspond to different materials but have the same intensity of incident radiations.
Note: For a frequency of the incident radiation which is less than the threshold frequency of the photosensitive material, no photoelectron emission is possible. Regardless of howsoever large is the intensity of the incident radiation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




