
The given diagram shows a boat made from iron. Some magnesium blocks are attached to the iron below the water line to prevent rusting. Why?
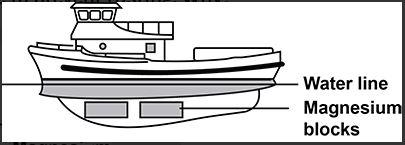
(A) Magnesium reacts in preference to the iron
(B) The magnesium forms an alloy with the iron
(C) Magnesium react to form a protective coating of magnesium hydroxide on iron
(D) The magnesium stops the oxygen in the water from getting to iron

Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Here, magnesium is used for the attachment below the water line to a boat made up of iron to protect it from rusting. The answer to this question can be multiple choice too.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first understand the basics of corrosion and reactivities of magnesium and iron relatively.
Corrosion- Corrosion is the redox reaction. It is the galvanic process by which metal deteriorates i.e. formation of rust. Under favourable conditions, the oxidation of metals is spontaneous, except gold and platinum. Chromium, magnesium, nickel and aluminium mostly form a coating over the most corrosive metals to prevent the rusting. As, the reactivity order of metal is as follows,
Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Sn > Pb > Cu > Ag (generally)
The metals which have more reactivity than Fe can protect it from rusting when coated over Fe. Thus, Mg corrodes instead of Fe sacrificing itself; thus, this is called sacrificial protection. Along with Mg, Zn is also used as sacrificial metal. They are more reactive in the ambient environment than Fe. They lose their electrons before iron, protecting it from getting oxidised. Most anti-corrosion methods are used to stop the corrosion of Fe which involves the cut of oxygen supply (may be from air or water). This includes adding some barrier like Mg coating on the surface of metal which needs to be protected, though Mg do not corrode very quickly.
Magnesium can form magnesium hydroxide (in $Mg-{{H}_{2}}O$ system) which would then act as a protective layer to stop the corrosion in a neutral or alkaline environment.
Therefore, option (A), (C) and (D) are correct.
Note: Do note that just by placing some Mg blocks over Fe, it would never form an alloy. Thus, option (B) can never be the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first understand the basics of corrosion and reactivities of magnesium and iron relatively.
Corrosion- Corrosion is the redox reaction. It is the galvanic process by which metal deteriorates i.e. formation of rust. Under favourable conditions, the oxidation of metals is spontaneous, except gold and platinum. Chromium, magnesium, nickel and aluminium mostly form a coating over the most corrosive metals to prevent the rusting. As, the reactivity order of metal is as follows,
Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Sn > Pb > Cu > Ag (generally)
The metals which have more reactivity than Fe can protect it from rusting when coated over Fe. Thus, Mg corrodes instead of Fe sacrificing itself; thus, this is called sacrificial protection. Along with Mg, Zn is also used as sacrificial metal. They are more reactive in the ambient environment than Fe. They lose their electrons before iron, protecting it from getting oxidised. Most anti-corrosion methods are used to stop the corrosion of Fe which involves the cut of oxygen supply (may be from air or water). This includes adding some barrier like Mg coating on the surface of metal which needs to be protected, though Mg do not corrode very quickly.
Magnesium can form magnesium hydroxide (in $Mg-{{H}_{2}}O$ system) which would then act as a protective layer to stop the corrosion in a neutral or alkaline environment.
Therefore, option (A), (C) and (D) are correct.
Note: Do note that just by placing some Mg blocks over Fe, it would never form an alloy. Thus, option (B) can never be the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




