
The genes for antibiotic resistance are located in
A. Chromosome.
B. Nucleus
C. Cell wall
D. Plasmid.
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: As we know that antibiotics are the medicines that are used for the prevention of bacterial infection. In response to these medicines the bacteria portrays some changes and this is when we see the occurrence of antibiotic resistance. It’s the bacteria that becomes antibiotic resistant, not the humans or the animals.
Complete answer-
The antibiotic resistance genes are found in the plasmids. These small extrachromosomal elements are mostly found in bacteria. They perform a unique mechanism of conjugation for the movement of plasmids from one bacterial cell to another. This occurs through a cell to cell contact between the bacteria after which the transfer of a copy of plasmid DNA from a donor to a recipient occurs.
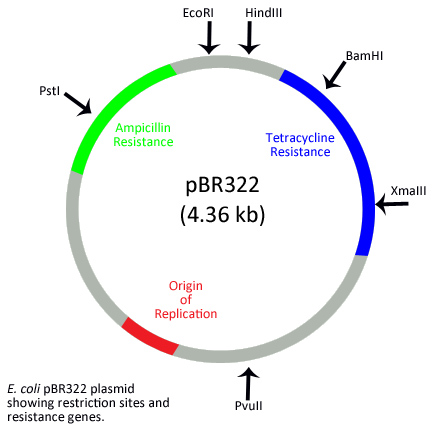
Plasmid or the drug resistance factor possess autonomous replication properties and are found in the bacterial cytoplasm. This small circular DNA performs the function of formation of sex pili which promotes conjugation between two bacteria. This ability of transferring a copy to a sensitive bacteria from a resistant one helps in gaining the drug resistance capability. The figure belows shows the structure of plasmid containing antibiotic resistance genes.
From the above discussion, we know that option (D) is our right answer.
Note-
Plasmid, being a small, circular, double stranded DNA molecule is different from the one that is present in the cell of the chromosomal DNA. These are present in bacteria as well as some eukaryotes. The genes that are carried in plasmids helps the bacteria by providing it with genetic advantages like the one we are discussing i.e. antibiotic resistance.
Complete answer-
The antibiotic resistance genes are found in the plasmids. These small extrachromosomal elements are mostly found in bacteria. They perform a unique mechanism of conjugation for the movement of plasmids from one bacterial cell to another. This occurs through a cell to cell contact between the bacteria after which the transfer of a copy of plasmid DNA from a donor to a recipient occurs.
Plasmid or the drug resistance factor possess autonomous replication properties and are found in the bacterial cytoplasm. This small circular DNA performs the function of formation of sex pili which promotes conjugation between two bacteria. This ability of transferring a copy to a sensitive bacteria from a resistant one helps in gaining the drug resistance capability. The figure belows shows the structure of plasmid containing antibiotic resistance genes.

From the above discussion, we know that option (D) is our right answer.
Note-
Plasmid, being a small, circular, double stranded DNA molecule is different from the one that is present in the cell of the chromosomal DNA. These are present in bacteria as well as some eukaryotes. The genes that are carried in plasmids helps the bacteria by providing it with genetic advantages like the one we are discussing i.e. antibiotic resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




