
The frequency of mutation in a species can be increased by the use of
A. X-rays
B. UV-rays
C. Nitrous acid
D. All the above
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: Mutations are promoted by mutagens. Mutagens are of different categories. Generally, radiations and chemical compounds increase mutations.
Complete answer: Mutations are alteration in DNA. It can result either in a change in chromosomes or individual genes. If they occur in germline cells then the mutation can be genetically passed on to the next generations. They are caused by mutagens.
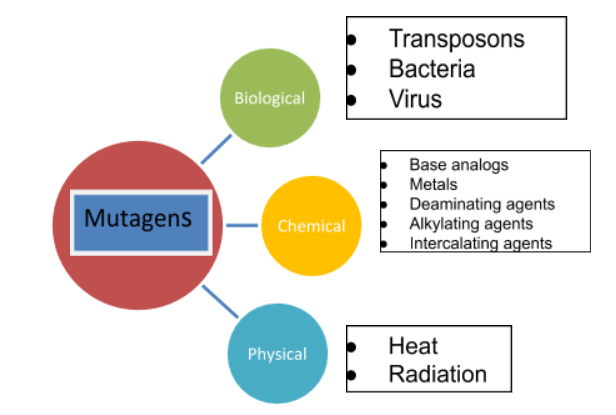
Radiation-induced mutations are caused by physical mutagens. Such radiation has only resulted in highly vicious diseases like cancer. The rays ionize molecules and pave the way to let them react with other biological compounds. They might break the DNA. They might damage the nitrogenous bases or sugars present in the DNA. They might crosslink the DNA to itself or to other proteins. The radiations could be gamma rays, X-rays, and UV rays.
Chemicals also act as mutagens. Many chemicals change the bases. This means that AT base is transitioned into GC or vice versa. Deamination can also be caused. Deamination is the process of scraping off the amino group from the DNA. The base pairing can also be affected, for example, guanine can be paired with thymine rather than cytosine. Some chemical mutagens can cause frameshifts, addition, or deletion of bases as well. Chemical mutagens include Bromo Uracil, Amino purine, Sodium azide, hydroxylamine, Nitrous Acid, Ethylene imines, and many more.
Hence option D is correct.
Note: Mutations are generally harmful to the human body. They may lead to cancer. They may cause defects that can even be passed on further. Mutations may cause proteins present in the body to dysfunction or change their function. This may cause certain diseases as well.
Complete answer: Mutations are alteration in DNA. It can result either in a change in chromosomes or individual genes. If they occur in germline cells then the mutation can be genetically passed on to the next generations. They are caused by mutagens.

Radiation-induced mutations are caused by physical mutagens. Such radiation has only resulted in highly vicious diseases like cancer. The rays ionize molecules and pave the way to let them react with other biological compounds. They might break the DNA. They might damage the nitrogenous bases or sugars present in the DNA. They might crosslink the DNA to itself or to other proteins. The radiations could be gamma rays, X-rays, and UV rays.
Chemicals also act as mutagens. Many chemicals change the bases. This means that AT base is transitioned into GC or vice versa. Deamination can also be caused. Deamination is the process of scraping off the amino group from the DNA. The base pairing can also be affected, for example, guanine can be paired with thymine rather than cytosine. Some chemical mutagens can cause frameshifts, addition, or deletion of bases as well. Chemical mutagens include Bromo Uracil, Amino purine, Sodium azide, hydroxylamine, Nitrous Acid, Ethylene imines, and many more.
Hence option D is correct.
Note: Mutations are generally harmful to the human body. They may lead to cancer. They may cause defects that can even be passed on further. Mutations may cause proteins present in the body to dysfunction or change their function. This may cause certain diseases as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




