
The four-daughter produced at the end of meiosis are
A. Without nucleus
B. Genetically identical to the parent cell
C. Genetically dissimilar to the parent cell
D. With four nuclei
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: All cells arise from other cells through the process of cell division. Meiosis is a highly specialized form of cell division that generates reproductive cells, such as plant and fungal spores and sperm and egg cells.
Complete answer: Meiosis is a type of cell division that lowers the chromosome number in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is needed to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction. Meiosis begins with a parent cell that is diploid, meaning it has two copies of each chromosome. The parent cell undergoes one round of DNA replication followed by two separate cycles of nuclear division. The process results in four daughter cells that are haploid in nature, which means they all contain half the chromosome number of the diploid parent cell. And thus we say they are dissimilar to the parent cells.
The diagram below shows the process of meiosis -
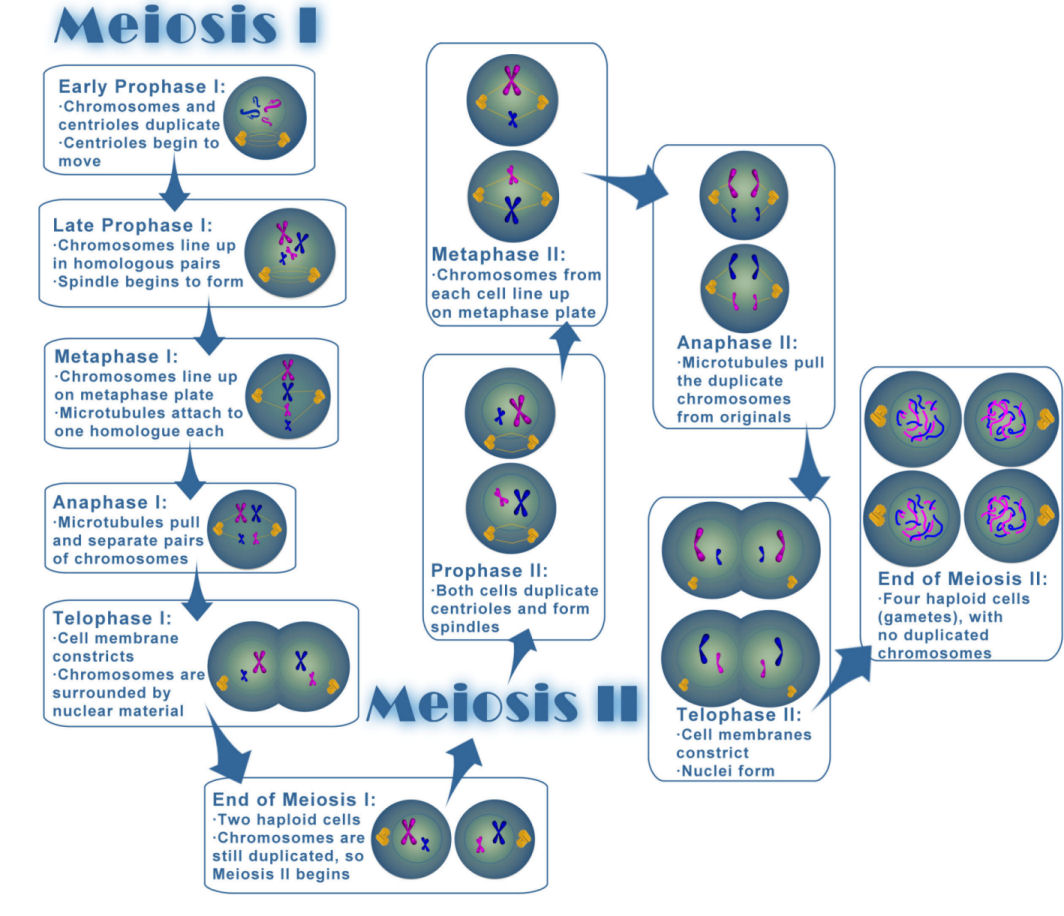
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
Meiosis I, the first meiotic division, begins with prophase I. During prophase, I, the complex of DNA and protein are known as chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Between prophase I and metaphase I, the pairs of homologous chromosomes form tetrads. Within the tetrad, any pair of chromatid arms can overlap and fuse in a process called crossing-over or recombination. In metaphase I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes align on the equatorial plane, and in anaphase I the two chromatids, pull away. Meiosis II is a mitotic division of each of the haploid cells produced in meiosis I.
Note: Proper “chromosomal segregation,” or the separation of sister chromatids during meiosis I and II are essential for generating healthy sperm and egg cells, and by extension, embryos. If chromosomes fail to segregate completely, it's called non-disjunction and can result in the formation of gametes that have missing or extra chromosomes.
Complete answer: Meiosis is a type of cell division that lowers the chromosome number in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is needed to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction. Meiosis begins with a parent cell that is diploid, meaning it has two copies of each chromosome. The parent cell undergoes one round of DNA replication followed by two separate cycles of nuclear division. The process results in four daughter cells that are haploid in nature, which means they all contain half the chromosome number of the diploid parent cell. And thus we say they are dissimilar to the parent cells.
The diagram below shows the process of meiosis -

Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Additional Information:
Meiosis I, the first meiotic division, begins with prophase I. During prophase, I, the complex of DNA and protein are known as chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Between prophase I and metaphase I, the pairs of homologous chromosomes form tetrads. Within the tetrad, any pair of chromatid arms can overlap and fuse in a process called crossing-over or recombination. In metaphase I, the homologous pairs of chromosomes align on the equatorial plane, and in anaphase I the two chromatids, pull away. Meiosis II is a mitotic division of each of the haploid cells produced in meiosis I.
Note: Proper “chromosomal segregation,” or the separation of sister chromatids during meiosis I and II are essential for generating healthy sperm and egg cells, and by extension, embryos. If chromosomes fail to segregate completely, it's called non-disjunction and can result in the formation of gametes that have missing or extra chromosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




