
The formal charge of carbon atom in carbonate ion is-
(A) + 1
(B) - 1
(C) + 4
(D) zero
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Formal charge is only a theoretical charge over an individual atom of an ion a molecule.
To find out the answer we have to follow a simple expression formal charge of an atom \[ = \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}valence{\text{ }}electron{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}free{\text{ }}state} \right] - \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}non - bonding{\text{ }}electron} \right] - [\dfrac{{Total\,no.\,of\,bonding\,electron}}{2}]\]
Complete step by step answer:
We will have to know that formal charge of an atom is not equal to real charge of an ion or a molecule. Real charge is distributed over a polyatomic molecule or ion as a whole and not over a single atom.
Formal charge is the difference between the valence electron of that atom in Free State and the total no. of electrons assigned to that atom in Lewis dot model.
A mathematical expression to find out the formal charge of an atom is-
\[Formal\,charge = \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}valence{\text{ }}{e^ - }\,in{\text{ }}free{\text{ }}state} \right] - \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}non - bonding{\text{ }}electron} \right] - \dfrac{1}{2}[Total\,no.\,of\,bonding\,electron]\]
First, we have to know the Lewis dot structure of carbonate ions.
Which is shown below-
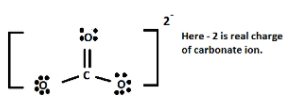
Now, we will find out the formal charge of the carbon atom.
Total no. of valence electron of electron in free state = 4
Total no. of non-bonding electron of carbon = 0
Total no of bonding electron of carbon = 8
So, the formal charge of carbon atom,
\[ = 4 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}[8]\]
= 4 - 4
= 0
Therefore the formal charge of the carbon atom is 0.
Hence the correct option is (D).
Note: 1. Formal charges help to select the lowest energy structure among different Lewis structures for a given species.
2. The smallest formal charges and the most distributed charges on atoms gives lowest energy structure.
To find out the answer we have to follow a simple expression formal charge of an atom \[ = \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}valence{\text{ }}electron{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}free{\text{ }}state} \right] - \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}non - bonding{\text{ }}electron} \right] - [\dfrac{{Total\,no.\,of\,bonding\,electron}}{2}]\]
Complete step by step answer:
We will have to know that formal charge of an atom is not equal to real charge of an ion or a molecule. Real charge is distributed over a polyatomic molecule or ion as a whole and not over a single atom.
Formal charge is the difference between the valence electron of that atom in Free State and the total no. of electrons assigned to that atom in Lewis dot model.
A mathematical expression to find out the formal charge of an atom is-
\[Formal\,charge = \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}valence{\text{ }}{e^ - }\,in{\text{ }}free{\text{ }}state} \right] - \left[ {Total{\text{ }}no.{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}non - bonding{\text{ }}electron} \right] - \dfrac{1}{2}[Total\,no.\,of\,bonding\,electron]\]
First, we have to know the Lewis dot structure of carbonate ions.
Which is shown below-

Now, we will find out the formal charge of the carbon atom.
Total no. of valence electron of electron in free state = 4
Total no. of non-bonding electron of carbon = 0
Total no of bonding electron of carbon = 8
So, the formal charge of carbon atom,
\[ = 4 - 0 - \dfrac{1}{2}[8]\]
= 4 - 4
= 0
Therefore the formal charge of the carbon atom is 0.
Hence the correct option is (D).
Note: 1. Formal charges help to select the lowest energy structure among different Lewis structures for a given species.
2. The smallest formal charges and the most distributed charges on atoms gives lowest energy structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




