
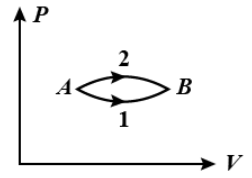
The figure shows two paths for the change of state of gas from A to B. The ratio of molar heat capacities in path 1 and path 2 is
A. < 1
B. > 1
C. 1
D. Data insufficient

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: This question can be solved using the formula that relates the internal energy of the gas and the heat capacity of that gas. For the given two paths, we will derive two different equations, and then, we will find the ratio of these equations in terms of the molar heat capacities.
Formula used:
\[Q=nC\Delta T\]
\[\Delta U=n{{C}_{v}}\Delta T\]
\[Q=\Delta U+W\]
Complete step by step answer:
The formula that relates the heat and the heat capacity of an ideal gas is as follows.
\[Q=nC\Delta T\]
Where Q is the heat, n is the number of moles, C is the molar heat capacity (can be a constant pressure or can be at constant volume) and \[\Delta T\]is the change in the temperature.
Express the above equation in terms of the molar heat capacity. So, we get,
\[C=\dfrac{Q}{n\Delta T}\]
As the gas chooses two paths to change the state from A to B, so, the number of moles of the gas and the change in the temperature remains the same for both the processes.
So, the above equation can be rewritten as follows.
\[C\propto Q\]….. (1)
The internal energy is given by the formula,
\[\Delta U=n{{C}_{v}}\Delta T\]
Where n is the number of moles, \[{{C}_{v}}\] is the molar heat capacity at a constant velocity and \[\Delta T\]is the change in the temperature.
\[{{C}_{v}}\]will be a constant value and as the parameters n and \[\Delta T\]remains constant, thus, in turn, the internal energy remains constant.
The work done by the gas is,
\[Q=\Delta U+W\]
The work done will be the area under the curve. So, from the given graph, it’s clear that the work done under the curve for path 2 is more than the work done under the curve for path 1.
\[{{W}_{2}}>{{W}_{1}}\]
As the change in the internal energy is constant, so, we can write,
\[{{Q}_{2}}>{{Q}_{1}}\]
As, from the equation (1), we have, \[C\propto Q\]. So, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{C}_{2}}>{{C}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{C}_{1}}}{{{C}_{2}}}<1 \\
\end{align}\]
As, the ratio of molar heat capacities in path 1 and path 2 is \[<1\].
Thus, the option (A) is correct.
Note:
From the graph, the work done through several paths can be compared by comparing the area under the path curves given. Smaller the curve, smaller will be the amount of work done by the gas and vice – versa.
Formula used:
\[Q=nC\Delta T\]
\[\Delta U=n{{C}_{v}}\Delta T\]
\[Q=\Delta U+W\]
Complete step by step answer:
The formula that relates the heat and the heat capacity of an ideal gas is as follows.
\[Q=nC\Delta T\]
Where Q is the heat, n is the number of moles, C is the molar heat capacity (can be a constant pressure or can be at constant volume) and \[\Delta T\]is the change in the temperature.
Express the above equation in terms of the molar heat capacity. So, we get,
\[C=\dfrac{Q}{n\Delta T}\]
As the gas chooses two paths to change the state from A to B, so, the number of moles of the gas and the change in the temperature remains the same for both the processes.
So, the above equation can be rewritten as follows.
\[C\propto Q\]….. (1)
The internal energy is given by the formula,
\[\Delta U=n{{C}_{v}}\Delta T\]
Where n is the number of moles, \[{{C}_{v}}\] is the molar heat capacity at a constant velocity and \[\Delta T\]is the change in the temperature.
\[{{C}_{v}}\]will be a constant value and as the parameters n and \[\Delta T\]remains constant, thus, in turn, the internal energy remains constant.
The work done by the gas is,
\[Q=\Delta U+W\]
The work done will be the area under the curve. So, from the given graph, it’s clear that the work done under the curve for path 2 is more than the work done under the curve for path 1.
\[{{W}_{2}}>{{W}_{1}}\]
As the change in the internal energy is constant, so, we can write,
\[{{Q}_{2}}>{{Q}_{1}}\]
As, from the equation (1), we have, \[C\propto Q\]. So, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& {{C}_{2}}>{{C}_{1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{C}_{1}}}{{{C}_{2}}}<1 \\
\end{align}\]
As, the ratio of molar heat capacities in path 1 and path 2 is \[<1\].
Thus, the option (A) is correct.
Note:
From the graph, the work done through several paths can be compared by comparing the area under the path curves given. Smaller the curve, smaller will be the amount of work done by the gas and vice – versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




