
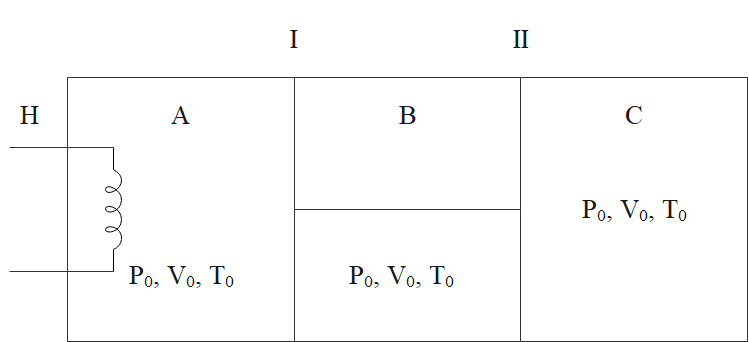
The figure shows an insulated cylinder divided into three parts A, B and C. Piston I and II are connected by a rigid rod and can move without friction inside the cylinder. Piston I is perfectly conducting while piston II is perfectly insulating. The initial state of gas $ (\gamma=1.5) $ present in each compartment A, B and C is as shown. Now, compartment A is slowly given heat through a heater H such that the final volume of C becomes $ \dfrac{4 V_{0}}{9} . $ Assume the gas to be ideal and find the heat supplied by the heater.
(A) $ \quad 18 P_{o} V_{o} $
(В) $ \quad 12 P_{o} V_{o} $
(C) $ \begin{array}{*{35}{l}}
\text{ } & 9{{P}_{o}}{{V}_{o}} \\
\end{array} $
(D) $ \quad 25 P_{o} V_{o} $

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint
We know that friction is a force between two surfaces that are sliding, or trying to slide, across each other. For example, when you try to push a book along the floor, friction makes this difficult. Friction always works in the direction opposite to the direction in which the object is moving, or trying to move. It is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Based on this concept we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer
We know that,
heat supplied $ \Delta \mathrm{Q}=\Delta \mathrm{U}+\Delta \mathrm{W} $
$ \Delta \mathrm{U}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+0 \quad $ [no heat change in case of compartment $ \left.\mathrm{C}\right] $
$ \Delta \mathrm{W}=\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}+0+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} \quad $ [no change in volume in case of compartment B hence work done $ \left.=0\right] $
initial conditions: $ \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} $ Pressure $ \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}} $ Volume $ \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}} $ Temperature
final conditions:
compartment C
$ \Rightarrow \mathrm{P} \mathrm{V}^{\gamma}=\mathrm{P} \mathrm{V}^{\gamma}=\mathrm{P} \times\left(\dfrac{4 \mathrm{V}_{0}}{9}\right)^{1.5}=\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}^{1.5} $ \Rightarrow
$ \Rightarrow P=\dfrac{27 P_{o}}{8} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{P_{0} V_{0}}{T_{0}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{27 P_{0}}{8} \times \dfrac{4 V_{0}}{9}}{T} $
$ \Rightarrow \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{3 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{2} $
compartment A
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{P}=\dfrac{27 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}{8} $ compartment $ \mathrm{A} $ and $ \mathrm{C} $ has to have same pressure for pistons to come at rest.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{27 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}{8} \times\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}+\dfrac{5 \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{9}\right)}{\mathrm{T}} $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4} $
compartment B
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{0}}{4} $ temperature of compartment $ \mathrm{A} $ and $ \mathrm{B} $ should be same at equilibrium $ \dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{P} \times \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4}} $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{P}=\dfrac{21 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4} $
$\Rightarrow \gamma=\dfrac{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{p}}}{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{f}+2}{\mathrm{f}} $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{f}=4 $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{fR}}{2}=2 \mathrm{R} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}=\mathrm{n} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}} \Delta \mathrm{T} $
$ \Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{0} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{RT}_{\mathrm{o}}} \times \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}}\left(\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4}-\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=\dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{RT}_{\mathrm{o}}} \times 2 \mathrm{R} \times \dfrac{17 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4}=\dfrac{17 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{2} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}=-\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} $ as the gas in chamber A is working on chamber $ \mathrm{C} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{C}}=0 $ as it’s a Adiabatic process hence
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{C}}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{C}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{C}}=-\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}}=\mathrm{n} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}} \Delta \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{RT}_{0}} \times 2 \mathrm{R} \times\left(\dfrac{3 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{2}-\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+0 \quad $ [no heat change in case of compartment $ \left.\mathrm{C}\right] $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{W}=\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}+0+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} \quad $ [no change in volume in case of compartment B hence work done $ \left.=\mathrm{O}\right] $
head supplied by the heater = heat supplied to compartment A + heat flow through piston I $\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{Q}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{AB}}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}=2 \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}} $
$ \Delta \mathrm{Q}=18 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}} $
Therefore, the correct answer is Option (A).
Note
We know that static friction is a force that keeps an object at rest. Static friction definition can be written as the friction experienced when individuals try to move a stationary object on a surface, without actually triggering any relative motion between the body and the surface which it is on.It hinders the movement of an object moving along the path. When two fabrics slide over each other, this friction occurs. There's friction all around us. When we walk, for instance, our feet are in touch with the floor. Static friction is caused by adhesion, light chemical attraction between two surfaces. And friction, in general, is caused by the imperfections in every surface gripping together and overlapping.
It should also be known to us that kinetic friction (also referred to as dynamic friction) is the force that resists the relative movement of the surfaces once they're in motion.
We know that friction is a force between two surfaces that are sliding, or trying to slide, across each other. For example, when you try to push a book along the floor, friction makes this difficult. Friction always works in the direction opposite to the direction in which the object is moving, or trying to move. It is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Based on this concept we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer
We know that,
heat supplied $ \Delta \mathrm{Q}=\Delta \mathrm{U}+\Delta \mathrm{W} $
$ \Delta \mathrm{U}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+0 \quad $ [no heat change in case of compartment $ \left.\mathrm{C}\right] $
$ \Delta \mathrm{W}=\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}+0+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} \quad $ [no change in volume in case of compartment B hence work done $ \left.=0\right] $
initial conditions: $ \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} $ Pressure $ \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}} $ Volume $ \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}} $ Temperature
final conditions:
compartment C
$ \Rightarrow \mathrm{P} \mathrm{V}^{\gamma}=\mathrm{P} \mathrm{V}^{\gamma}=\mathrm{P} \times\left(\dfrac{4 \mathrm{V}_{0}}{9}\right)^{1.5}=\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}^{1.5} $ \Rightarrow
$ \Rightarrow P=\dfrac{27 P_{o}}{8} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{P_{0} V_{0}}{T_{0}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{27 P_{0}}{8} \times \dfrac{4 V_{0}}{9}}{T} $
$ \Rightarrow \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{3 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{2} $
compartment A
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{P}=\dfrac{27 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}{8} $ compartment $ \mathrm{A} $ and $ \mathrm{C} $ has to have same pressure for pistons to come at rest.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{27 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}{8} \times\left(\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}+\dfrac{5 \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{9}\right)}{\mathrm{T}} $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4} $
compartment B
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{0}}{4} $ temperature of compartment $ \mathrm{A} $ and $ \mathrm{B} $ should be same at equilibrium $ \dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{P} \times \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4}} $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{P}=\dfrac{21 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4} $
$\Rightarrow \gamma=\dfrac{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{p}}}{\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{f}+2}{\mathrm{f}} $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{f}=4 $
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{fR}}{2}=2 \mathrm{R} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}=\mathrm{n} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}} \Delta \mathrm{T} $
$ \Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{0} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{RT}_{\mathrm{o}}} \times \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}}\left(\dfrac{21 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4}-\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=\dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{RT}_{\mathrm{o}}} \times 2 \mathrm{R} \times \dfrac{17 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{4}=\dfrac{17 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{2} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}=-\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} $ as the gas in chamber A is working on chamber $ \mathrm{C} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{C}}=0 $ as it’s a Adiabatic process hence
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{C}}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{C}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{C}}=-\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}}=\mathrm{n} \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}} \Delta \mathrm{T}=\dfrac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}}}{\mathrm{RT}_{0}} \times 2 \mathrm{R} \times\left(\dfrac{3 \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}}{2}-\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{o}}\right)=\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}} $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{U}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+0 \quad $ [no heat change in case of compartment $ \left.\mathrm{C}\right] $
$\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{W}=\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}+0+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{C}} \quad $ [no change in volume in case of compartment B hence work done $ \left.=\mathrm{O}\right] $
head supplied by the heater = heat supplied to compartment A + heat flow through piston I $\Rightarrow \Delta \mathrm{Q}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{AB}}=\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{B}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}}=2 \Delta \mathrm{U}_{\mathrm{A}}+\Delta \mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{A}} $
$ \Delta \mathrm{Q}=18 \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{o}} \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{o}} $
Therefore, the correct answer is Option (A).
Note
We know that static friction is a force that keeps an object at rest. Static friction definition can be written as the friction experienced when individuals try to move a stationary object on a surface, without actually triggering any relative motion between the body and the surface which it is on.It hinders the movement of an object moving along the path. When two fabrics slide over each other, this friction occurs. There's friction all around us. When we walk, for instance, our feet are in touch with the floor. Static friction is caused by adhesion, light chemical attraction between two surfaces. And friction, in general, is caused by the imperfections in every surface gripping together and overlapping.
It should also be known to us that kinetic friction (also referred to as dynamic friction) is the force that resists the relative movement of the surfaces once they're in motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




