
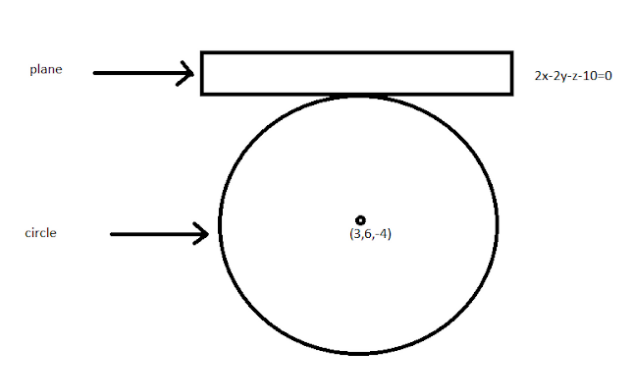
The equation of the sphere with center \[(3,6,-4)\] and touching the plane \[\,2x-2y-z-10\] is
(A) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-6x+12y-8z+45=0\]
(B) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}+6x-9y+8z+35=0\]
(C) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-6x+9y+8z+35=0\]
(D) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-6x-12y+8z+45=0\]
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to find the equation of the sphere. The points of the center and the equation of the plane are given to us. As we know that radius is the distance between the center of the sphere and the surface of the sphere, so by using the distance formula we will get the radius of the sphere, and using that we will find the equation of the sphere.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A sphere is a three-dimensional figure in space and it looks like the shape of a football. The sphere can also be defined as the set of all points which are placed from the center of the sphere. The distance between the center of the sphere and the points on the surface of the sphere is known as the radius of the sphere.
We know that the general equation of the sphere is given as shown below.
\[{{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}+{{(z-c)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]…….eq(1)
Where, a, b, and c are known as the center of the sphere, and ‘r’ is known as the radius of the sphere, and x, y, and z are the coordinates of the point on the sphere.
the center of the sphere is known to us, we have to find the radius of the sphere so that we can find out the general equation of the sphere.
In the question, it is given that the sphere touches the plane \[2x-2y-z-10=0\].
So the radius is the distance between the center of the sphere and the point where the sphere touches the plane.
Also, we know that the distance of a plane from a given point is given as shown below.
\[dis\tan ce=\dfrac{\left| ax+by+cz-d \right|}{\sqrt{{{(x)}^{2}}+{{(y)}^{2}}+{{(z)}^{2}}}}\]
We know that distance is equal to the radius of the sphere, so on applying the above formula.
\[radius=\dfrac{\left| 2\times 3-2\times 6+4-10 \right|}{\sqrt{{{(2)}^{2}}+{{(-2)}^{2}}+{{(-1)}^{2}}}}\]
On solving the above expression,
\[\begin{align}
& radius=\dfrac{12}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow radius=4 \\
\end{align}\]
On putting the values of a, b, c, and radius of the sphere, the equation of the sphere will be obtained which is as follows.
\[{{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}+{{(z-c)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{(x-3)}^{2}}+{{(y-6)}^{2}}+{{(z+4)}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\]
On solving the above equation, we get the equation of the sphere.
\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-6x-12y+8z+45=0\]
So the correct answer is (D) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-6x-12y+8z+45=0\]
Note: The two-dimensional figure of the sphere is known as the circle. The maximum distance measured between the two points of the circle or the sphere is known as the diameter of the sphere. The distance between the center and the surface of the sphere can be calculated by distance formula and the radius calculated will help calculate the equation of the sphere.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A sphere is a three-dimensional figure in space and it looks like the shape of a football. The sphere can also be defined as the set of all points which are placed from the center of the sphere. The distance between the center of the sphere and the points on the surface of the sphere is known as the radius of the sphere.

We know that the general equation of the sphere is given as shown below.
\[{{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}+{{(z-c)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]…….eq(1)
Where, a, b, and c are known as the center of the sphere, and ‘r’ is known as the radius of the sphere, and x, y, and z are the coordinates of the point on the sphere.
the center of the sphere is known to us, we have to find the radius of the sphere so that we can find out the general equation of the sphere.
In the question, it is given that the sphere touches the plane \[2x-2y-z-10=0\].
So the radius is the distance between the center of the sphere and the point where the sphere touches the plane.
Also, we know that the distance of a plane from a given point is given as shown below.
\[dis\tan ce=\dfrac{\left| ax+by+cz-d \right|}{\sqrt{{{(x)}^{2}}+{{(y)}^{2}}+{{(z)}^{2}}}}\]
We know that distance is equal to the radius of the sphere, so on applying the above formula.
\[radius=\dfrac{\left| 2\times 3-2\times 6+4-10 \right|}{\sqrt{{{(2)}^{2}}+{{(-2)}^{2}}+{{(-1)}^{2}}}}\]
On solving the above expression,
\[\begin{align}
& radius=\dfrac{12}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow radius=4 \\
\end{align}\]
On putting the values of a, b, c, and radius of the sphere, the equation of the sphere will be obtained which is as follows.
\[{{(x-a)}^{2}}+{{(y-b)}^{2}}+{{(z-c)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{(x-3)}^{2}}+{{(y-6)}^{2}}+{{(z+4)}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\]
On solving the above equation, we get the equation of the sphere.
\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-6x-12y+8z+45=0\]
So the correct answer is (D) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}-6x-12y+8z+45=0\]
Note: The two-dimensional figure of the sphere is known as the circle. The maximum distance measured between the two points of the circle or the sphere is known as the diameter of the sphere. The distance between the center and the surface of the sphere can be calculated by distance formula and the radius calculated will help calculate the equation of the sphere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




