
The equation of the other normal to the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ which passes through the intersection of those at $\left( 4a,-4a \right)$ and $\left( 9a,-6a \right)$ is:
(a) $5x-y+115a=0$
(b) $5x+y-135a=0$
(c) $5x-y-115a=0$
(d) $5x+y+115=0$
Answer
610.5k+ views
Hint:For solving this problem first we will find the slope of the normal with the help of value of $-\dfrac{dx}{dy}$ . After that, we will write the general equal equation of normal to the parabola in terms of the slope $m$ and prove that if three normal are concurrent then, the sum of their slopes will be zero. And then, we will use this rule to find the slope of the required normal which will be used further to find the desired equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
We have to find the equation of other normal to the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ which passes through the intersection of those at $\left( 4a,-4a \right)$ and $\left( 9a,-6a \right)$ .
Now, as we know that for any point $\left( x,y \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ slope of normal $\left( m \right)$ can be written as $-\dfrac{dx}{dy}$ . So, we will differentiate the equation ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ with respect to $x$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d{{y}^{2}}}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( 4ax \right)}{dx} \\
& \Rightarrow 2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=4a \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{2a}{y} \\
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{dx}{dy}=-\dfrac{y}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow m=-\dfrac{y}{2a}.....................\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, the slope of normal of any point $\left( x,y \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ will be $m=-\dfrac{y}{2a}$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& m=-\dfrac{y}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow y=-2am \\
\end{align}$
Now, as we know that point $\left( x,y \right)$ lies on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -2am \right)}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow x=a{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result we conclude that for any point $\left( a{{m}^{2}},-2am \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ , the slope of the normal will be $m$ . And as we know that, if any line of slope $m$ passes through point $A\equiv \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ the equation of line will be $\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$ . So, we will now find the equation of normal of slope $m$ through point $\left( a{{m}^{2}},-2am \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{L}_{Normal}}:\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:\left( y-\left( -2am \right) \right)=m\left( x-a{{m}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}}.........................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, if the equation ${{L}_{Normal}}:y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}}$ always passes through a particular point $\left( h,k \right)$ which is not on the parabola so, value $x=h$ and $y=k$ will satisfy the equation $y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}}$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow k+2am=mh-a{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow a{{m}^{3}}+\left( 2a-h \right)m+k=0 \\
\end{align}$
Now, as the equation ${{a}^{2}}{{m}^{3}}+\left( 2a-h \right)m+k=0$ is a cubic equation in $m$ so, there will be utmost three real values of $m$ . Which means for any parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ we can draw a maximum three normal on it from any point $\left( h,k \right)$ and these normal will be concurrent.
Now, here if $a{{m}^{3}}+\left( 2a-h \right)m+k=0$ and let, ${{m}_{1}}$ , ${{m}_{2}}$ and ${{m}_{3}}$ be its root. And as we know that some of the roots will be equal to $\dfrac{-coefficient\text{ }of\text{ }{{m}^{2}}}{coefficient\text{ }of\text{ }{{m}^{3}}}$ . Then,
${{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}=0.................\left( 3 \right)$
Now, we conclude that for any three concurrent normal to the parabola sum of their slopes will be zero.
Now, let ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the slopes of normal for the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ at the points $\left( 4a,-4a \right)$ and $\left( 9a,-6a \right)$ respectively. And from equation (1) we know that slope of normal of any point $\left( x,y \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ will be $m=-\dfrac{y}{2a}$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{-\left( -4a \right)}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}=2...............\left( 4 \right) \\
& {{m}_{2}}=\dfrac{-\left( -6a \right)}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{2}}=3..............\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, let ${{m}_{3}}$ be the slope of the normal which is concurrent with the normal at points $\left( 4a,-4a \right)$ and $\left( 9a,-6a \right)$ . And from the equation (3) we know that for any three concurrent normal to the parabola sum of their slopes will be zero. Then,
${{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}=0$
Now, put ${{m}_{1}}=2$ form equation (4) and ${{m}_{2}}=3$ from equation (5) in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2+3+{{m}_{3}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{3}}=-5 \\
\end{align}$
Now, put the value of $m=-5$ in the equation (2) to get the equation of normal to the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ having a slope $-5$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& {{L}_{Normal}}:y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:y+2a\left( -5 \right)=-5x-a{{\left( -5 \right)}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:y-10a+5x=125a \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:5x+y-135a=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the equation of the required normal will be \[5x+y-135a=0\] . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
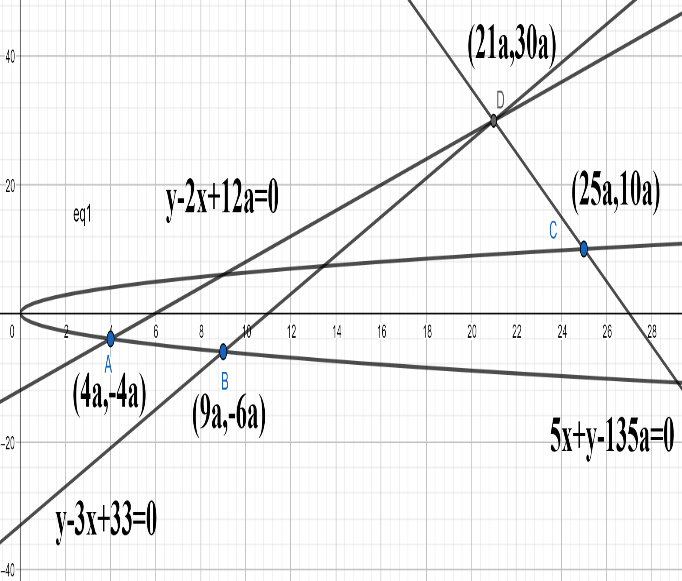
In the above figure equation $y-2x+12a=0$ is normal at point $A\equiv \left( 4a,-4a \right)$ , equation $y-3x+33a=0$ is normal at point $B\equiv \left( 9a,-6a \right)$ and equation $5x+y-135a=0$ is normal at point $C\equiv \left( 25a,10a \right)$ . And all three normally intersect at a common point $D\equiv \left( 21a,30a \right)$ .
Hence, (b) will be the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. Moreover, for solving objective problems we should remember that if there are three points on any parabola such that normal on that points are concurrent then, some of their slopes will be zero and also the sum of their ordinates will be also zero. And we should directly apply this rule to get the correct answer.Solving any two normal equations we get intersection of three normals at a common point i.e $D\equiv \left( 21a,30a \right)$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
We have to find the equation of other normal to the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ which passes through the intersection of those at $\left( 4a,-4a \right)$ and $\left( 9a,-6a \right)$ .
Now, as we know that for any point $\left( x,y \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ slope of normal $\left( m \right)$ can be written as $-\dfrac{dx}{dy}$ . So, we will differentiate the equation ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ with respect to $x$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d{{y}^{2}}}{dx}=\dfrac{d\left( 4ax \right)}{dx} \\
& \Rightarrow 2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=4a \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{2a}{y} \\
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{dx}{dy}=-\dfrac{y}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow m=-\dfrac{y}{2a}.....................\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, the slope of normal of any point $\left( x,y \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ will be $m=-\dfrac{y}{2a}$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& m=-\dfrac{y}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow y=-2am \\
\end{align}$
Now, as we know that point $\left( x,y \right)$ lies on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{y}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -2am \right)}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{a}^{2}}{{m}^{2}}=4ax \\
& \Rightarrow x=a{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, from the above result we conclude that for any point $\left( a{{m}^{2}},-2am \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ , the slope of the normal will be $m$ . And as we know that, if any line of slope $m$ passes through point $A\equiv \left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ the equation of line will be $\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$ . So, we will now find the equation of normal of slope $m$ through point $\left( a{{m}^{2}},-2am \right)$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{L}_{Normal}}:\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:\left( y-\left( -2am \right) \right)=m\left( x-a{{m}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}}.........................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, if the equation ${{L}_{Normal}}:y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}}$ always passes through a particular point $\left( h,k \right)$ which is not on the parabola so, value $x=h$ and $y=k$ will satisfy the equation $y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}}$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow k+2am=mh-a{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow a{{m}^{3}}+\left( 2a-h \right)m+k=0 \\
\end{align}$
Now, as the equation ${{a}^{2}}{{m}^{3}}+\left( 2a-h \right)m+k=0$ is a cubic equation in $m$ so, there will be utmost three real values of $m$ . Which means for any parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ we can draw a maximum three normal on it from any point $\left( h,k \right)$ and these normal will be concurrent.
Now, here if $a{{m}^{3}}+\left( 2a-h \right)m+k=0$ and let, ${{m}_{1}}$ , ${{m}_{2}}$ and ${{m}_{3}}$ be its root. And as we know that some of the roots will be equal to $\dfrac{-coefficient\text{ }of\text{ }{{m}^{2}}}{coefficient\text{ }of\text{ }{{m}^{3}}}$ . Then,
${{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}=0.................\left( 3 \right)$
Now, we conclude that for any three concurrent normal to the parabola sum of their slopes will be zero.
Now, let ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the slopes of normal for the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ at the points $\left( 4a,-4a \right)$ and $\left( 9a,-6a \right)$ respectively. And from equation (1) we know that slope of normal of any point $\left( x,y \right)$ on the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ will be $m=-\dfrac{y}{2a}$ . Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}=\dfrac{-\left( -4a \right)}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{1}}=2...............\left( 4 \right) \\
& {{m}_{2}}=\dfrac{-\left( -6a \right)}{2a} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{2}}=3..............\left( 5 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, let ${{m}_{3}}$ be the slope of the normal which is concurrent with the normal at points $\left( 4a,-4a \right)$ and $\left( 9a,-6a \right)$ . And from the equation (3) we know that for any three concurrent normal to the parabola sum of their slopes will be zero. Then,
${{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}=0$
Now, put ${{m}_{1}}=2$ form equation (4) and ${{m}_{2}}=3$ from equation (5) in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2+3+{{m}_{3}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{3}}=-5 \\
\end{align}$
Now, put the value of $m=-5$ in the equation (2) to get the equation of normal to the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ having a slope $-5$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& {{L}_{Normal}}:y+2am=mx-a{{m}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:y+2a\left( -5 \right)=-5x-a{{\left( -5 \right)}^{3}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:y-10a+5x=125a \\
& \Rightarrow {{L}_{Normal}}:5x+y-135a=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from the above result, we conclude that the equation of the required normal will be \[5x+y-135a=0\] . For more clarity look at the figure given below:

In the above figure equation $y-2x+12a=0$ is normal at point $A\equiv \left( 4a,-4a \right)$ , equation $y-3x+33a=0$ is normal at point $B\equiv \left( 9a,-6a \right)$ and equation $5x+y-135a=0$ is normal at point $C\equiv \left( 25a,10a \right)$ . And all three normally intersect at a common point $D\equiv \left( 21a,30a \right)$ .
Hence, (b) will be the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. Moreover, for solving objective problems we should remember that if there are three points on any parabola such that normal on that points are concurrent then, some of their slopes will be zero and also the sum of their ordinates will be also zero. And we should directly apply this rule to get the correct answer.Solving any two normal equations we get intersection of three normals at a common point i.e $D\equiv \left( 21a,30a \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




