
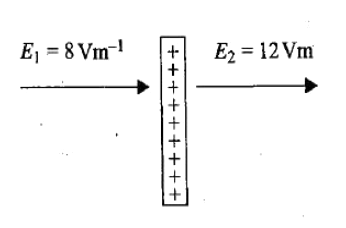
The electric field on two sides of a large charged plate is shown in Fig. The charge density on the plate in SI units is given by (\[\varepsilon {}_0\] is the permittivity of free space in SI units) :
A. $2{\varepsilon _o}$
B. $4{\varepsilon _o}$
C. $10{\varepsilon _o}$
D. zero

Answer
556.2k+ views
Hint: Electric Field is a vector quantity that exists at every point in space, electric field at a location indicates the force that would act on a unit positive test charge if placed at that location.
Complete step by step answer:
From the fig. it is clear that the plate is placed in an external electric field. Let the electric field due to plate be \[E\], and \[{E_0}\] is the external electric field.
Therefore,
${E_o} + E = 12V{m^{ - 1}}$ ------(1)
${E_o} - E = 8V{m^{ - 1}}$ ----(2)
Solving equations (1) and (2), we get-
\[E = 2V{m^{ - 1}}\;\]and \[{E_0} = 10V{m^{ - 1}}\]
Now electric field due to plate is
\[E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _o}}}\]
But \[E = 2\]
So, \[\sigma = 4{\varepsilon _o}\]
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Additional information:
One way to visualize the electric field (this is my mental model): Imagine a small positive test charge sticking to the end of an imaginary stick. (Make sure your imaginary stick does not behave like wood or plastic).
Explore the electric field with your test charge in different places. The test charge will be pushed or pulled through the surrounding charge.
The use of test charge (both width and direction) is divided by the value of the small test charge. The force is the electric field vector at that point. Even if you remove the test charge, there is still an electric field at that place.
Note: The electric field from the positive charge is away from the charge; Indicates the electric field charge from the negative charge. Like electrical energy, the electric field is a vector. If the electric field is known at a certain point, then the \[q\] of the ball is experienced at that point:
$F = qE$
If \[q\] is positive, the force is the same as the field; If \[q\] is negative, the ball is in the opposite direction of the field.
Complete step by step answer:
From the fig. it is clear that the plate is placed in an external electric field. Let the electric field due to plate be \[E\], and \[{E_0}\] is the external electric field.
Therefore,
${E_o} + E = 12V{m^{ - 1}}$ ------(1)
${E_o} - E = 8V{m^{ - 1}}$ ----(2)
Solving equations (1) and (2), we get-
\[E = 2V{m^{ - 1}}\;\]and \[{E_0} = 10V{m^{ - 1}}\]
Now electric field due to plate is
\[E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _o}}}\]
But \[E = 2\]
So, \[\sigma = 4{\varepsilon _o}\]
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Additional information:
One way to visualize the electric field (this is my mental model): Imagine a small positive test charge sticking to the end of an imaginary stick. (Make sure your imaginary stick does not behave like wood or plastic).
Explore the electric field with your test charge in different places. The test charge will be pushed or pulled through the surrounding charge.
The use of test charge (both width and direction) is divided by the value of the small test charge. The force is the electric field vector at that point. Even if you remove the test charge, there is still an electric field at that place.
Note: The electric field from the positive charge is away from the charge; Indicates the electric field charge from the negative charge. Like electrical energy, the electric field is a vector. If the electric field is known at a certain point, then the \[q\] of the ball is experienced at that point:
$F = qE$
If \[q\] is positive, the force is the same as the field; If \[q\] is negative, the ball is in the opposite direction of the field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




