
The decreasing order of the electron density on the ring is:
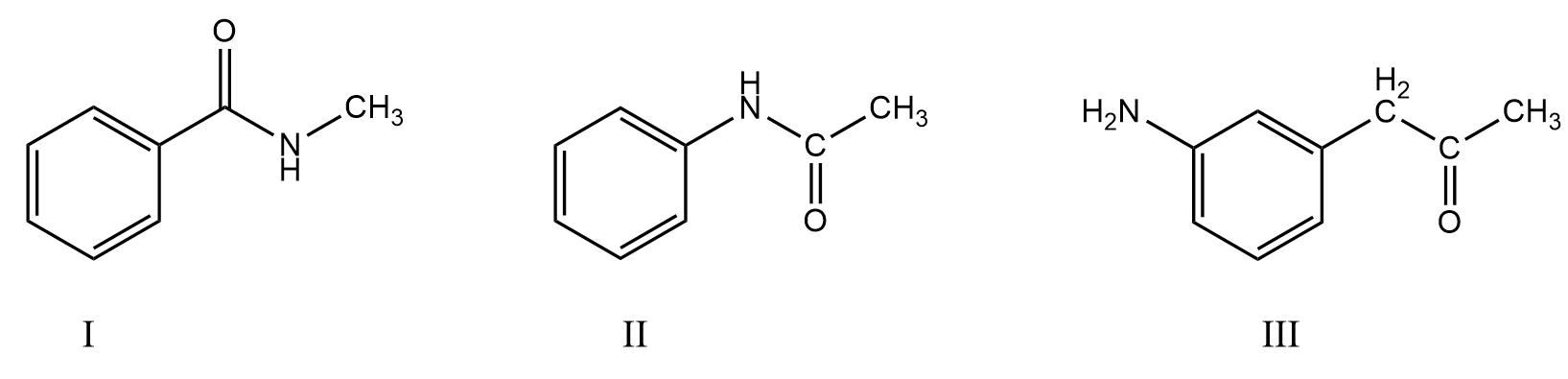
A. $III > II > I$
B. $II > III > I$
C. $I > III > II$
D. $III > I > II$

Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: For comparing the electron density on the ring in aromatic compounds, check the nature of the substituent groups on the ring. If the groups attached to the ring are electron donating, then the electron density on the ring increases whereas if the groups attached to the ring are electron withdrawing, then the electron density on the ring decreases.
Complete answer:
Electron donating groups: The type of functional groups which donate some of its electron density into a conjugated $\pi $ system through resonance, mesomerism or inductive effect are known as electron donating or electron releasing groups.
Electron withdrawing groups: The type of functional groups which accepts the electron density from neighbouring atoms towards itself, generally by resonance or inductive effect are known as electron withdrawing groups.
Now, let’s check the nature of functional groups present on the each given compound as follows:
Compound $ - I$:
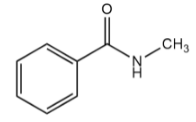
The benzene ring in the given compound is attached to $ - CONHC{H_3}$ in which the carbonyl group i.e., $C = O$ is electron withdrawing group since it is directly attached to a highly electronegative oxygen atom. Thus, in this compound the electron density on the ring will be minimum.
Compound $ - II$:
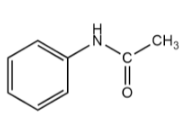
The benzene ring in the given compound is bonded to $ - NHCOC{H_3}$ in which the nitrogen atom consists of a lone pair of electrons due to which the functional group will act as the electron donating group.
Compound $ - III$:
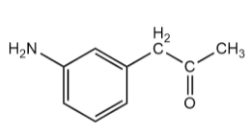
The benzene ring in the given compound is bonded to two functional groups i.e., $N{H_2}$ which is an electron donating group due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom and $C{H_2}COC{H_3}$ which is also an electron donating group due to $ + I$ effect of the alkyl group. Thus, the electron density on the ring will be maximum for this compound.
Hence, the correct decreasing order of the electron density on the ring in the given compounds is $III > II > I$. So, option (A) is the correct answer.
Hence, option (A), (B) and (C) are the right answers.
Note:
Remember that on increasing the electron density of the ring, the nucleophilic character of the ring increases which means the ring will more readily give electrophilic substitution reactions. The electron donating groups are considered as ring activating groups and direct the substitution at ortho and para positions whereas the electron withdrawing groups are considered as ring deactivating groups and direct the substitution at meta position.
Complete answer:
Electron donating groups: The type of functional groups which donate some of its electron density into a conjugated $\pi $ system through resonance, mesomerism or inductive effect are known as electron donating or electron releasing groups.
Electron withdrawing groups: The type of functional groups which accepts the electron density from neighbouring atoms towards itself, generally by resonance or inductive effect are known as electron withdrawing groups.
Now, let’s check the nature of functional groups present on the each given compound as follows:
Compound $ - I$:

The benzene ring in the given compound is attached to $ - CONHC{H_3}$ in which the carbonyl group i.e., $C = O$ is electron withdrawing group since it is directly attached to a highly electronegative oxygen atom. Thus, in this compound the electron density on the ring will be minimum.
Compound $ - II$:

The benzene ring in the given compound is bonded to $ - NHCOC{H_3}$ in which the nitrogen atom consists of a lone pair of electrons due to which the functional group will act as the electron donating group.
Compound $ - III$:

The benzene ring in the given compound is bonded to two functional groups i.e., $N{H_2}$ which is an electron donating group due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom and $C{H_2}COC{H_3}$ which is also an electron donating group due to $ + I$ effect of the alkyl group. Thus, the electron density on the ring will be maximum for this compound.
Hence, the correct decreasing order of the electron density on the ring in the given compounds is $III > II > I$. So, option (A) is the correct answer.
Hence, option (A), (B) and (C) are the right answers.
Note:
Remember that on increasing the electron density of the ring, the nucleophilic character of the ring increases which means the ring will more readily give electrophilic substitution reactions. The electron donating groups are considered as ring activating groups and direct the substitution at ortho and para positions whereas the electron withdrawing groups are considered as ring deactivating groups and direct the substitution at meta position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




