
The correct sequence of reagents used to convert phenol into aspirin is:
A. ${H_2}O,{H^ + } > NaOH > C{O_2} > C{H_3}COCl,{H^ + }$
B. $C{H_3}COCl,{H^ + } > {H_2}O,{H^ + } > C{O_2} > NaOH$
C. $NaOH > C{O_2} > {H_2}O,{H^ + } > C{H_3}COCl,{H^ + }$
D. $C{O_2} > NaOH > {H_2}O,{H^ + } > C{H_3}COCl,{H^ + }$
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint:Aspirin is also known as acetyl salicylic acid, and is obtained by the acetylation of salicylic acid. To convert phenol to salicylic acid, we use a carbonyl compound like carbon dioxide in an alkaline medium and then to convert salicylic acid to aspirin, we can use an acetylation agent like acetyl chloride.
Complete step by step answer:
The production of aspirin from phenol is a three-step reaction. In the first step, phenol is treated with sodium hydroxide to yield the sodium salt of phenol, known as sodium phenoxide. This compound is then treated with carbon dioxide to introduce the carbonyl group ($C = O$) to the ortho position of the sodium phenoxide. This when subjected to acid hydrolysis (treatment with water rich in hydrogen ions) yields salicylic acid. In the final step, salicylic acid obtained in the previous step is acetylated using acetyl chloride, to obtain the final product, aspirin, otherwise known as acetyl salicylic acid. Acetylation is the process of introducing an acetyl group ($ - COC{H_3}$) to a certain species. The whole process is given below in the figure:
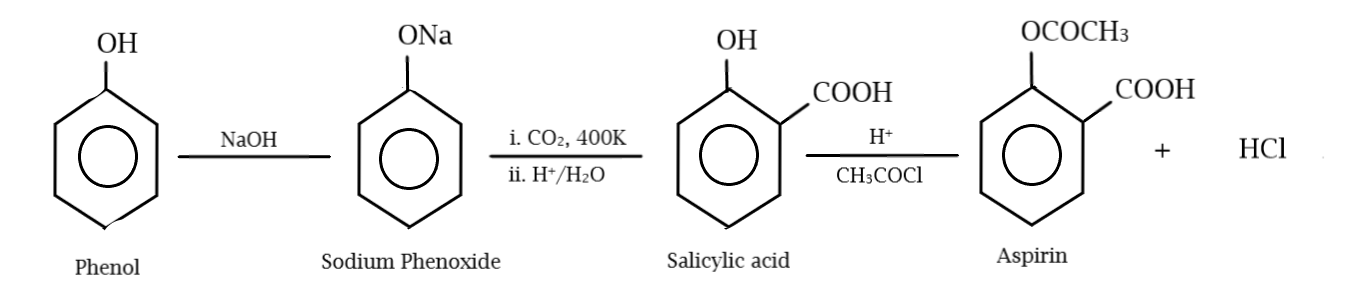
Thus, we can conclude from our observations that the correct order of reagents for the conversion of phenol to aspirin is:
$NaOH > C{O_2} > {H_2}O,{H^ + } > C{H_3}COCl,{H^ + }$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:
There is an alternate method to produce aspirin. In this, the phenol is first converted to salicylaldehyde in a process known as the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. An intermediate is produced here, which is dichlorocarbene. This salicylic aldehyde can then be oxidised to get salicylic acid, which on acetylation yields aspirin. Note that for acetylation, we may also use acetic anhydride (${(C{H_3}CO)_2}O$), in which case the by-product would be ethanoic acid ($C{H_3}COOH$).
Complete step by step answer:
The production of aspirin from phenol is a three-step reaction. In the first step, phenol is treated with sodium hydroxide to yield the sodium salt of phenol, known as sodium phenoxide. This compound is then treated with carbon dioxide to introduce the carbonyl group ($C = O$) to the ortho position of the sodium phenoxide. This when subjected to acid hydrolysis (treatment with water rich in hydrogen ions) yields salicylic acid. In the final step, salicylic acid obtained in the previous step is acetylated using acetyl chloride, to obtain the final product, aspirin, otherwise known as acetyl salicylic acid. Acetylation is the process of introducing an acetyl group ($ - COC{H_3}$) to a certain species. The whole process is given below in the figure:

Thus, we can conclude from our observations that the correct order of reagents for the conversion of phenol to aspirin is:
$NaOH > C{O_2} > {H_2}O,{H^ + } > C{H_3}COCl,{H^ + }$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:
There is an alternate method to produce aspirin. In this, the phenol is first converted to salicylaldehyde in a process known as the Riemer-Tiemann reaction. An intermediate is produced here, which is dichlorocarbene. This salicylic aldehyde can then be oxidised to get salicylic acid, which on acetylation yields aspirin. Note that for acetylation, we may also use acetic anhydride (${(C{H_3}CO)_2}O$), in which case the by-product would be ethanoic acid ($C{H_3}COOH$).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




