
The correct order of acidity for the compounds following:
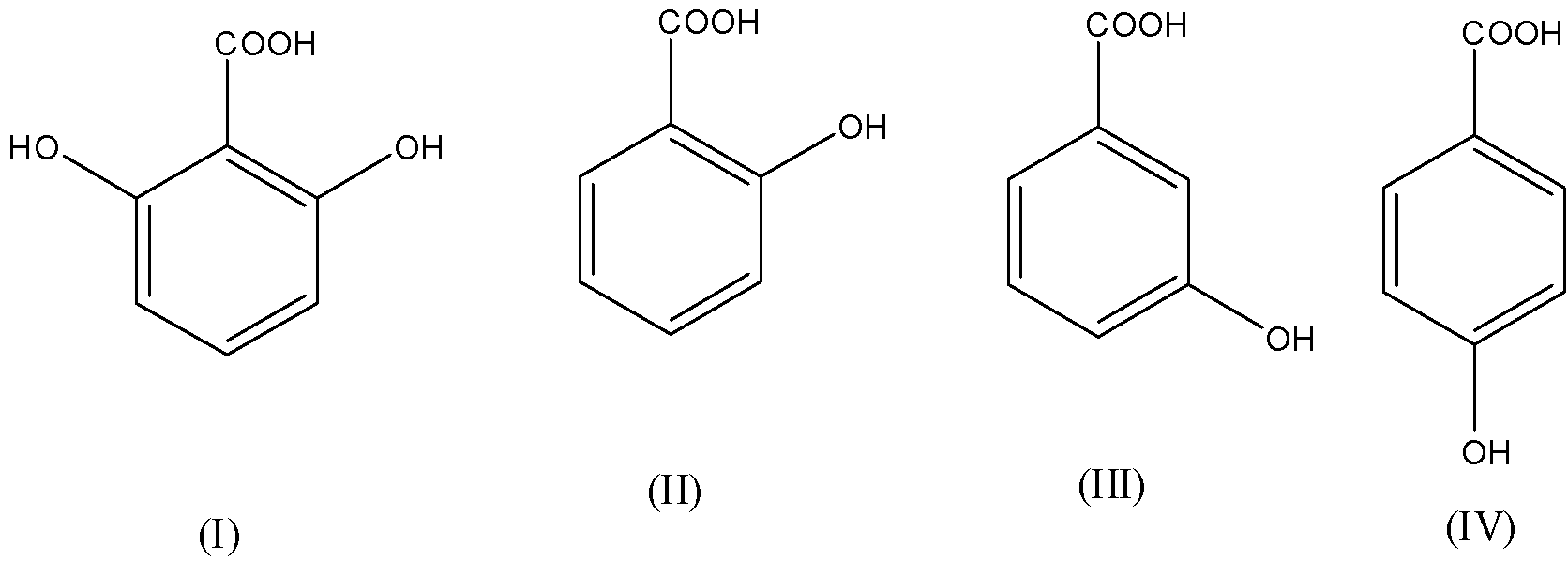
(a)- I > II > III > IV
(b)- III > I > II > IV
(c)- III > IV > II > I
(d)- I > III > IV > II

Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Electron-donating substituents decrease the acidity of the benzoic acid because they decrease the stability of the carboxylate ion. Electron-withdrawing substituents increase the acidity of the benzoic acid because they increase the stability of the carboxylate ion.
Complete step by step answer:
When benzoic acid is substituted by electron-withdrawing groups like nitro ($N{{O}_{2}}$) the acidity increases.
When benzoic acid is substituted by electron-donating groups like hydroxyl ($OH$) the acidity decreases.
The ortho-substituted benzoic acids are usually stronger than benzoic acid despite the nature of the substituents. This is due to a combination of steric and electronic factors which alter the chemical and physical properties of benzoic acid and is called ortho-effect.
Among all the structures (I) is the most acidic because two hydroxyl groups are present at both ortho positions. So due to the ortho-effect, it is most acidic.
The displacement of $\sigma -electrons$along the saturated carbon chain whenever an electron withdrawing or electron donating group is present at the end of the carbon chain is called inductive effect or I-effect.
If the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron withdrawing, the effect is called –I-Effect.
If the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron donating, the effect is +I-Effect.
The flow of electrons from one part of the conjugated system to the other creating centers of low and high electron density due to the phenomenon of resonance is called resonance effect or R-effect.
Groups which donate electrons to the double bond are said to have +R-effect.

Groups which withdraw electrons from the double bond are said to have –R-effect

In structure (II) is more acidic than the meta and para-substituted benzoic acid.
+I-Effect and +R-Effect intensifies the negative charge on the carboxylate ion thereby making the carboxylate ion less stable and decreases the acidity of the benzoic acid. –I-Effect and –R-Effect disperse the negative charge on the carboxylate ion thereby making the carboxylate ion more stable and increase the acidity of the benzoic acid.
Now in structure (III) and (IV), the meta-hydroxybenzoic acid, OH group cannot exerts +R-effect but can only exert –I-effect and in para-hydroxybenzoic acid, the OH group has a strong +R-effect and it has a weak –I-effect. So, meta-hydroxybenzoic acid is more acidic than para-hydroxybenzoic acid.
So, the order of acidity will be: I > II > III > IV
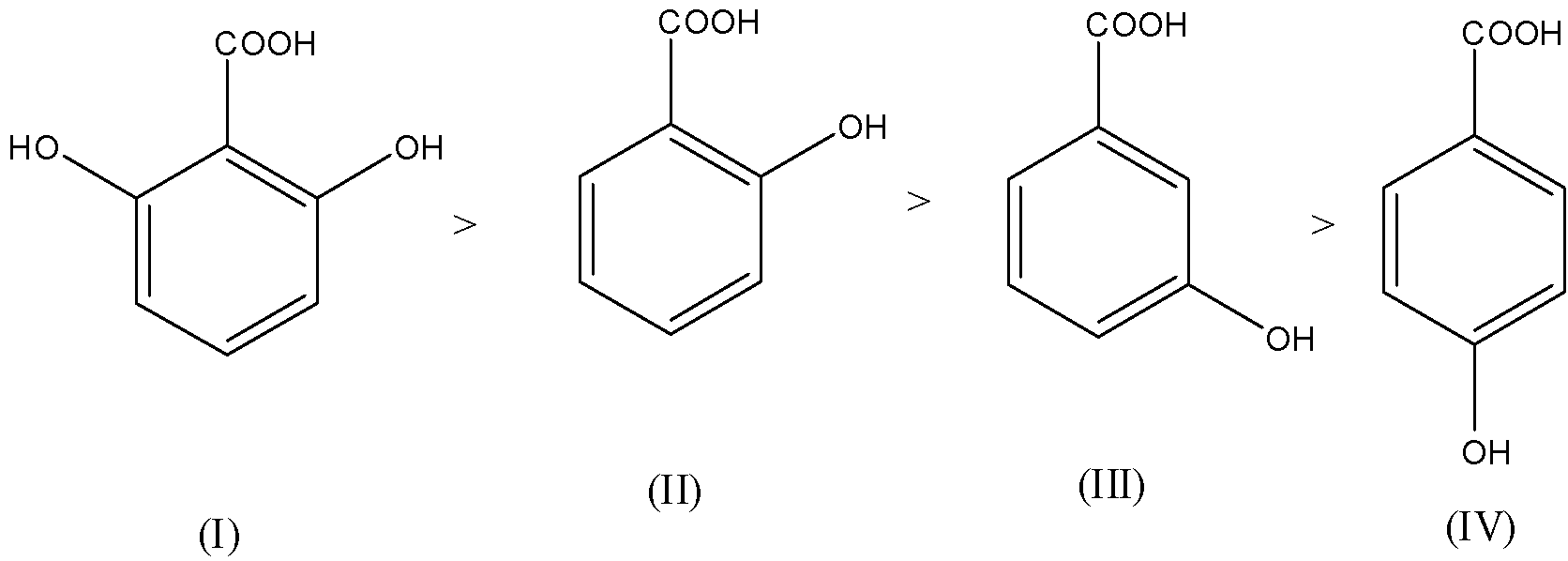
Hence the correct answer is an option (a)- I > II > III > IV
Note: The acid-weakening effect of the electron-donating group and acid-strengthening effect of the electron-withdrawing group is more pronounced at the para than at meta position of the benzoic acid. This is due to the resonating structure of the benzoic acid. The positive charge is on para position but not on meta position.
Complete step by step answer:
When benzoic acid is substituted by electron-withdrawing groups like nitro ($N{{O}_{2}}$) the acidity increases.
When benzoic acid is substituted by electron-donating groups like hydroxyl ($OH$) the acidity decreases.
The ortho-substituted benzoic acids are usually stronger than benzoic acid despite the nature of the substituents. This is due to a combination of steric and electronic factors which alter the chemical and physical properties of benzoic acid and is called ortho-effect.
Among all the structures (I) is the most acidic because two hydroxyl groups are present at both ortho positions. So due to the ortho-effect, it is most acidic.
The displacement of $\sigma -electrons$along the saturated carbon chain whenever an electron withdrawing or electron donating group is present at the end of the carbon chain is called inductive effect or I-effect.
If the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron withdrawing, the effect is called –I-Effect.
If the substituent attached to the end of the carbon chain is electron donating, the effect is +I-Effect.
The flow of electrons from one part of the conjugated system to the other creating centers of low and high electron density due to the phenomenon of resonance is called resonance effect or R-effect.
Groups which donate electrons to the double bond are said to have +R-effect.

Groups which withdraw electrons from the double bond are said to have –R-effect

In structure (II) is more acidic than the meta and para-substituted benzoic acid.
+I-Effect and +R-Effect intensifies the negative charge on the carboxylate ion thereby making the carboxylate ion less stable and decreases the acidity of the benzoic acid. –I-Effect and –R-Effect disperse the negative charge on the carboxylate ion thereby making the carboxylate ion more stable and increase the acidity of the benzoic acid.
Now in structure (III) and (IV), the meta-hydroxybenzoic acid, OH group cannot exerts +R-effect but can only exert –I-effect and in para-hydroxybenzoic acid, the OH group has a strong +R-effect and it has a weak –I-effect. So, meta-hydroxybenzoic acid is more acidic than para-hydroxybenzoic acid.
So, the order of acidity will be: I > II > III > IV

Hence the correct answer is an option (a)- I > II > III > IV
Note: The acid-weakening effect of the electron-donating group and acid-strengthening effect of the electron-withdrawing group is more pronounced at the para than at meta position of the benzoic acid. This is due to the resonating structure of the benzoic acid. The positive charge is on para position but not on meta position.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




