
The CFSE for octahedral ${{[CoC{{l}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ is 18,000 $c{{m}^{-1}}$. The CFSE for tetrahedral ${{[CoC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ will be:
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: Draw the CFSE diagram for${{[CoC{{l}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ and ${{[CoC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$ to understand the difference in splitting of orbitals in case of octahedral and tetrahedral geometry. Apply the formula given below to find the CFSE for the tetrahedral complex.
Formula: ${{\Delta }_{t}}=\dfrac{4}{9}{{\Delta }_{o}}$
Where,
${{\Delta }_{t}}$ is the CFSE for tetrahedral complex,
${{\Delta }_{o}}$ is the CFSE for an octahedral complex.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us try to understand the crystal field theory.
-The Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is a model for the bonding interaction between transition metal atoms and ligands.
-It describes the attraction between the positive charge of the metal cation and negative charge on the non-bonding electrons of the ligand.
-When the ligands approach the central metal ion, the degeneracy of electronic orbitals (usually d or f orbitals) are broken due to the static electric field produced by the surrounding charge distribution.
CFSE (Crystal field stabilisation energy) is the calculation of energy of a complex compound. When ligands attack the metal ion the d-orbitals of metal loses their degeneracy and split into two groups i.e. ${{e}_{g}}({{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}})$ and ${{t}_{2g}}({{d}_{xy}},{{d}_{yz}},{{d}_{xz}})$.
If electron enters the ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals it destabilizes the complex and if electron enters the ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals it stabilizes the complex in case of an octahedral complex . The below diagrams will help you understand the splitting of orbitals.
For an octahedral complex:
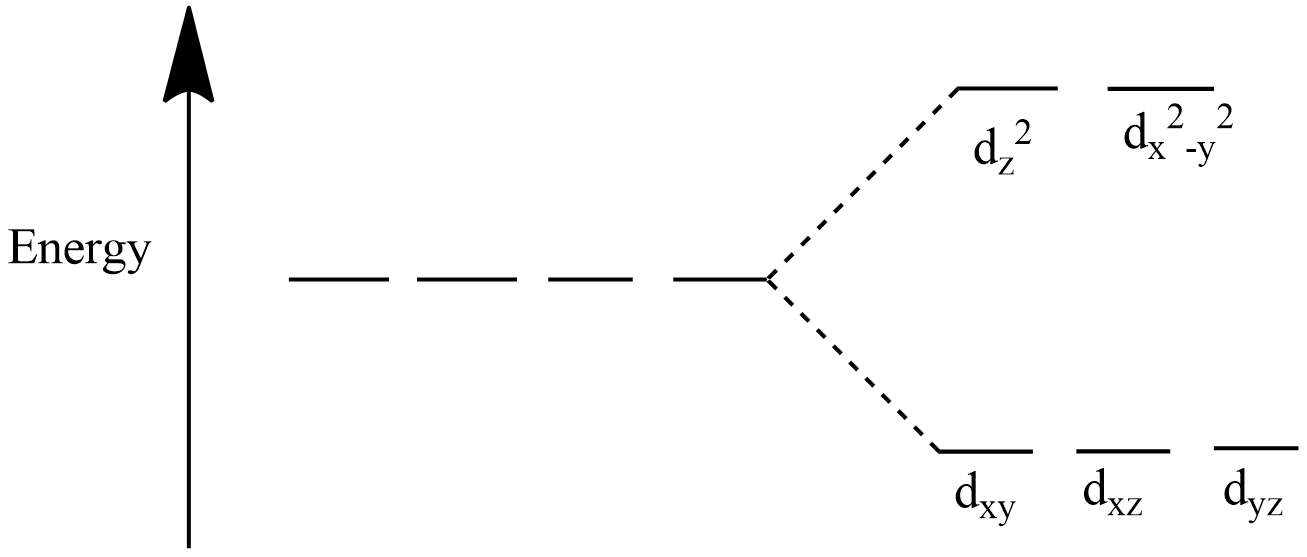
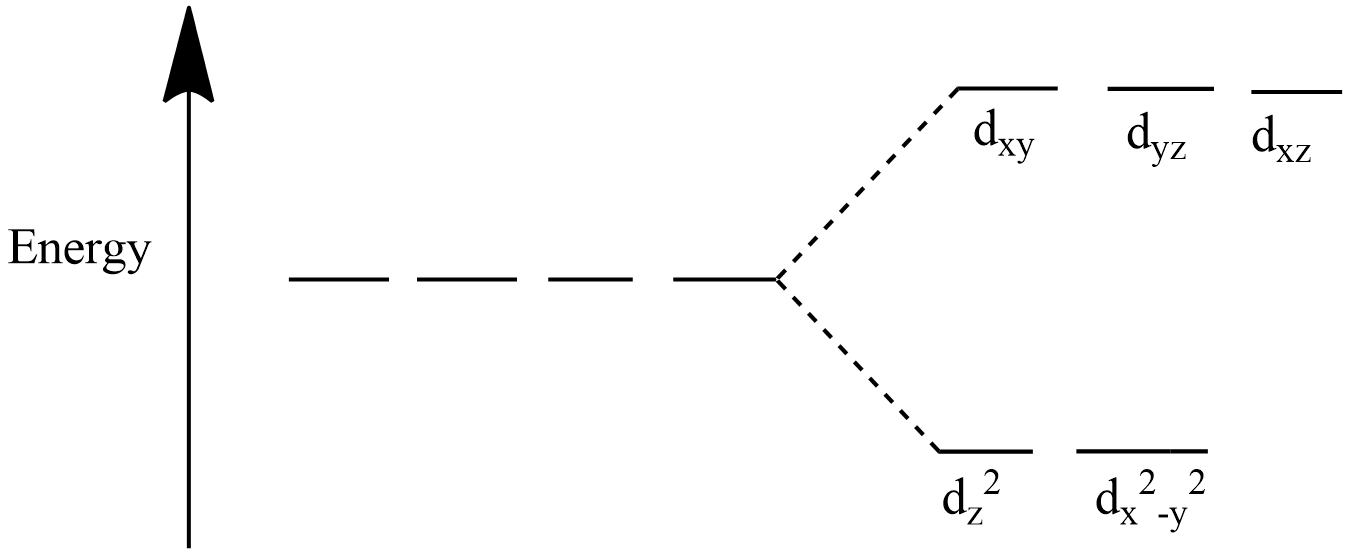
We will now apply the formula given above to find the CFSE of the tetrahedral complex.
${{\Delta }_{t}}=\dfrac{4}{9}{{\Delta }_{o}}$
The CFSE for octahedral complex, ${{[CoC{{l}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ is given as 18,000 $c{{m}^{-1}}$. Substituting the value of ${{\Delta }_{o}}$ in the equation:
${{\Delta }_{t}}=\dfrac{4}{9}{{.18000}_{{}}}c{{m}^{-1}}$
${{\Delta }_{t}}={{8000}_{{}}}c{{m}^{-1}}$
The CFSE for ${{[CoC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$is ${{8000}_{{}}}c{{m}^{-1}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The CFSE for octahedral and tetrahedral complexes are not equal because the splitting of orbitals happens differently for the two types of complex as given in the diagram. In case of tetrahedral complex, electrons entering the ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals destabilise the complex and entering ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals stabilize the complex.
Formula: ${{\Delta }_{t}}=\dfrac{4}{9}{{\Delta }_{o}}$
Where,
${{\Delta }_{t}}$ is the CFSE for tetrahedral complex,
${{\Delta }_{o}}$ is the CFSE for an octahedral complex.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us try to understand the crystal field theory.
-The Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is a model for the bonding interaction between transition metal atoms and ligands.
-It describes the attraction between the positive charge of the metal cation and negative charge on the non-bonding electrons of the ligand.
-When the ligands approach the central metal ion, the degeneracy of electronic orbitals (usually d or f orbitals) are broken due to the static electric field produced by the surrounding charge distribution.
CFSE (Crystal field stabilisation energy) is the calculation of energy of a complex compound. When ligands attack the metal ion the d-orbitals of metal loses their degeneracy and split into two groups i.e. ${{e}_{g}}({{d}_{{{z}^{2}}}},{{d}_{{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}}})$ and ${{t}_{2g}}({{d}_{xy}},{{d}_{yz}},{{d}_{xz}})$.
If electron enters the ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals it destabilizes the complex and if electron enters the ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals it stabilizes the complex in case of an octahedral complex . The below diagrams will help you understand the splitting of orbitals.
For an octahedral complex:


We will now apply the formula given above to find the CFSE of the tetrahedral complex.
${{\Delta }_{t}}=\dfrac{4}{9}{{\Delta }_{o}}$
The CFSE for octahedral complex, ${{[CoC{{l}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ is given as 18,000 $c{{m}^{-1}}$. Substituting the value of ${{\Delta }_{o}}$ in the equation:
${{\Delta }_{t}}=\dfrac{4}{9}{{.18000}_{{}}}c{{m}^{-1}}$
${{\Delta }_{t}}={{8000}_{{}}}c{{m}^{-1}}$
The CFSE for ${{[CoC{{l}_{4}}]}^{2-}}$is ${{8000}_{{}}}c{{m}^{-1}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The CFSE for octahedral and tetrahedral complexes are not equal because the splitting of orbitals happens differently for the two types of complex as given in the diagram. In case of tetrahedral complex, electrons entering the ${{t}_{2g}}$ orbitals destabilise the complex and entering ${{e}_{g}}$ orbitals stabilize the complex.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




