
The bond order of \[{N_2}^ + \] ion is:
A.\[1\]
B.\[2\]
C.\[2.5\]
D.\[3\]
Answer
494.4k+ views
Hint: The bond order is a measure of the number of bonds that exist between two atoms and can be calculated by multiplying the difference of number of electrons present in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals by half.
Complete answer:
A simple nitrogen molecule is diatomic in nature and consists of triple bonds that are strong enough to make the nitrogen molecule stable and inert at room temperature. The triple bond present in a nitrogen molecule is an indicator of the fact that its bond order is \[3\] .
\[{N_2}^ + \] is chemically different from the simple nitrogen molecule as it has lost one electron or it has one electron less as compared to the nitrogen molecule.
The placement of electrons in bonding or antibonding molecular orbitals can be determined by drawing the molecular orbital diagram of the molecule. This diagram is the virtual representation of the linear combination of atomic orbitals that combine to give molecular orbitals.
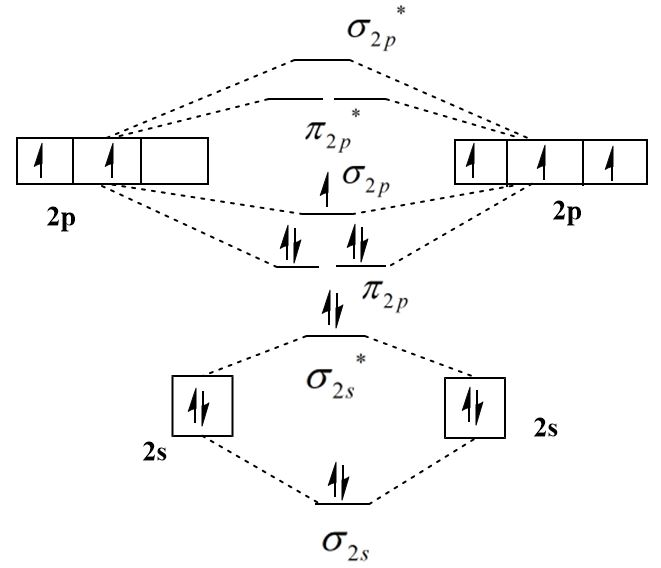
Thus, the outermost electronic configuration of \[{N_2}^ + \] molecule is \[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma ^*}{_{2s}^2}{\pi _{2p}}^4{\sigma _{2p}}^1\] which indicates that there are a total of seven electrons in bonding molecular orbitals and two electrons in the antibonding molecular orbitals. The following formula can be used to calculate the bond order:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{{\text{bonding electrons}} - anti{\text{ - }}bonding{\text{ electrons}}}}{2}\]
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{7 - 2}}{2} = 2.5\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Thus, the bond order of \[{N_2}^ + \] ion is \[2.5\] and therefore option (C) is correct.
Note:
The star marked molecular orbitals are the anti-bonding molecular orbitals that are formed due to the destructive overlap that takes place between atomic orbitals. The electrons present in anti-bonding molecular orbital do not contribute in the bond formation and are therefore subtracted.
Complete answer:
A simple nitrogen molecule is diatomic in nature and consists of triple bonds that are strong enough to make the nitrogen molecule stable and inert at room temperature. The triple bond present in a nitrogen molecule is an indicator of the fact that its bond order is \[3\] .
\[{N_2}^ + \] is chemically different from the simple nitrogen molecule as it has lost one electron or it has one electron less as compared to the nitrogen molecule.
The placement of electrons in bonding or antibonding molecular orbitals can be determined by drawing the molecular orbital diagram of the molecule. This diagram is the virtual representation of the linear combination of atomic orbitals that combine to give molecular orbitals.

Thus, the outermost electronic configuration of \[{N_2}^ + \] molecule is \[{\sigma _{2s}}^2{\sigma ^*}{_{2s}^2}{\pi _{2p}}^4{\sigma _{2p}}^1\] which indicates that there are a total of seven electrons in bonding molecular orbitals and two electrons in the antibonding molecular orbitals. The following formula can be used to calculate the bond order:
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{{\text{bonding electrons}} - anti{\text{ - }}bonding{\text{ electrons}}}}{2}\]
\[{\text{bond order}} = \dfrac{{7 - 2}}{2} = 2.5\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Thus, the bond order of \[{N_2}^ + \] ion is \[2.5\] and therefore option (C) is correct.
Note:
The star marked molecular orbitals are the anti-bonding molecular orbitals that are formed due to the destructive overlap that takes place between atomic orbitals. The electrons present in anti-bonding molecular orbital do not contribute in the bond formation and are therefore subtracted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




