
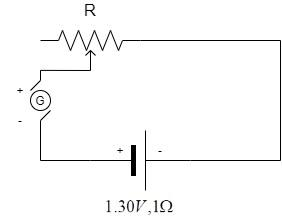
The battery in the diagram is to be charged by the generator G. The generator has a terminal voltage of 120 volts when the charging current is 10 amperes. The battery has an emf of 100 volts and internal resistance of 1 ohm. In order to charge the battery at 10 amperes charging current, the resistance R should be set at:

Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint:There are two kinds of battery: Primary and Secondary. Primary battery is a single use battery which cannot be recharged for reusing again. Secondary battery is a reusable battery which can be charged and discharged. Examples of such battery are –
Primary – Dry Leclanche cell made of zinc-carbon, Zinc manganese dioxide cell
Secondary – Lead acid, Nickel-Cadmium
Complete step-by-step answer:
The emf is defined as the total voltage that is available for the discharge in the circuit. However, due to internal resistance, not all the emf is completely used. Therefore, some of the emf gets wasted in overcoming the internal resistance, and what remains flows in the circuit, which is termed as the terminal voltage.
For example, if 12 V is the emf of the cell, not all 12V is the potential difference in the circuit. The terminal voltage can be equal to 9V or 10V.
Here, given:
Terminal voltage of generator, $V = 120V$
Charging current, $I = 10A$
Internal resistance, $r = 1\Omega $
By the definition of terminal voltage, we have –
$V = E - Ir$ where $E$ is the emf.
By substituting the above values, we can calculate the emf of the generator –
$
E = V + Ir \\
E = 120 + 10(1) \\
\to E = 130V \\
$
In the circuit, the net resistance of the circuit,
$R = \dfrac{{E - V}}{I}$
Substituting the values, we get –
$
R = \dfrac{{E - V}}{I} \\
R = \dfrac{{130 - 120}}{{10}} \\
\to R = \dfrac{{10}}{{10}} = 1\Omega \\
$
Therefore, the resistance R must be set to $1\Omega $.
Note: The students must keep in mind that the terminal voltage value is always lesser than the emf. So, if you ever get the value of emf lesser than the terminal voltage, stop right there and trace back the steps because there is a 100% chance that you are doing the problem wrong. This can help you avoid computational errors in your competitive exams.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The emf is defined as the total voltage that is available for the discharge in the circuit. However, due to internal resistance, not all the emf is completely used. Therefore, some of the emf gets wasted in overcoming the internal resistance, and what remains flows in the circuit, which is termed as the terminal voltage.
For example, if 12 V is the emf of the cell, not all 12V is the potential difference in the circuit. The terminal voltage can be equal to 9V or 10V.
Here, given:
Terminal voltage of generator, $V = 120V$
Charging current, $I = 10A$
Internal resistance, $r = 1\Omega $
By the definition of terminal voltage, we have –
$V = E - Ir$ where $E$ is the emf.
By substituting the above values, we can calculate the emf of the generator –
$
E = V + Ir \\
E = 120 + 10(1) \\
\to E = 130V \\
$
In the circuit, the net resistance of the circuit,
$R = \dfrac{{E - V}}{I}$
Substituting the values, we get –
$
R = \dfrac{{E - V}}{I} \\
R = \dfrac{{130 - 120}}{{10}} \\
\to R = \dfrac{{10}}{{10}} = 1\Omega \\
$
Therefore, the resistance R must be set to $1\Omega $.
Note: The students must keep in mind that the terminal voltage value is always lesser than the emf. So, if you ever get the value of emf lesser than the terminal voltage, stop right there and trace back the steps because there is a 100% chance that you are doing the problem wrong. This can help you avoid computational errors in your competitive exams.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




