
The attractive forces between polar molecules are _____________forces and between non-polar molecules are____________ forces.
A) dipole-dipole, London
B) London, dipole-dipole
C) Induced dipole-induced dipole, London
D) London, induced dipole-induced dipole
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: The difference in electronegativity between two elements determines the type of bond. A small difference results in nonpolar covalent bond, an intermediate difference results in polar covalent bond and a large difference in electronegativity results in ionic bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first see what are polar and nonpolar bonds. Polar bonds are those in which there is unequal sharing of electrons. This means that the electron density between two atoms has an unequal distribution between them. For example, in case of HCl, hydrogen has just one electron and iodine has 7 electrons. This results in development of partial charges. Hydrogen gets partial positive charge and Cl gets partial negative charge.
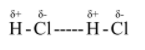
-This results in development of attractive force between positive end of one dipole (in this case ${H^ + }$) and negative end of other dipole ($C{l^ - }$) between many $HCl$ molecules. Such attractive forces occurring between dipoles of the polar molecules are called Dipole-dipole forces.
-Hence, we come to know that polar molecules form dipole-dipole interaction.
-Let us see what happens in case of non-polar molecules.
-In case of non- polar molecules, there is distortion of electron cloud .e.g. in case $He$ atom, there are two electrons which are distributed evenly but at any given time if the distribution becomes uneven results in development of an instantaneous dipole. This results in fluctuation of electron density between neighboring He molecules. These attractive forces between the instantaneous dipoles and induced dipoles are called London dispersion forces. -Thus, it can be noted that the interaction between non- polar molecules results in London forces.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
Dipole-dipole and Dipole-induced dipole are not the same. The former is a weak bond resulting from formation of permanent dipole. But in case of dipole-induced dipole the bond is between a permanent dipole and between a temporary dipole also known as London forces.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first see what are polar and nonpolar bonds. Polar bonds are those in which there is unequal sharing of electrons. This means that the electron density between two atoms has an unequal distribution between them. For example, in case of HCl, hydrogen has just one electron and iodine has 7 electrons. This results in development of partial charges. Hydrogen gets partial positive charge and Cl gets partial negative charge.
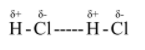
-This results in development of attractive force between positive end of one dipole (in this case ${H^ + }$) and negative end of other dipole ($C{l^ - }$) between many $HCl$ molecules. Such attractive forces occurring between dipoles of the polar molecules are called Dipole-dipole forces.
-Hence, we come to know that polar molecules form dipole-dipole interaction.
-Let us see what happens in case of non-polar molecules.
-In case of non- polar molecules, there is distortion of electron cloud .e.g. in case $He$ atom, there are two electrons which are distributed evenly but at any given time if the distribution becomes uneven results in development of an instantaneous dipole. This results in fluctuation of electron density between neighboring He molecules. These attractive forces between the instantaneous dipoles and induced dipoles are called London dispersion forces. -Thus, it can be noted that the interaction between non- polar molecules results in London forces.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A.
Note:
Dipole-dipole and Dipole-induced dipole are not the same. The former is a weak bond resulting from formation of permanent dipole. But in case of dipole-induced dipole the bond is between a permanent dipole and between a temporary dipole also known as London forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




