
The area of the parallelogram whose diagonals represent the vectors $3\overrightarrow{i}+\overrightarrow{j}-2\overrightarrow{k}$ and $\overrightarrow{i}-3\overrightarrow{j}+4\overrightarrow{k}$ is.
(a) $10\sqrt{3}$
(b) $5\sqrt{3}$
(c) $8$
(d) $4$
Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint: For solving this question we will use the concept that if $AC$ and $BD$ are the diagonals of a quadrilateral, then its vector area is $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ . After that, we will find the cross product of the given vectors and multiply its magnitude by 0.5 to find the value of the area of the parallelogram easily.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given:
It is given that vectors $3\overrightarrow{i}+\overrightarrow{j}-2\overrightarrow{k}$ and $\overrightarrow{i}-3\overrightarrow{j}+4\overrightarrow{k}$ are the diagonals of a parallelogram and we have to find its area.
Now, here before we proceed we should know that if $AC$ and $BD$ are the diagonals of a quadrilateral, then its vector area is $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
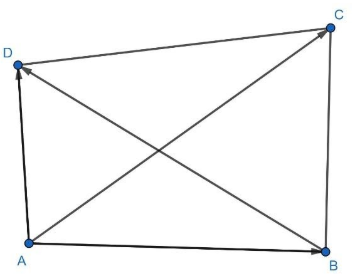
Now, in the above figure consider the $\Delta ABD$ and apply the triangle law of vector addition. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{AD} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB}...............\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, as we know that the vector area of any triangle is equal to half of the cross product of any two adjacent side vectors. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\text{ Vector area of }\Delta ABC+\text{ Vector area of }\Delta ACD \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AB}\times \overrightarrow{AC} \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{AD} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{AB} \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{AD} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \left( \overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB} \right) \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute $\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB}$ from equation (1) in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \left( \overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB} \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, to get the magnitude of the area of the quadrilateral $ABCD$ we have to find the magnitude of the vector $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ .
Now, we come back to our question in which we have to find the area of the parallel gram whose diagonals represent the vectors $3\overrightarrow{i}+\overrightarrow{j}-2\overrightarrow{k}$ and $\overrightarrow{i}-3\overrightarrow{j}+4\overrightarrow{k}$ . So, let $\overrightarrow{AC}=3\overrightarrow{i}+\overrightarrow{j}-2\overrightarrow{k}$ and $\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{i}-3\overrightarrow{j}+4\overrightarrow{k}$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:
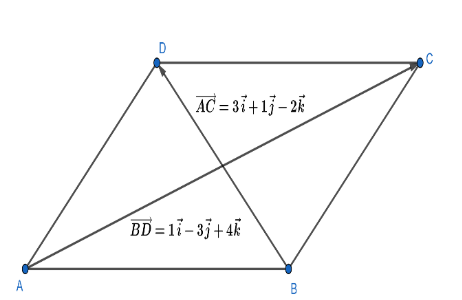
Now, to find the area of the given parallelogram we have to find the magnitude of the vector $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ . Then,
$\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
\overrightarrow{i} & \overrightarrow{j} & \overrightarrow{k} \\
3 & 1 & -2 \\
1 & -3 & 4 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
Now, we will use the following formula of determinant to find the determinant value:
$\begin{align}
& \left| A \right|=\left| \begin{matrix}
{{a}_{11}} & {{a}_{12}} & {{a}_{13}} \\
{{a}_{21}} & {{a}_{22}} & {{a}_{23}} \\
{{a}_{31}} & {{a}_{32}} & {{a}_{33}} \\
\end{matrix} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \left| A \right|={{a}_{11}}\left( {{a}_{22}}{{a}_{33}}-{{a}_{23}}{{a}_{32}} \right)-{{a}_{12}}\left( {{a}_{21}}{{a}_{33}}-{{a}_{23}}{{a}_{31}} \right)+{{a}_{13}}\left( {{a}_{21}}{{a}_{32}}-{{a}_{22}}{{a}_{31}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
\overrightarrow{i} & \overrightarrow{j} & \overrightarrow{k} \\
3 & 1 & -2 \\
1 & -3 & 4 \\
\end{matrix} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \left( 1\times 4-\left( -2 \right)\times \left( -3 \right) \right)\overrightarrow{i}-\left(3\times 4-(-2)\times 1 \right)\overrightarrow{j}+\left( -3\times 3-1\times 1 \right)\overrightarrow{k} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \left( 4-6 \right)\overrightarrow{i}-\left( 12+2 \right)\overrightarrow{j}+\left( -9-1 \right)\overrightarrow{k} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ -2\overrightarrow{i}-14\overrightarrow{j}-10\overrightarrow{k} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=-\overrightarrow{i}-7\overrightarrow{j}-5\overrightarrow{k} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, as we know that magnitude of the vector $x\overrightarrow{i}+y\overrightarrow{j}+z\overrightarrow{k}$ is equal to $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=-\overrightarrow{i}-7\overrightarrow{j}-5\overrightarrow{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{7}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{1+49+25} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{75} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{25\times 3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=5\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, as the magnitude of the vector \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=5\sqrt{3}\] .
Thus, the area of the given parallelogram will be $5\sqrt{3}$ .
Hence, (b) is the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. And we should make use of the geometric meaning of $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ to solve this question without any difficulty. Moreover, we should solve the cross product of the given vectors without any calculation mistake and select the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given:
It is given that vectors $3\overrightarrow{i}+\overrightarrow{j}-2\overrightarrow{k}$ and $\overrightarrow{i}-3\overrightarrow{j}+4\overrightarrow{k}$ are the diagonals of a parallelogram and we have to find its area.
Now, here before we proceed we should know that if $AC$ and $BD$ are the diagonals of a quadrilateral, then its vector area is $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:

Now, in the above figure consider the $\Delta ABD$ and apply the triangle law of vector addition. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{AD} \\
& \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB}...............\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, as we know that the vector area of any triangle is equal to half of the cross product of any two adjacent side vectors. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\text{ Vector area of }\Delta ABC+\text{ Vector area of }\Delta ACD \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AB}\times \overrightarrow{AC} \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{AD} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{AB} \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{AD} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \left( \overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB} \right) \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, substitute $\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB}$ from equation (1) in the above equation. Then,
$\begin{align}
& \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \left( \overrightarrow{AD}-\overrightarrow{AB} \right) \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Vector area of the quadrilateral }ABCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, to get the magnitude of the area of the quadrilateral $ABCD$ we have to find the magnitude of the vector $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ .
Now, we come back to our question in which we have to find the area of the parallel gram whose diagonals represent the vectors $3\overrightarrow{i}+\overrightarrow{j}-2\overrightarrow{k}$ and $\overrightarrow{i}-3\overrightarrow{j}+4\overrightarrow{k}$ . So, let $\overrightarrow{AC}=3\overrightarrow{i}+\overrightarrow{j}-2\overrightarrow{k}$ and $\overrightarrow{BD}=\overrightarrow{i}-3\overrightarrow{j}+4\overrightarrow{k}$ . For more clarity look at the figure given below:

Now, to find the area of the given parallelogram we have to find the magnitude of the vector $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ . Then,
$\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
\overrightarrow{i} & \overrightarrow{j} & \overrightarrow{k} \\
3 & 1 & -2 \\
1 & -3 & 4 \\
\end{matrix} \right|$
Now, we will use the following formula of determinant to find the determinant value:
$\begin{align}
& \left| A \right|=\left| \begin{matrix}
{{a}_{11}} & {{a}_{12}} & {{a}_{13}} \\
{{a}_{21}} & {{a}_{22}} & {{a}_{23}} \\
{{a}_{31}} & {{a}_{32}} & {{a}_{33}} \\
\end{matrix} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \left| A \right|={{a}_{11}}\left( {{a}_{22}}{{a}_{33}}-{{a}_{23}}{{a}_{32}} \right)-{{a}_{12}}\left( {{a}_{21}}{{a}_{33}}-{{a}_{23}}{{a}_{31}} \right)+{{a}_{13}}\left( {{a}_{21}}{{a}_{32}}-{{a}_{22}}{{a}_{31}} \right) \\
\end{align}$
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \begin{matrix}
\overrightarrow{i} & \overrightarrow{j} & \overrightarrow{k} \\
3 & 1 & -2 \\
1 & -3 & 4 \\
\end{matrix} \right| \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \left( 1\times 4-\left( -2 \right)\times \left( -3 \right) \right)\overrightarrow{i}-\left(3\times 4-(-2)\times 1 \right)\overrightarrow{j}+\left( -3\times 3-1\times 1 \right)\overrightarrow{k} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ \left( 4-6 \right)\overrightarrow{i}-\left( 12+2 \right)\overrightarrow{j}+\left( -9-1 \right)\overrightarrow{k} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ -2\overrightarrow{i}-14\overrightarrow{j}-10\overrightarrow{k} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=-\overrightarrow{i}-7\overrightarrow{j}-5\overrightarrow{k} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, as we know that magnitude of the vector $x\overrightarrow{i}+y\overrightarrow{j}+z\overrightarrow{k}$ is equal to $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$ . Then,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)=-\overrightarrow{i}-7\overrightarrow{j}-5\overrightarrow{k} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{7}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{1+49+25} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{75} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=\sqrt{25\times 3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=5\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, as the magnitude of the vector \[\dfrac{1}{2}\left| \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right|=5\sqrt{3}\] .
Thus, the area of the given parallelogram will be $5\sqrt{3}$ .
Hence, (b) is the correct option.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed in the right direction to get the correct answer quickly. And we should make use of the geometric meaning of $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \overrightarrow{AC}\times \overrightarrow{BD} \right)$ to solve this question without any difficulty. Moreover, we should solve the cross product of the given vectors without any calculation mistake and select the correct answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




