
The area of a loop of the curve \[r = a\sin 3\theta\] is:
A. \[\dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{2}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{6}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{8}\]
D. \[\dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{{12}}\]
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: In this problem, first we need to find the upper and lower limits of the first loop of the curve. Then, apply the formula for the area under the curve in polar coordinates to obtain the area of the first loop.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The diagram of the curve \[r = a\sin 3\theta\] is shown below.
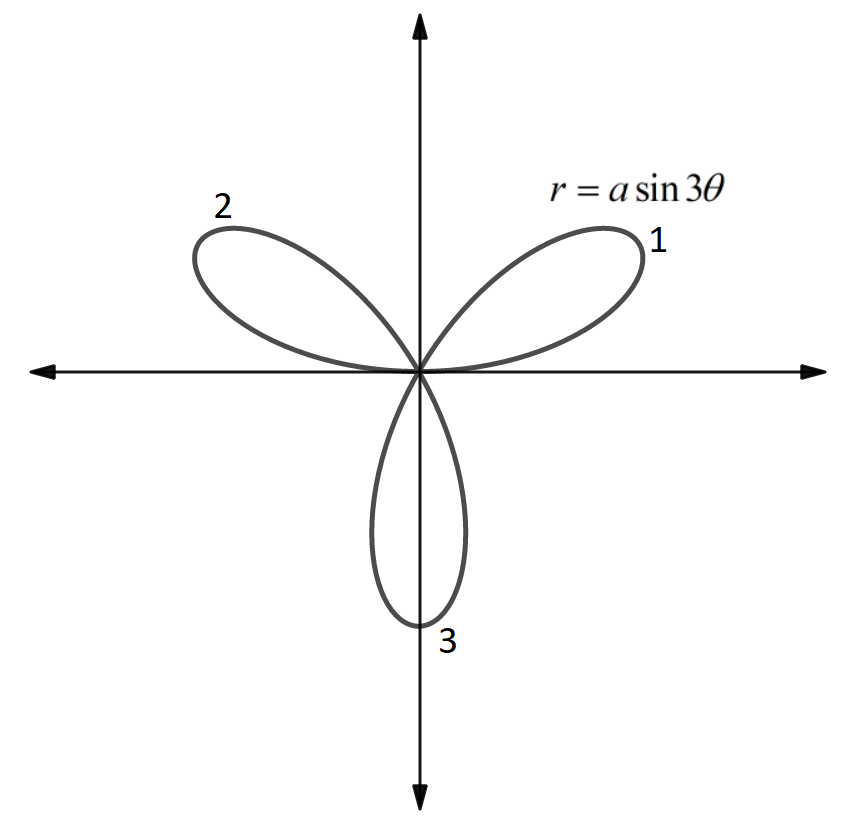
From the above figure, it can be observed that the curve\[ r = a\sin 3\theta \] consists of three loops.
Substitute 0 for \[r\] in the equation of the curve \[r = a\sin 3\theta \] to obtain the upper and lower limits of the loop.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,0 = a\sin 3\theta \\
\Rightarrow \sin 3\theta = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 3\theta = 0\,\,{\text{or}}\,\,\pi \\
\Rightarrow \theta = 0\,\,{\text{or}}\,\,\dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
\]
Here, 0 is the lower limits and \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] is the upper limit of the first loop.
Now, the area \[A\] of the first loop is calculated as follows:
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,A = \dfrac{1}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {{r^2}d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {{a^2}{{\sin }^2}3\theta d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {{{\sin }^2}3\theta d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {\left( {\dfrac{{1 - \cos 6\theta }}{2}} \right)d\theta } \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left( {{{\sin }^2}\theta = \dfrac{{1 - \cos 2\theta }}{2}} \right) \\
\]
Further, solve the above integral as shown below.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {\left( {1 - \cos 6\theta } \right)d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\left[ {\theta - \dfrac{{\sin 6\theta }}{6}} \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\left[ {\dfrac{\pi }{3} - \dfrac{{\sin 2\pi }}{6}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\left[ {\dfrac{\pi }{3} - 0} \right] \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{{12}} \\
\]
Thus, the area of a loop of the curve \[r = a\sin 3\theta \] is \[\dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{{12}}\], hence, option (D) is correct answer.
Note: In this problem, there are three identical loops. The area of each loop is the same. While evaluating the integral, convert \[{\sin ^2}3\theta \] into \[\cos 6\theta \] using trigonometric identity.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The diagram of the curve \[r = a\sin 3\theta\] is shown below.

From the above figure, it can be observed that the curve\[ r = a\sin 3\theta \] consists of three loops.
Substitute 0 for \[r\] in the equation of the curve \[r = a\sin 3\theta \] to obtain the upper and lower limits of the loop.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,0 = a\sin 3\theta \\
\Rightarrow \sin 3\theta = 0 \\
\Rightarrow 3\theta = 0\,\,{\text{or}}\,\,\pi \\
\Rightarrow \theta = 0\,\,{\text{or}}\,\,\dfrac{\pi }{3} \\
\]
Here, 0 is the lower limits and \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] is the upper limit of the first loop.
Now, the area \[A\] of the first loop is calculated as follows:
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,A = \dfrac{1}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {{r^2}d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {{a^2}{{\sin }^2}3\theta d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {{{\sin }^2}3\theta d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{2}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {\left( {\dfrac{{1 - \cos 6\theta }}{2}} \right)d\theta } \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\left( {{{\sin }^2}\theta = \dfrac{{1 - \cos 2\theta }}{2}} \right) \\
\]
Further, solve the above integral as shown below.
\[
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\int_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} {\left( {1 - \cos 6\theta } \right)d\theta } \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\left[ {\theta - \dfrac{{\sin 6\theta }}{6}} \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\left[ {\dfrac{\pi }{3} - \dfrac{{\sin 2\pi }}{6}} \right] \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{4}\left[ {\dfrac{\pi }{3} - 0} \right] \\
\Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{{12}} \\
\]
Thus, the area of a loop of the curve \[r = a\sin 3\theta \] is \[\dfrac{{\pi {a^2}}}{{12}}\], hence, option (D) is correct answer.
Note: In this problem, there are three identical loops. The area of each loop is the same. While evaluating the integral, convert \[{\sin ^2}3\theta \] into \[\cos 6\theta \] using trigonometric identity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




