
The apparatus which is used at C is known as
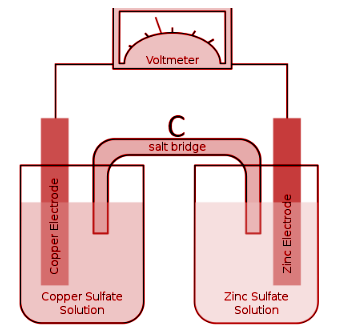
(A) Anode
(B) Cathode
(C) Salt bridge
(D) lon bridge
(E) Osmotic bridge

Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: An electrochemical cell is a device that may either create electrical energy from chemical processes taking place inside it or use electrical energy given to it to aid chemical processes taking place inside it. Chemical energy may be converted to electrical energy or vice versa using these technologies.
Complete answer:
A salt bridge is a device that connects the oxidation and reduction halves of an electrochemical cell using a weak electrolyte. In other terms, a salt bridge is a connection in a cell or electrolytic solution that connects the anodic and cathodic compartments.
A powerful electrolyte, which is further made up of ions, generally makes up the salt bridge. For instance, \[AgN{O_3}\], KCl, and so on. In a galvanic cell, such as a voltaic cell or a Daniel cell, salt bridges are commonly utilised.
A salt bridge's primary role is to aid in the maintenance of electrical neutrality inside the internal circuit. It also aids in keeping the cell from reaching equilibrium with its response. If salt bridges aren't present or aren't employed, the process will likely proceed and the solution in half of the electrodes will accumulate a negative charge. Similarly, electrodes in the other half would accrue a positive charge. As a result, the reaction will come to a halt, and no energy will be created.
As a result, a salt bridge serves to avoid the buildup of positive and negative charges surrounding the corresponding electrodes, allowing for a smooth reaction to occur. It also contributes to the smooth passage of electrons. However, because the electrons are going from one half cell to the other, the objective of a salt bridge is to maintain charge balance rather than to transport electrons from the electrolyte.
Note:
The salt bridge stops solution from diffusing or flowing mechanically from one half cell to the other.
It avoids or reduces the possibility of a liquid-liquid junction. (When two solutions come into touch with each other, potential occurs.)
Between two half cells, a salt bridge works as an electrical contact.
Complete answer:
A salt bridge is a device that connects the oxidation and reduction halves of an electrochemical cell using a weak electrolyte. In other terms, a salt bridge is a connection in a cell or electrolytic solution that connects the anodic and cathodic compartments.
A powerful electrolyte, which is further made up of ions, generally makes up the salt bridge. For instance, \[AgN{O_3}\], KCl, and so on. In a galvanic cell, such as a voltaic cell or a Daniel cell, salt bridges are commonly utilised.
A salt bridge's primary role is to aid in the maintenance of electrical neutrality inside the internal circuit. It also aids in keeping the cell from reaching equilibrium with its response. If salt bridges aren't present or aren't employed, the process will likely proceed and the solution in half of the electrodes will accumulate a negative charge. Similarly, electrodes in the other half would accrue a positive charge. As a result, the reaction will come to a halt, and no energy will be created.
As a result, a salt bridge serves to avoid the buildup of positive and negative charges surrounding the corresponding electrodes, allowing for a smooth reaction to occur. It also contributes to the smooth passage of electrons. However, because the electrons are going from one half cell to the other, the objective of a salt bridge is to maintain charge balance rather than to transport electrons from the electrolyte.
Note:
The salt bridge stops solution from diffusing or flowing mechanically from one half cell to the other.
It avoids or reduces the possibility of a liquid-liquid junction. (When two solutions come into touch with each other, potential occurs.)
Between two half cells, a salt bridge works as an electrical contact.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




