
The anti-cancer drug cis-platin has the formula $Pt{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$. There is another isomer, trans-platin, that is not medically active. What is the shape of cis-platin?
(A) Tetrahedral
(B) Octahedral
(C) Square planar
(D) Trigonal Bipyramidal
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: Generally the metal complexes attain the shape which gives them highest stability. If four ligands are there, then most of the metals form tetrahedral complexes. In the case of six ligands, octahedral complexes are formed. There is an exception in Ni group elements which form square planar complexes more often.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all cis-platin is a transition metal complex as we can see and Palladium (Pd) is the central metal atom in this complex. In order to predict its shape, we will need to understand how Pd metal atoms will bind to the ligands.
- We know that Pd metal is situated under Ni metal in the periodic table. So, it has the same number of electrons in its valence orbital, d-orbital. So, the electronic configuration of Pd is $[Kr]4{{d}^{10}}$.
- Now, all the metals that are in the Ni group in the periodic table, show square planar geometry. They do so because it provides the complex very high crystal field stabilization energy.
- Crystal field stabilization energy shows the stabilization of all the d-orbital after their splitting occurs in presence of ligand field. Actually splitting of d-orbitals is characterized by the change in energy of d-orbitals which are otherwise degenerated in absence of ligand field.
- So, due to this reason, cis-platin also being a Pd metal complex which is a Ni group metal, will show square plannar geometry. The molecule is drawn as below.
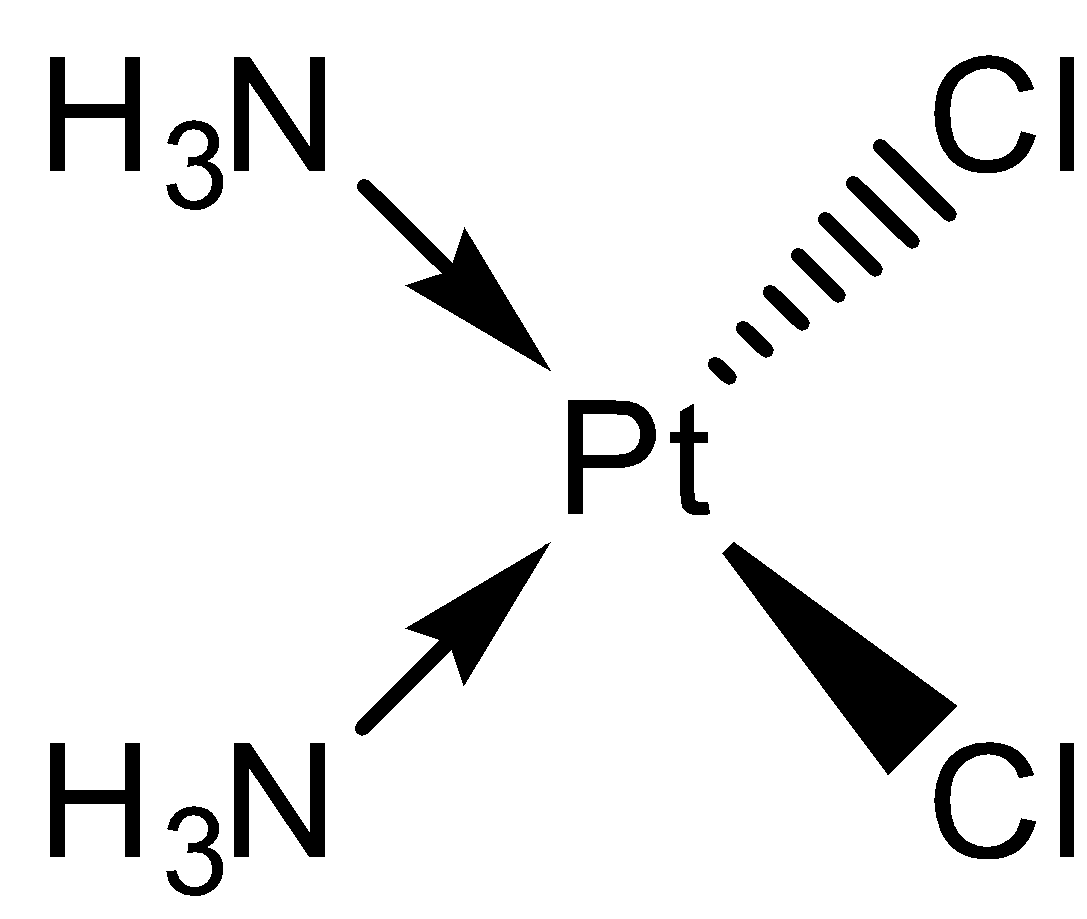
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that even though Pd has only four ligands attached to it, the complex formed is not tetrahedral. Here, the repulsive force between the ligands is overcome by the stabilization provided by crystal field splitting. So, we get a square planar complex in case of Ni group elements.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all cis-platin is a transition metal complex as we can see and Palladium (Pd) is the central metal atom in this complex. In order to predict its shape, we will need to understand how Pd metal atoms will bind to the ligands.
- We know that Pd metal is situated under Ni metal in the periodic table. So, it has the same number of electrons in its valence orbital, d-orbital. So, the electronic configuration of Pd is $[Kr]4{{d}^{10}}$.
- Now, all the metals that are in the Ni group in the periodic table, show square planar geometry. They do so because it provides the complex very high crystal field stabilization energy.
- Crystal field stabilization energy shows the stabilization of all the d-orbital after their splitting occurs in presence of ligand field. Actually splitting of d-orbitals is characterized by the change in energy of d-orbitals which are otherwise degenerated in absence of ligand field.
- So, due to this reason, cis-platin also being a Pd metal complex which is a Ni group metal, will show square plannar geometry. The molecule is drawn as below.

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that even though Pd has only four ligands attached to it, the complex formed is not tetrahedral. Here, the repulsive force between the ligands is overcome by the stabilization provided by crystal field splitting. So, we get a square planar complex in case of Ni group elements.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




