
The angle of contact for the pair of pure water with clean glass is
A. acute
B. obtuse
C. \[{90^ \circ }\]
D. \[{0^ \circ }\]
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Angle of contact depends on the container and also the type of liquid it contains. It differs for the materials that wet the glass and the materials that do not wet the glass. For example, pure water and mercury do not wet the container made up of clean glass.
Complete step by step answer:
Surface tension is the property of liquids by virtue of which its free surface behaves like a stretched membrane.
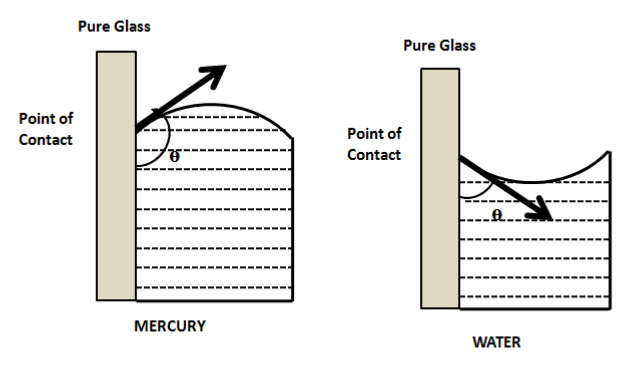
The free surface of the liquid in a container is curved near the walls of the container. The free surface of mercury is convex upwards and that of water is concave upwards. Then, the angle that the surface makes with the walls of the container is called the angle of contact. It is denoted by\[\theta \].
The angle of contact also depends on the nature of the material of the container. For glass as the material of the container, \[\theta \] is more than \[{90^ \circ }\]for mercury (obtuse) and less than \[{90^ \circ }\]for (acute) water. This also may be because mercury does not wet the material of capillary and glass wets the material of capillary. That is why, water rises in the capillary and mercury falls off the normal level in a capillary tube. Because normal water or tap water has some impurities in it, it forms an acute angle of contact with the glass.
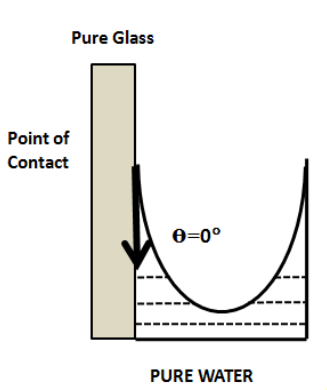
But in case of pure water and clean glass, the angle of contact will be \[{0^ \circ }\]since it is pure and does not have any type of impurities (like salt) dissolved in it.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The angle of contact \[\theta \] is measured within the liquid and is tangent to the surface of the liquid. In the case of pure water, the tangent almost touches to the surface of the glass container.
Also, impure water can wet the glass and can spread out on it because the adhesive forces between the liquid molecules and the glass molecules are stronger than the cohesive forces within the molecules of water.
Complete step by step answer:
Surface tension is the property of liquids by virtue of which its free surface behaves like a stretched membrane.
The free surface of the liquid in a container is curved near the walls of the container. The free surface of mercury is convex upwards and that of water is concave upwards. Then, the angle that the surface makes with the walls of the container is called the angle of contact. It is denoted by\[\theta \].
The angle of contact also depends on the nature of the material of the container. For glass as the material of the container, \[\theta \] is more than \[{90^ \circ }\]for mercury (obtuse) and less than \[{90^ \circ }\]for (acute) water. This also may be because mercury does not wet the material of capillary and glass wets the material of capillary. That is why, water rises in the capillary and mercury falls off the normal level in a capillary tube. Because normal water or tap water has some impurities in it, it forms an acute angle of contact with the glass.

But in case of pure water and clean glass, the angle of contact will be \[{0^ \circ }\]since it is pure and does not have any type of impurities (like salt) dissolved in it.

So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The angle of contact \[\theta \] is measured within the liquid and is tangent to the surface of the liquid. In the case of pure water, the tangent almost touches to the surface of the glass container.
Also, impure water can wet the glass and can spread out on it because the adhesive forces between the liquid molecules and the glass molecules are stronger than the cohesive forces within the molecules of water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




