
Terylene is a:
A. Polyamide
B. Polyester
C. Polyether
D. Long-chain hydrocarbon
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint:
We can classify the polymers on the basis of the nature of linkages that are present in a polymer or the process by which they are made among many other ways.
Complete step by step solution
We can make a simple and better understanding of the term ‘polymer’ by looking at the Greek words, ‘poly’ (which means ‘many’) and ‘mer’ (which means ‘unit’). So, in simple terms, a polymer can be defined as a large molecule which is made of many small units. In fact, these molecules are very large and have high molecular mass $\left( {{{10}^3} - {{10}^7}u} \right)$.These small and basic structural units are called monomers. Examples include: polypropene which is made with propene as its monomer. The process of repetition of monomeric units to give a polymer is called polymerization.
There are various ways in which polymers can be categorized such as on the basis of their source or the nature of linkage between the monomeric units or the process by which a polymer is made. Here, we will talk about some categories based on the nature of linkages.
- Polyamides: These polymers have amide linkages resulting from condensation of monomeric units. Examples include ${\rm{nylon}}\;{\rm{6,6}}$ and ${\rm{nylon}}\;{\rm{6}}$.
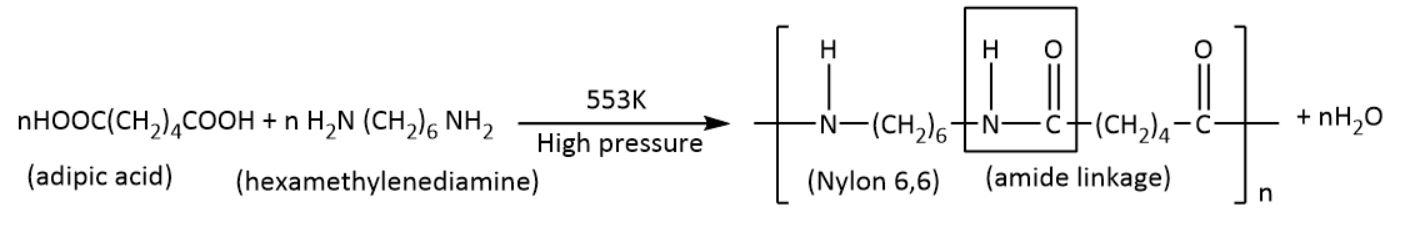
- Polyesters: These polymers have ester linkages resulting from condensation of the carboxylic group and hydroxyl group in monomeric units. Examples include terylene.
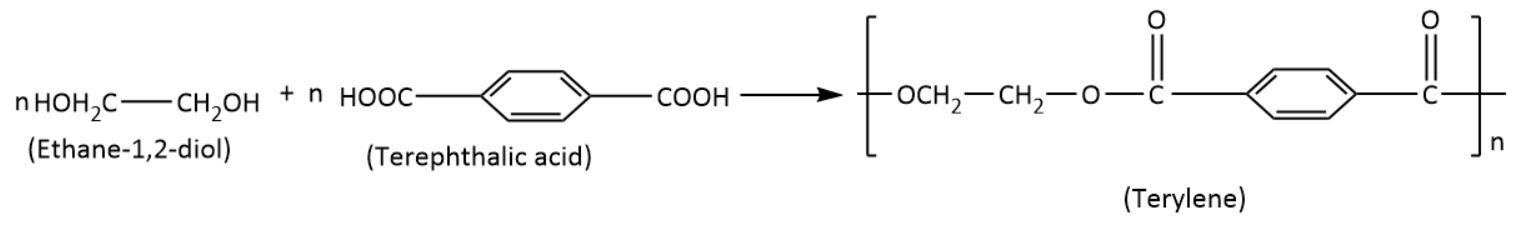
From the above discussion, we can infer that terylene is a polyester.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:
We have to first look at the structure of the given compound/molecule before deducing its nature or type.
We can classify the polymers on the basis of the nature of linkages that are present in a polymer or the process by which they are made among many other ways.
Complete step by step solution
We can make a simple and better understanding of the term ‘polymer’ by looking at the Greek words, ‘poly’ (which means ‘many’) and ‘mer’ (which means ‘unit’). So, in simple terms, a polymer can be defined as a large molecule which is made of many small units. In fact, these molecules are very large and have high molecular mass $\left( {{{10}^3} - {{10}^7}u} \right)$.These small and basic structural units are called monomers. Examples include: polypropene which is made with propene as its monomer. The process of repetition of monomeric units to give a polymer is called polymerization.
There are various ways in which polymers can be categorized such as on the basis of their source or the nature of linkage between the monomeric units or the process by which a polymer is made. Here, we will talk about some categories based on the nature of linkages.
- Polyamides: These polymers have amide linkages resulting from condensation of monomeric units. Examples include ${\rm{nylon}}\;{\rm{6,6}}$ and ${\rm{nylon}}\;{\rm{6}}$.

- Polyesters: These polymers have ester linkages resulting from condensation of the carboxylic group and hydroxyl group in monomeric units. Examples include terylene.

From the above discussion, we can infer that terylene is a polyester.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:
We have to first look at the structure of the given compound/molecule before deducing its nature or type.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




