
How is the structure of a villi in the small intestine related to its function?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint: The small intestine is also known as small bowel and it is a part of the Gastrointestinal tract. It is the organ where the majority of the absorption of minerals and nutrients from the food we eat takes place.
Complete answer:
Villi are vascular projections present in the small intestine projecting into the intestinal cavity
Each villus has many microvilli projecting from its epithelial surface. Villi are specialised for absorption and have very thin walls which are single cell in thickness. They have a rich blood supply to keep a concentration gradient.
The villi of the intestine moves in swaying, contracting motions. These movements increase the flow of blood and lymph and enhance absorption. The villi number about 10 to 40 per square millimetre (6,000 to 25,000 per square inch) of tissue. Digestive enzymes are present on the villi surface for digestion. Villus capillaries collect amino acids and simple sugars taken up by the villi into the bloodstream.
This specific and elaborate structure of the villi helps in increasing the surface area of the membrane. Important villous membranes include the placenta and the mucous-membrane coating of the small intestine.The villi of the small intestine, greatly increasing the surface area for food absorption and adding digestive secretions. An increased absorptive area is useful because digested nutrients exceptionally and efficiently absorb nutrients from the lumen.
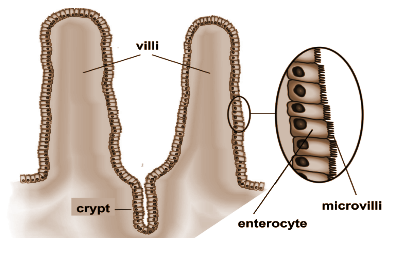
Note: Every villus has a focal centre made out of one artery and one vein, a strand of muscle, a midway found lymphatic capillary (lacteal), and connective tissue that adds support to the structures. The blood vessels transport proteins and carbohydrates absorbed by the cells of the villi, while the lacteal eliminates emulsified fat.
Complete answer:
Villi are vascular projections present in the small intestine projecting into the intestinal cavity
Each villus has many microvilli projecting from its epithelial surface. Villi are specialised for absorption and have very thin walls which are single cell in thickness. They have a rich blood supply to keep a concentration gradient.
The villi of the intestine moves in swaying, contracting motions. These movements increase the flow of blood and lymph and enhance absorption. The villi number about 10 to 40 per square millimetre (6,000 to 25,000 per square inch) of tissue. Digestive enzymes are present on the villi surface for digestion. Villus capillaries collect amino acids and simple sugars taken up by the villi into the bloodstream.
This specific and elaborate structure of the villi helps in increasing the surface area of the membrane. Important villous membranes include the placenta and the mucous-membrane coating of the small intestine.The villi of the small intestine, greatly increasing the surface area for food absorption and adding digestive secretions. An increased absorptive area is useful because digested nutrients exceptionally and efficiently absorb nutrients from the lumen.

Note: Every villus has a focal centre made out of one artery and one vein, a strand of muscle, a midway found lymphatic capillary (lacteal), and connective tissue that adds support to the structures. The blood vessels transport proteins and carbohydrates absorbed by the cells of the villi, while the lacteal eliminates emulsified fat.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




