
How many structural isomers of ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ exist?
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: The isomers which have the same molecular or chemical formula but contain different structures are known as structural isomers. Structural isomers are also called constitutional isomers. The number of possible structural isomers is going to depend on the number of carbons in it.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked about the structural isomers which are formed by ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
- The molecular formula of the given compound is ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
- The possible structural isomers with the molecular of ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ are as follows.
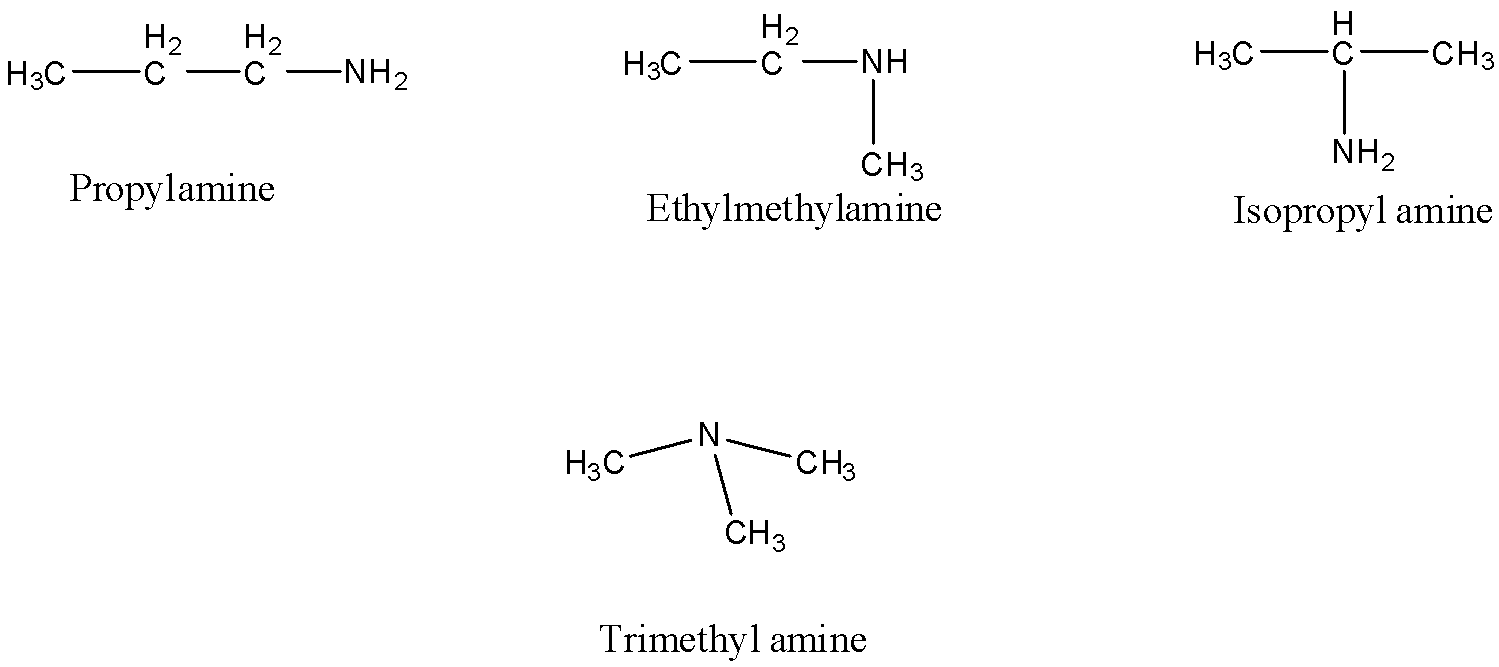
- Means by seeing above possible structural isomers we can say that these four structural isomers are going to form with the molecular formula ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
- In the above structures propylamine is an example for primary amine.
- Ethyl methyl amine is an example for secondary amine.
- In isopropyl amine also the amine is primary amine.
- In trimethylamine the amine is tertiary in nature.
- Tertiary amines are more basic in nature when compared to primary and secondary due to the presence of +I effect caused by the three methyl groups in trimethylamine.
- Therefore there are four structural isomers that are going to be possible with the molecular formula of ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
Note:
If there is an absence of a plane of symmetry and non-superimposable structures in the amines then we can call them that they are having chiral carbons in it. With the structural formula by using ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ we cannot form any chiral compound.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked about the structural isomers which are formed by ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
- The molecular formula of the given compound is ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
- The possible structural isomers with the molecular of ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ are as follows.

- Means by seeing above possible structural isomers we can say that these four structural isomers are going to form with the molecular formula ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
- In the above structures propylamine is an example for primary amine.
- Ethyl methyl amine is an example for secondary amine.
- In isopropyl amine also the amine is primary amine.
- In trimethylamine the amine is tertiary in nature.
- Tertiary amines are more basic in nature when compared to primary and secondary due to the presence of +I effect caused by the three methyl groups in trimethylamine.
- Therefore there are four structural isomers that are going to be possible with the molecular formula of ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ .
Note:
If there is an absence of a plane of symmetry and non-superimposable structures in the amines then we can call them that they are having chiral carbons in it. With the structural formula by using ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{9}}N$ we cannot form any chiral compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




