
How many structural and stereoisomers could be obtained by monochlorination of propene with chlorine?
(A) 2
(B) 5
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint :chlorine is pale yellow colour gas which is considered as a strong oxidizing agent. The liquid chlorine has the tendency to burn skin and being in gaseous state it can irritate the mucous membrane. The monochlorination word means that the process of chlorination with a single atom even if the multiple chlorination can take place.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The structural isomerism is also known as constitutional isomerism. The atoms of the molecules and the functional groups are arranged or linked with each other in various ways. The various structural isomers have been written and assigned different IUPAC names because they do not contain the same functional group at the same position. The different types of structural isomerism are chain isomerism, metamerism, functional isomerism, tautomerism, ring chain isomerism and position isomerism. Whereas stereoisomerism is the isomerism in which the compound has the same chemical formula but the arrangement of the atoms is different so their structure is different. The equation for monochlorination of propene with chlorine is following:
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} = C{H_2} + Cl \to C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HCl $
So the different structural and stereoisomers for the above product formed are
(1) $ ClC{H_2} - CH = C{H_2} $
(2)
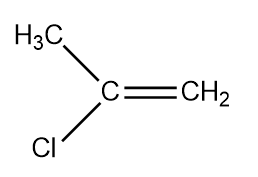
(3)
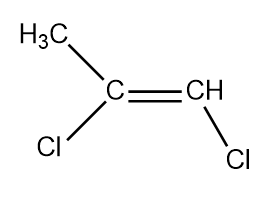
(4)
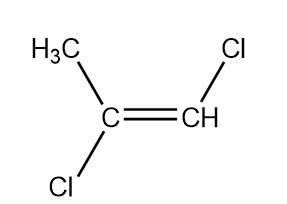
So there are four structural and stereoisomers.
So the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note :
One of the types of structural isomerism is chain isomerism in which the components of these isomers are branched in different structures. The other is position isomerism in which functional groups are positioned in different ways. The other is functional isomerism in which the functional groups of the compounded are bonded to different atoms but having the same chemical formula. In stereoisomerism the geometric isomerism has a different spatial arrangement of atoms. In optical isomerism the atoms are arranged in different spatial arrangements by forming non superimposable mirror images.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The structural isomerism is also known as constitutional isomerism. The atoms of the molecules and the functional groups are arranged or linked with each other in various ways. The various structural isomers have been written and assigned different IUPAC names because they do not contain the same functional group at the same position. The different types of structural isomerism are chain isomerism, metamerism, functional isomerism, tautomerism, ring chain isomerism and position isomerism. Whereas stereoisomerism is the isomerism in which the compound has the same chemical formula but the arrangement of the atoms is different so their structure is different. The equation for monochlorination of propene with chlorine is following:
$ C{H_3} - C{H_2} = C{H_2} + Cl \to C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + HCl $
So the different structural and stereoisomers for the above product formed are
(1) $ ClC{H_2} - CH = C{H_2} $
(2)

(3)

(4)

So there are four structural and stereoisomers.
So the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note :
One of the types of structural isomerism is chain isomerism in which the components of these isomers are branched in different structures. The other is position isomerism in which functional groups are positioned in different ways. The other is functional isomerism in which the functional groups of the compounded are bonded to different atoms but having the same chemical formula. In stereoisomerism the geometric isomerism has a different spatial arrangement of atoms. In optical isomerism the atoms are arranged in different spatial arrangements by forming non superimposable mirror images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




