
What is the state of an ideal diode in the region of non-conduction?
A. Open circuit
B. Short circuit
C. Undefined
D. None of the above
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: No current flows through a diode in the field of non-conduction, in an ideal diode. An open circuit is one in which continuity of current to flow has been interrupted by an interference in the road. One that is complete, with strong continuity within, is a short circuit.
Complete step by step solution:
A diode is an electronic two-terminal component that mostly transports current in only one direction; that has minimum resistance in one direction, and greater resistance in another. By joining two equally doped P-Type and N-Type semiconductors, a diode is formed.
An ideal diode is indeed a diode that, when voltage applied is forward biased, behaves like a perfect conductor and when voltage is applied reverse biased, like a perfect insulator. So, the diode conducts forward current immediately as positive voltage is applied through the anode to the cathode.
Below is a graph of an ideal diode curve of I-V characteristics:
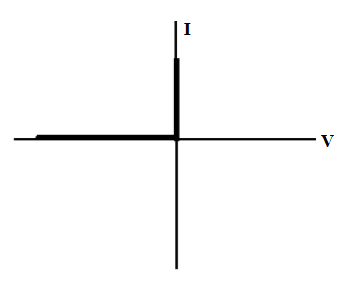
Conduction region means for the field where electrons are allowed to pass. Non-conduction area means where electrons flow is interrupted, so there is no current. The area where there is no current is called an open circuit.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: In order to answer this question we need to have a clear vision regarding ideal diode, real diode, open circuit, short circuit, region of conduction, and region of non-conduction.
A short circuit means that \[R = 0\] resistance connects the two terminals externally, the same as an ideal cable. This implies that for every current value, there is zero voltage difference. An open circuit means that the two endpoints are separated externally, which is similar to a resistance \[R = \propto \].
The area of conduction means the field where electrons are authorised to travel. Non-conduction field indicates that the flow of electrons is disrupted and thus there is no current. An open circuit is called the zone where there is no current.
Complete step by step solution:
A diode is an electronic two-terminal component that mostly transports current in only one direction; that has minimum resistance in one direction, and greater resistance in another. By joining two equally doped P-Type and N-Type semiconductors, a diode is formed.
An ideal diode is indeed a diode that, when voltage applied is forward biased, behaves like a perfect conductor and when voltage is applied reverse biased, like a perfect insulator. So, the diode conducts forward current immediately as positive voltage is applied through the anode to the cathode.
Below is a graph of an ideal diode curve of I-V characteristics:

Conduction region means for the field where electrons are allowed to pass. Non-conduction area means where electrons flow is interrupted, so there is no current. The area where there is no current is called an open circuit.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: In order to answer this question we need to have a clear vision regarding ideal diode, real diode, open circuit, short circuit, region of conduction, and region of non-conduction.
A short circuit means that \[R = 0\] resistance connects the two terminals externally, the same as an ideal cable. This implies that for every current value, there is zero voltage difference. An open circuit means that the two endpoints are separated externally, which is similar to a resistance \[R = \propto \].
The area of conduction means the field where electrons are authorised to travel. Non-conduction field indicates that the flow of electrons is disrupted and thus there is no current. An open circuit is called the zone where there is no current.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




