
How many \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised carbon atoms are present in benzaldehyde?
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: To determine the answer to this question we should the structure of benzaldehyde and the formation of \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised atom. The \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised orbital is formed by one s and two p-orbitals. Carbon atoms have one s and three p-orbital in the valence shell.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of the benzaldehyde is as follows:
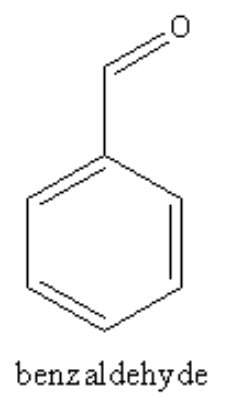
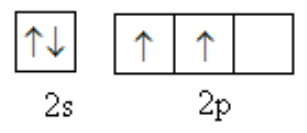
The valence shell of carbon is as follows:
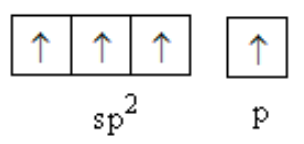
One s and two p-orbitals combine to form \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised orbital of carbon.
Four un-hybridised p-orbital form pi bonds. Hybridised orbitals form sigma bonds only. So, we can say from the structure of the benzaldehyde that each carbon of the ring is forming three sigma bond and one pi bond so, each carbon of the ring is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized. The carbon of aldehyde is also forming three sigma and one pi bond so, the carbon of aldehyde is also ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized.
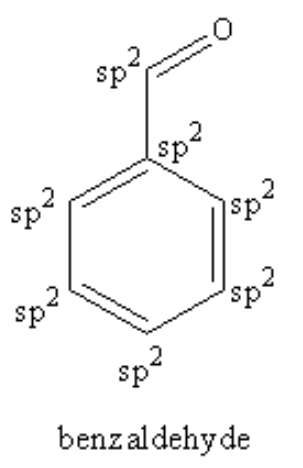
Therefore, $7$ \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised carbon atoms are present in benzaldehyde.
Note: The number of hybridized orbitals is equal to the number of sigma bonds. Hybridized orbitals have the same energy. The hybridization tells the number of hybrid orbitals. \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridization means three (one s and two p-orbital) hybrid orbitals or three sigma bonds. Each carbon of benzene ring is\[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised. We can also determine the hybridization of an atom by counting the total number of sigma electron pairs around the atom. The oxygen atom has one sigma bond and two lone pairs, so a total of three electron pairs. Oxygen atom is also \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised.in benzaldehyde a total of eight \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised atoms are present.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of the benzaldehyde is as follows:

The valence shell of carbon is as follows:

One s and two p-orbitals combine to form \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised orbital of carbon.

Four un-hybridised p-orbital form pi bonds. Hybridised orbitals form sigma bonds only. So, we can say from the structure of the benzaldehyde that each carbon of the ring is forming three sigma bond and one pi bond so, each carbon of the ring is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized. The carbon of aldehyde is also forming three sigma and one pi bond so, the carbon of aldehyde is also ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ hybridized.

Therefore, $7$ \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised carbon atoms are present in benzaldehyde.
Note: The number of hybridized orbitals is equal to the number of sigma bonds. Hybridized orbitals have the same energy. The hybridization tells the number of hybrid orbitals. \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridization means three (one s and two p-orbital) hybrid orbitals or three sigma bonds. Each carbon of benzene ring is\[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised. We can also determine the hybridization of an atom by counting the total number of sigma electron pairs around the atom. The oxygen atom has one sigma bond and two lone pairs, so a total of three electron pairs. Oxygen atom is also \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised.in benzaldehyde a total of eight \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\] hybridised atoms are present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




