
Why is soap referred to as salt?
(A). It does not contain hydroxide ions
(B). It has water of crystallization
(C). It is prepared by reacting fatty acid with a strong base
(D). All of above
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Soap is a mixture of sodium salts of various naturally occurring fatty acids. Soap is produced by a saponification of basic hydrolysis reaction of a fat or oil. Currently, sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide is used to neutralize the fatty acid and convert it to the salt
Complete step by step answer:
Saponification: Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids when trigly carbides in fat/oil react with aqueous $NaOH$or $KOH$ they are converted into & sap and glycerol. This is called alkaline hydrolysis of esters. Since this reaction leads to the formation of soap, it is called the saponification process.
Manufacture: The fats and oils are heated with an alkali, usually sodium hydroxide, and the esters are hydrolyzed to form a sodium salt of the carboxylic acid and the alcohol, propane$ - 1,2,3 $ triol
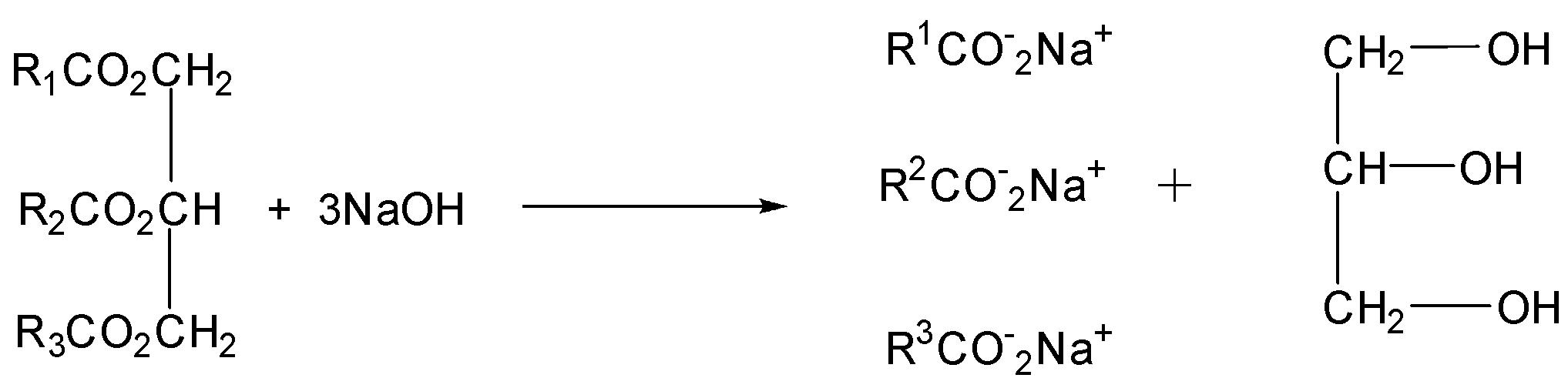
The process is known as saponification and the sodium salts of the acids are soaps. Modern plants have continuous processes. The oils are purified, blended and then mixed with sodium hydroxide solution very rapidly. The mixture is passed into a heated reaction chamber where saponification occurs. The glycerol is more valuable than the soap and most of it is recovered. Same is left in the soap to make it smooth and soft after saponification the soap and glycerol mixture is usually passed on to a rotating disc contact or RDC where the mixture is washed with a counter- current of sodium chloride solution.
Soap is not very soluble in salt water and separated out. Glycerol stays in solution which is known as lye. The washed soap is then further treated with sodium chloride solutions and centrifuged to give soap at the required concentration.
The soap in dried by spraying into a vacuum chamber to give a final product suitable for stamping
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note:
The glycerol solution is concentrated by evaporating off the water and the glycerol is then purified by distillation; its main use is in producing alkyd resins, used in paints. It is also used to make explosives (nitro glycerine) and in many cosmetic and pharmaceutical products.
Complete step by step answer:
Saponification: Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids when trigly carbides in fat/oil react with aqueous $NaOH$or $KOH$ they are converted into & sap and glycerol. This is called alkaline hydrolysis of esters. Since this reaction leads to the formation of soap, it is called the saponification process.
Manufacture: The fats and oils are heated with an alkali, usually sodium hydroxide, and the esters are hydrolyzed to form a sodium salt of the carboxylic acid and the alcohol, propane$ - 1,2,3 $ triol

The process is known as saponification and the sodium salts of the acids are soaps. Modern plants have continuous processes. The oils are purified, blended and then mixed with sodium hydroxide solution very rapidly. The mixture is passed into a heated reaction chamber where saponification occurs. The glycerol is more valuable than the soap and most of it is recovered. Same is left in the soap to make it smooth and soft after saponification the soap and glycerol mixture is usually passed on to a rotating disc contact or RDC where the mixture is washed with a counter- current of sodium chloride solution.
Soap is not very soluble in salt water and separated out. Glycerol stays in solution which is known as lye. The washed soap is then further treated with sodium chloride solutions and centrifuged to give soap at the required concentration.
The soap in dried by spraying into a vacuum chamber to give a final product suitable for stamping
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note:
The glycerol solution is concentrated by evaporating off the water and the glycerol is then purified by distillation; its main use is in producing alkyd resins, used in paints. It is also used to make explosives (nitro glycerine) and in many cosmetic and pharmaceutical products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




