
How would you show the bonding of Hydrogen and Oxygen using Lewis Dot diagrams?
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: The hydrogen and oxygen combine to form a molecule of water. The electrons are arranged in between the two hydrogens and one oxygen atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogen is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[1\] and electronic configuration \[1{s^1}\]. It has only one electron available for combination with other elements. The valence shell of a hydrogen atom is \[1\].
Oxygen is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[8\] and electronic configuration\[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^4}\]. The valence shell of an oxygen atom is \[2\] having six electrons in the outermost shell with two in \[2s\] and four in \[2p\] orbitals.
The valency of hydrogen atom is one and that of oxygen atom is two. It is because hydrogen needs one electron to reach the nearest noble gas configuration and the oxygen atom needs two electrons to complete the octet.
Thus for completing the octet of hydrogen two electrons are shared between a hydrogen atom and an oxygen atom. But the total number of electrons in that case is\[7\]. So the oxygen atom bonds with another hydrogen atom by sharing an electron pair. Thus there are \[2\] valence electrons on each of the hydrogen atoms and \[8\] valence electrons on the oxygen atom.
Hence the Lewis Dot diagram showing the bonding of Hydrogen and Oxygen is as follows:
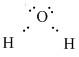
Note:
Every element in the Lewis dot structure must have a complete octet of electrons. The central atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized with two lone pairs and two bond pairs. The molecular geometry of the molecule is bent and the electronic geometry is tetrahedral. The \[\angle H - O - H\;\] is \[104.5^\circ \] .
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrogen is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[1\] and electronic configuration \[1{s^1}\]. It has only one electron available for combination with other elements. The valence shell of a hydrogen atom is \[1\].
Oxygen is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[8\] and electronic configuration\[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^4}\]. The valence shell of an oxygen atom is \[2\] having six electrons in the outermost shell with two in \[2s\] and four in \[2p\] orbitals.
The valency of hydrogen atom is one and that of oxygen atom is two. It is because hydrogen needs one electron to reach the nearest noble gas configuration and the oxygen atom needs two electrons to complete the octet.
Thus for completing the octet of hydrogen two electrons are shared between a hydrogen atom and an oxygen atom. But the total number of electrons in that case is\[7\]. So the oxygen atom bonds with another hydrogen atom by sharing an electron pair. Thus there are \[2\] valence electrons on each of the hydrogen atoms and \[8\] valence electrons on the oxygen atom.
Hence the Lewis Dot diagram showing the bonding of Hydrogen and Oxygen is as follows:
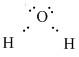
Note:
Every element in the Lewis dot structure must have a complete octet of electrons. The central atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized with two lone pairs and two bond pairs. The molecular geometry of the molecule is bent and the electronic geometry is tetrahedral. The \[\angle H - O - H\;\] is \[104.5^\circ \] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




