
Show formation of $MgO$ by transfer of electron in two elements using electron dot structures.
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: The electron dot structure represents the atoms that contain valence electrons using dots around the symbol. Here, the dots represent the number of valence electrons present in an atom. The dots can be arranged right, left, above, and below the symbol.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that the atomic number of magnesium $(Mg)$ is $12$ .
The electron per shell of magnesium can be written as $2,8,2$
As we can see that the number of valence electrons in magnesium is two. As every atom wants to be stable and the stability can be achieved only when the octet is complete. Therefore, the magnesium will lose its two valence electrons to complete its octet and become stable.
Now, again we know that the atomic number of oxygen $(O)$ is $8$ .
The electron per shell of magnesium can be written as $2,6$
It requires two electrons to complete its octet and become stable. Hence, oxygen will gain two electrons and complete its octet.
During the formation of bonds between magnesium and oxygen, one magnesium atom loses two electrons to oxygen atom. The reaction can be written as:
$Mg\to M{{g}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}$
This is equation $(1)$
$O+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{O}^{2-}}$
And this is equation $(2)$
Now, writing both the equations together, two electrons cancel out each other, and we get,
$MgO\to M{{g}^{2+}}+{{O}^{2-}}$
The electron dot structure for the formation of $MgO$ can be drawn as:
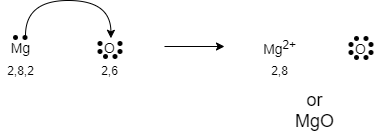
Additional information:
In octet rule, the atoms, mainly the main group elements bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in their valence shell and attain stability.
Note: The electron dot structure uses dots to represent the number of valence electrons.
In electron dot structure, the cations will have fewer dots as compared to the anions.
Electron shell is defined as an orbit that is surrounded by electrons and has a nucleus at the center.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know that the atomic number of magnesium $(Mg)$ is $12$ .
The electron per shell of magnesium can be written as $2,8,2$
As we can see that the number of valence electrons in magnesium is two. As every atom wants to be stable and the stability can be achieved only when the octet is complete. Therefore, the magnesium will lose its two valence electrons to complete its octet and become stable.
Now, again we know that the atomic number of oxygen $(O)$ is $8$ .
The electron per shell of magnesium can be written as $2,6$
It requires two electrons to complete its octet and become stable. Hence, oxygen will gain two electrons and complete its octet.
During the formation of bonds between magnesium and oxygen, one magnesium atom loses two electrons to oxygen atom. The reaction can be written as:
$Mg\to M{{g}^{2+}}+2{{e}^{-}}$
This is equation $(1)$
$O+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{O}^{2-}}$
And this is equation $(2)$
Now, writing both the equations together, two electrons cancel out each other, and we get,
$MgO\to M{{g}^{2+}}+{{O}^{2-}}$
The electron dot structure for the formation of $MgO$ can be drawn as:

Additional information:
In octet rule, the atoms, mainly the main group elements bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in their valence shell and attain stability.
Note: The electron dot structure uses dots to represent the number of valence electrons.
In electron dot structure, the cations will have fewer dots as compared to the anions.
Electron shell is defined as an orbit that is surrounded by electrons and has a nucleus at the center.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




