
Reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and conc. HCl is called
(A) Cope reduction
(B) Dow reduction
(C) Wolf-Kishner reduction
(D) Clemmensen reduction
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Clemmensen reduction is a reaction which involves the reduction of carbonyl compounds to form corresponding simple hydrocarbon.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss all the reduction methods mentioned above.
1. Cope reduction- A tertiary amine oxide bearing one or more beta hydrogen when converted to alkene by heating, the mechanism is called as cope reduction or elimination.
2. Dow reduction- It is a process for the production of phenol. Chlorobenzene reacts with sodium hydroxide to give sodium phenoxide ion which when treated with hydrochloric acid gives phenol.
3. Wolf-Kishner reduction- Here, aldehydes and ketones are reduced to alkanes using hydrazine. During the mechanism hydrazone anion is formed which then releases the nitrogen atom to form carbanion. This carbanion reacts with water to give a hydrocarbon.
4. Clemmensen reduction- Clemmensen reduction is complementary to Wolf-Kishner reduction. Here, in clemmensen reduction aldehydes or ketones reduce with zinc amalgam (Zn/Hg alloy) and concentrated hydrochloric acid to give hydrocarbon. The mechanism to the clemmensen reduction cannot be understood fully, so two mechanisms are proposed for these types of reductions.
a. Carbanionic mechanism
b. Carbenoid mechanism
The general reaction can be described as,
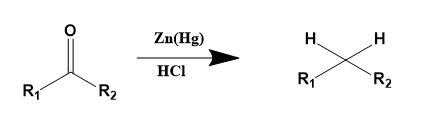
Thus, according to the above explained processes, the reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and conc. HCl is called Clemmenson reduction.
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note to evaluate all the processes before reaching the final answer; as two of them (Wolf-Kishner and Clemmensen reduction) have the reactant and product similar just the reagents and mechanisms are different which makes a huge impact.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss all the reduction methods mentioned above.
1. Cope reduction- A tertiary amine oxide bearing one or more beta hydrogen when converted to alkene by heating, the mechanism is called as cope reduction or elimination.
2. Dow reduction- It is a process for the production of phenol. Chlorobenzene reacts with sodium hydroxide to give sodium phenoxide ion which when treated with hydrochloric acid gives phenol.
3. Wolf-Kishner reduction- Here, aldehydes and ketones are reduced to alkanes using hydrazine. During the mechanism hydrazone anion is formed which then releases the nitrogen atom to form carbanion. This carbanion reacts with water to give a hydrocarbon.
4. Clemmensen reduction- Clemmensen reduction is complementary to Wolf-Kishner reduction. Here, in clemmensen reduction aldehydes or ketones reduce with zinc amalgam (Zn/Hg alloy) and concentrated hydrochloric acid to give hydrocarbon. The mechanism to the clemmensen reduction cannot be understood fully, so two mechanisms are proposed for these types of reductions.
a. Carbanionic mechanism
b. Carbenoid mechanism
The general reaction can be described as,

Thus, according to the above explained processes, the reduction of aldehydes and ketones into hydrocarbons using zinc amalgam and conc. HCl is called Clemmenson reduction.
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note to evaluate all the processes before reaching the final answer; as two of them (Wolf-Kishner and Clemmensen reduction) have the reactant and product similar just the reagents and mechanisms are different which makes a huge impact.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




